Copy of Falx Meningioma
-
Upload
eugenemachine18 -
Category
Documents
-
view
27 -
download
7
Transcript of Copy of Falx Meningioma

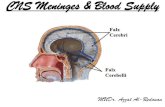
Falx Meningioma
Michael Norman, Iskandar JapardiDepartemen Ilmu Bedah Saraf
Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatra Utara
RSUP. H. Adam Malik

Case Report
• Male, 30 y.o. with left leg monoparesis since 4 months before admission
• He felt numbness and weakness on his leg which occured in gradual fashioned. He also experiece mild to moderate headache a year before the symptoms noted. 3 weeks before admission, he got seizure and resolve spontaenously without antiepileptic medication

Physical and Neurological Findings• Level of Consciousness: compos mentis• Pupillary examination: isokor, 3/3 mm, with normal
pupilary reflex• Cranial nerves: no deficits • Motor strength: • Sensory exam: normal light and touch sensation• Physiologic reflexes: normal• Pathologic reflexes: absent• Meningeal sign: absent• Cerebellar sign: absent

Above: NECT
CECT

NCCT CECT

MRI Brain axial view T1 Weighted Image
MRI Brain axial view T1 with contrast

MRI Brain axial view T2 Weighted Image
MRI Brain axial view T2 FLAIR




Surgical Techniques
• After skin preparation with supine positioning, desinfection was made with povidone iodine followed by drapping procedure
• Horse shoe incision was made across midline• Four burrhole to made bone flap• Bleeding from superior sagittal sinus was controlled with
muscle patch, duramater was hanging with sutures• Dural flap was made, and the tumor rest subcortically• The tumor was firm, well demarcated, and yellowish in color• We did simpsons grade II piecemeal tumor debulking• Dural closure was made with fascia lata graft

Incision design Bone flap dan Dural flap

Dural Opening
• The dura need not be opened more than 2.5 cm from the midline
• The dura is opened in anticipation of the draining cortical veins that have been identified on the venous phase of the angiogram (prevent venous infarction)
• The dura is first incised at the anterior lateral corner of the craniotomy and is carried posteriorly, then medially
• The dural flap is hinged on the sagittal sinus

Extension craniotomy with superior sagital sinus preservation
Pictorial view from lateral side: noted that the sinus margin was cauterized to preserve medial third of superior sagittal sinus. Slight retraction was made to avoid sensory motor
deficit after surgery

Operative Approach
• Approach from both sides of the falx to ensure safe and complete resection (this allow surgeon to inspect and safely resect the contralateral falx dura under direct vision)
• Eloquent cortex is prevalent and needs greater care in retraction and tumor resection

Relaxing Brain and Avoiding Cortical Injury
• Retracting the falx without sagittal sinus occlusion is preferable to directly retracting the cerebral cortex and, therefore, one side of the tumor is best removed by retracting the falx to that side and working through the tumor-infiltrated falx under the sagittal sinus from the opposite side

Dural closure with fascia lata Skin closure with subcutaneous drain
Piecemeal removal of the tumor

Microscopic view 10x40 augmentation with HE preparation shows whorl like appearance among
uniform cell structure which denotes arachnoid cap cells associated with meningothelial type of
meningioma

Discussion
• Classification: Anterior, middle, and posterior thirds of the falx
• The middle third of the falx extends from the coronal to the lambdoid sutures
• This region lies adjacent to the paracentral lobule bordering the Rolandic fissure and the sensorimotor cortex for the foot and lower leg
• Focal motor (in front of the central sulcus) or Jacksonian sensory march seizure (behind), loss of consciousness, Todd’s paralysis

MRI Brain with contrast in axial, coronal and sagittal view

Important issues in surgical planning
• Skull invasion• Tumor vascularity• Arterial supply and location of main
arterial branches• Sagittal sinus involvement• Degree of contralateral invasion through
the falx• Location of cortical draining veins

Exposure
• Frequently, the pia arachnoid is adherent to the falx secondary to large arachnoid and pacchionian granulations
• The overlying surface cortex may be markedly thinned and erroneously believed to be nonfunctional
• Dissection along both sides of the falx is complete when the anterior-posterior extent of the tumor capsule is readily accessible or the inferior edge of the falx is encountered

Conclusion
• Minimal retraction and positioning are important in falx meningioma surgery
• Bridging veins which lies from cortex to superior sagittal sinus should be well studied before surgery by MRI
• Preservation of adjacent and eloquent area would be a key success in falx meningioma surgery

Thank You









![A Case of Benign Meningioma Presented with Subdural Hemorrhage · Meningioma with Subdural Hemorrhage Martínez-Lage et al. [4] studied 57 cases of meningioma with hemorrhagic onset](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5eca99262fcc5c7ee06897d3/a-case-of-benign-meningioma-presented-with-subdural-hemorrhage-meningioma-with-subdural.jpg)
![Case Report Anaplastic meningioma: a case report and ... · Meningioma is the most common intracranial brain tumor, accounting for over one-third of primary brain neoplasms [3]. Meningioma](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5f0d4eca7e708231d439b3ab/case-report-anaplastic-meningioma-a-case-report-and-meningioma-is-the-most.jpg)