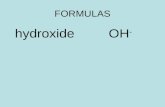
Conceptual Chemistry. Objective 1 Read and express information given in chemical formulas.
-
Upload
april-francis -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Conceptual Chemistry. Objective 1 Read and express information given in chemical formulas.

UNIT 2 – MATTER AND CHANGE
Conceptual Chemistry

Objective 1
Read and express information given in chemical formulas.

What is matter?
Matter: Anything that has mass and takes up space.

Pure Substances
Matter that has fixed composition and properties.
Cannot be broken down by physical methods.

Elements
A substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means.
i.e. iron (Fe), carbon (C), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N)

Compounds
A substance made of elements that are chemically combined.
i.e. water (H2O), salt (NaCl), sugar (C12H22O11)

Compounds
Every compound is composed of the elements it contains.

Chemical Formula
Shows the type and number of atoms present in a substance.

Chemical Formula
• In the chemical formula, subscripts show how many atoms are in the compound.
C6H10N2O2
C = 6H= 10N= 2O= 2

Chemical Formula
The large numbers in front of the chemical formula, called coefficients, show the number of particles.
3C6H10N2O2
C6H10N2O2 = 3 total

Practice Problems: How atoms of each element are in the following?
1. CH4
2. AlCl3
3. 4 H2O
4. 10 Fe3P2
5. 6 Zn(NO3)2
6. Al2(SO3)3

Objective 2
Classify matter as a pure substance or a mixture.

Mixtures
Matter that has compositions that are not uniform or definite.

Mixtures
Mixtures can be separated by physical means into the substances that are mixed with in them.

Homogeneous Mixtures
Homo = same The composition is the same
throughout

Examples Solid Solid: Brass
(Zinc and Copper)
Liquid Liquid: Alcohol (Ethanol and Water)
Gas Gas: Air (Nitrogen and Oxygen)
Solid (dissolves) Liquid: Salt Water (Sodium Chloride and Water)
Gas (dissolves) Liquid: Carbonation (Carbon Dioxide and Water)

Heterogeneous Mixture
Hetero = different The composition is different
throughout.


Objective 3
Distinguish between chemical and physical changes, as well as chemical and physical properties.

Practice ProblemsHetero or Homo Mixture Why?
Tap Water :_______________
A Rock: ________________
Stainless Steel:________________
Brewed Coffee: ________________
Sand: ________________
Oatmeal: ________________
Dust Free Air: ________________
Rusty Metal: _________________

Properties of Matter
Physical Properties: Can be measured without changing the substance’s chemical composition.
i.e. melting point, boiling point, density, solubility,
odor, hardness, color, etc.
Chemical Properties: Potential reactivity of substance with other substances. Can only be measured by trying the reactions.
i.e. Any particular reaction a substance undergoes.

Changes of Matter
Physical Change Chemical Change

Physical Change
Alters a substance without changing the substance’s chemical composition.
i.e. melting, boiling, cutting, smashing, dissolving

Chemical Change
Occur when one or more substances are changed into another substance that have different chemical compositions.
i.e. rusting, exploding, decomposing, corroding, spoiling

Practice ProblemsChemical or Physical
Property?Chemical or Physical Change?
Tarnishes in Rain: Lighting a firework:
Bends easily: Boiling Pasta:
Decomposes: Chewing gum:
Reusable/Recyclable: Running your car:
Shiny: Rolling your bike:
Not Flammable: Melting a crayon:
Perishable Food: Rusting a nail:
Freezable Food: Opening a can of pop:

Objective 4
Balancing chemical equations.

Chemical Equation
Ex: 2 KClO3 2 KCl + 3 O2
Describes the original beginning substances (called reactants) using chemical formulas. Then an arrow points to the newly created substances (called products) using chemical formulas again.
Reactants Products

Symbols
(s) = (l) = (g) = (aq) =
+ = = ∆ = H2 (subscripts) =
2 H2 = (Coefficients) =

Balancing Equations
The law of conservation of mass states that matter cannot be created or destroyed. So, the number of atoms reacting must equal the number of atoms produced. However, a chemical change rearranges these atoms into new substances.

To balance equations, follow these steps:
1. Count atoms on each side of the arrow. They should be equal. If not, you need to balance them.
2. Balance both sides by using coefficients. Remember, they multiply through everything inside of that compound. NEVER change subscripts.
3. Double check work.

Practice Problems
____ KClO3 ____ KCl + ____ O2
____AlBr3 + ____ K2SO4 ____ KBr + ____ Al2(SO4)3
____ C3H8 + ____ O2 ____ CO2 + ____ H2O

Objective 5
Describing chemical reactions and calculate percent yield and percent error.

Error Calculations
Error = experimental value – accepted value
Magnitude of the value tells whether or not the experimental value is too high or too low
Accepted value: Accurate value based on a reliable reference
Experimental value: value measured in lab
Percent Error = | Error | x 100%
Accepted Value

Percent Yield
Used to determine completeness of a reaction
Actual Yield: actual amount of products produced in an experiment
Theoretical Yield: maximum amount of products predicted from conservation of mass
Percent Yield = Actual Yield x 100%
Theoretical Yield















![A GENERALIZED PROFITS RELEASED MODEL FOR …...Conceptual Analysis of Nonparticipating Life Insurance Gross Premium and Profit Formulas" [2]. The profits released method, however,](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5e86273634112322d7389bc8/a-generalized-profits-released-model-for-conceptual-analysis-of-nonparticipating.jpg)