Common Uses & Lab Ideas: Tips, Tricks & Calibration Notes Measurements Sensor Exploration Challenge...
-
Upload
alban-patterson -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Common Uses & Lab Ideas: Tips, Tricks & Calibration Notes Measurements Sensor Exploration Challenge...

Common Uses & Lab Ideas:
Tips, Tricks & Calibration Notes
Measurements
Sensor Exploration Challenge
Materials
EKG SensorPS-2111
• Identify fluctuations in electrical current that occur before, during, and after heart contractions.
• Compare EKG results for• before/after exercise, • males/females
• Determine heart rate.• Compare EKG results to a “typical
range”. Compare to examples of abnormal EKG images.
• Voltage (mV)• Heart Beats
(BPM)
1. Connect the EKG Sensor2. Apply the electrode patches as
shown at right3. Clip the leads to the patches4. Open the show path for
voltage and navigate to the graph
5. Begin collecting data6. Stop after 30 seconds7. Optimize graph to view a single
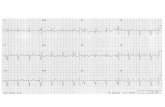
heart cycle8. Determine the QRS complex
duration (interval) from your data
• Skin patches should only be used by one person
• Clean skin before applying patches• Have subject remain still• Use 200hz or greater sample rate
• SPARK• EKG Sensor• Electrode
Patches
“Typical” resting state EKG:QRS complex is less than 0.100 seconds
*The EKG sensor is not intended to be used as a medical instrument.

Common Uses & Lab Ideas:
Tips, Tricks & Calibration Notes
Measurements
Sensor Exploration Challenge
Materials
Hand Grip Heart Rate SensorPS-2186
• Compare resting heart rate to heart rate after exercise.• Determine recovery time following exercise.• Use data to help determine and understand:
• Maximum heart rate and target heart rate• Heart rate and fitness level
• Compare heart rate results for:• Sitting/standing/laying down• Jogging vs. squatting
• Beats per minute
1. Connect the sensor to the SPARK, an orange light should be on2. Use the show path to obtain a graph display3. Grip the heart rate sensors, wait until the red light flashes
indicating the heart beats (this can take 30-60sec)4. Start collecting data5. Let collection continue for 60 seconds to get your resting heart
rate6. Stop data collection7. Use the statistics tool to determine your mean resting heart rate8. Start collecting data and see how much you can elevate your
heart rate by jogging in place for 60 seconds9. Stop data collection10. Use the statistics tool to determine your maximum beats per
minute during your exercise
• Clean paddles after each use• Wait for the red beats light to flash
for at least 30 seconds before beginning data collection
• Hold with normal grip strength, with the metallic side of the grip touching the center of the palm
• Use extension cable to avoid accidentally pulling equipment off the lab table
• A sample rate of one sample per 5 seconds works well
• SPARK• Hand grip
heart rate sensor

Common Uses & Lab Ideas:
Tips, Tricks & Calibration Notes
Measurements
Sensor Exploration Challenge
Materials
Breath Rate SensorPS-2187
• Compare breath rate at rest, during exercise, and recovery after exercise.
• Compare different types of exercises:• Jogging vs. sprinting (in place)• Jogging vs. stepping up/down
• Relate recovery time to fitness level.
• Breath rate (bpm)
• Breath rate avg (bpm)
1. Connect breath rate sensor to the SPARK2. Connect new unused clip to the sensor tubes3. Attach clip to a new unused dusk mask4. Select breath rate and enter the show path then navigate to the
graph display5. Set the data collection to rate at 1hz and to stop after 60sec6. Place the mask on your face and attach strain-relief clip7. Breath normally and wait for EXHALE light to illuminate8. Begin collecting data9. For the 2nd run of data, jump up and down or jog in place10. Compare your breathing rate from each run
• Each mask clip must only be used by one person
• If EXHALE light does not illuminate, adjust fit of the mask
• Use sensor extension cable if test subject will be moving
• SPARK• Breath rate
sensor• Clip (PS-
2658)• Dust mask

Common Uses & Lab Ideas:
Tips, Tricks & Calibration Notes
Measurements
Sensor Exploration Challenge
Materials
Force SensorPS-2152
Muscle Fatigue experiments:• Compare sustained squeezing pressure to repeated
squeezing.• Compare dominant hand to non-dominant hand• Compare hand at normal temperature to hand held in ice
water• Compare males to females
• Newtons
1. Connect the sensor to the SPARK2. Navigate to a graph display of force vs. time3. Put the middle and ring fingers of your dominant hand through
the finger holes of the sensor.4. Press the “zero” button.5. Place your thumb on the rubber bumper and begin squeezing.6. Start recording data. Adjust the scale of the graph.7. Stop recording data after 60 seconds.8. Do one or more additional runs, changing one factor.9. Compare the results.
• Try to maintain a force of 40 N for at least 60 seconds.– If this isn’t possible, try to
maintain a force of 30 N.• Press the “zero” button before
beginning data collection for each run.
• SPARK• Force sensor
Insert Sensor Image Here

Common Uses & Lab Ideas:
Tips, Tricks & Calibration Notes
Measurements
Sensor Exploration Challenge
Materials
SpirometerPS-2152
• Determine the volume of one normal breath.
• Determine the maximum amount of air in the lungs.
• Relate the results to conditions such as asthma and emphysema.
• Flow rate (L/s)• Total flow (L)• Max flow
rate (L/s)
1. Connect the mouthpiece to the handle (look for pin alignment)2. Connect the sensor to the SPARK3. Select total flow and enter the show path, then navigate to the
graph display4. Hold mouthpiece away from any air currents and start data
collection. Wait for READY light to illuminate5. Place in mouth between your front teeth and seal it with your lips6. Breath in the following sequence
-Breathe quietly for 4 breaths-Inhale deeply, followed immediately by exhaling through the mouth with maximum effort. -Breath quietly for two breaths.
7. Stop data collection8. Compare one normal breath to the maximum exhalation.
Compare the normal breaths before/after maximum exhalation.
• Each mouth piece must only be used by one person
• Do not wiggle mouthpiece when removing it
• Use nose clip or have test subject close their nose
• Practice 2-3 times before saving data
• Prompt test subject to avoid distractions
• Test subject should stand/sit comfortably
• SPARK• Spirometer
sensor• Disposable
single use mouthpiece