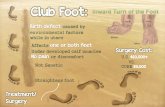
Club foot
-
Upload
sandy-kaur -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
811 -
download
2
Transcript of Club foot


It is a common birth defect, occurring
in about one in every 1,000 live births.
Approximately 50% of cases of
clubfoot are bilateral.
This occurs in males more often than
in females by a ratio of 2:1.
Main cause is the result of arrested or
anomalous development in utero.

Clubfoot is a condition in which
one or both feet are twisted into an
abnormal position at birth. The
condition is also known as talipes
or talipes equinovarus.

The cause of clubfoot isn't known
(idiopathic).
family history .
Abnormal position and restricted
movements in uterus.

Talipes varus
Talipes valgus
Talipes equinovarus
Talipes calcaneovalgus
Talipes calcaneovarus
Talipes equinovalgus



Ante-natal ultrasound scan.
After birth it can be detected by
means of looking at the shape
and position of the foot.
X-ray


Application of
cast

Use of Denis
Browne splint

Special club foot shoes
Observation for reoccurrence
deformity.

For releasing tight ligaments
or to lengthen the tendon.

Assessment
Manipulation of the foot.
Care of infant in Denis Browne splint
Care of infant in a cast


Most common congenital
malformation.
It occur about 1 in 750 live birth.
Caused by various degree of
displacement of the femoral head
from the acetabulum.

A hip dislocation occurs when the
femoral head--the ball portion of
the hip joint--leaves the pelvic
socket.

1. Acetabulum dysplacia
2. Subluxation
3. Dislocation


Hereditary factor
Fetal position
Extra uterine compression
Breech presentation
Neurological disorder

Physical examination
Ortolani maneuver and the Barlow
maneuver.
Allis ‘s sign
ultrasound and X-ray.
MRI


baby wearing a Bock harness
Diagram of Pavlik harness
Diagram of Frejka pillow
Traction

]
]



Fracture is defined as any
breakage to the bone
continuity due to
accident and child
abused .

Falling
Climbing
Struck by moving objects
Accidental injuries
Child abuse
Blowing , punching during play

Physical assessment
Bone continuity
Pain
Swelling
Open or close injury
X-ray


Swelling
Bruising
4 p’s
1. Pain
2. Pulse
3. Paraesthesia
4. Paralysis
Breakage of bone continuity

Goals
To restore the fracture fragment to
their normal position.(reduction)
To maintain the bone fragment in place
until healing occur. (immobilization)
To help the children to regain normal
function. (rehabilitation)

Closed reduction
Traction
Open reduction

Bandage
Cast
Splint
Continue traction
Pins
Plaster cast
Internal fixation include
Plates ,Screw ,Rods

Provide every information to the
parents.
Encourage the child for play .
Maintain position of fractured part.
Provide analgesics when required .
Prevention of respiratory ,
circulatory , neurologic disturbance .

Maintain body temperature.
Maintain skin integrity.
Promotion of muscle activity.
Provision of comfort measures
Prevention of urinary stasis and
constipation.
Health education.
Follow up health education.