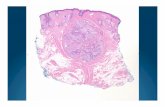
Clinical case of mixed tumor of the testis
-
Upload
antonio-pio-masciotra -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
502 -
download
1
Transcript of Clinical case of mixed tumor of the testis

Antonio Pio MasciotraCampobasso – Molise – Italy
Website www.masciotra.net
YouTube channelhttps://www.youtube.com/channel/UCgCj21nKGAhR997Ia3-QegQ
Clinical caseMale 30 years old with a mass on his left
testisUS and SWE features

EFSUMB Guidelines and Recommendations on clinical use of US Elastography takes only five lines to pursue the testis issue, then limited to a very rare tumor (the Leydig cell tumor).Here I’ll present a clinical case of mixed germ cell tumor with its features at Shear Wave Elastography.


Cellular Classification of Testicular Cancer
The following histologic classification of malignant testicular germ cell tumors (testicular cancer) reflects the classification used by the World Health Organization (WHO).Less than 50% of malignant testicular germ cell tumors have a single cell type, of which roughly 50% are seminomas. The rest have more than one cell type, and the relative proportions of each cell type should be specified. The cell type of these tumors is important for estimating the risk of metastases and the response to chemotherapy. Polyembryoma presents an unusual growth pattern and is sometimes listed as a single histologic type, though it might better be regarded as a mixed tumor.
1.Intratubular germ cell neoplasia, unclassified.
2.Malignant pure germ cell tumor (showing a single cell type):1. Seminoma.
2. Embryonal carcinoma.3. Teratoma.
4. Choriocarcinoma.5. Yolk sac tumor.
3.Malignant mixed germ cell tumor (showing more than one histologic pattern):1. Embryonal carcinoma and teratoma with or without seminoma.
2. Embryonal carcinoma and yolk sac tumor with or without seminoma.3. Embryonal carcinoma and seminoma.
4. Yolk sac tumor and teratoma with or without seminoma.5. Choriocarcinoma and any other element.
4.Polyembryoma.





Right testis normal kPa 3,3Left testis
Normal parenchima kPa 5,1-6,5
Cancer solid kPa 61,4 Cancer mixed kPa 40,9

Left testis Normal parenchima kPa 5,1-6,5
Cancer solid kPa 61,4 Cancer mixed kPa 40,9
Left testis Normal parenchima kPa 5,0-7,7
Cancer solid kPa 64,8 Cancer mixed kPa 93,8
Left testisCancer solid kPa 16,1 – 19,2 – 89,7
Left testisCancer mixed kPa 35,3


Bidimensional 3D
On the SWE image are displayed different information on elasticity
(or stiffness) quantification for each ROI selected in the colored box:
• Mean value in kPa or m/s (mean elasticity or stiffness)• Minimum value in kPa or m/s (softest)• Maximum value in kPa or m/s (stiffest)• Standard deviation in kPa or m/s (its an index of more or less
homogeneity)• Elasticity ratio (if are selected 2 ROIs) < or > than 1• Diameter of the ROI selected in mm


Normal parenchima kPa 5,1-6,5 Cancer solid and cystic (Yolk Sac) kPa 40,9 Cancer solid (seminoma)
kPa 61,4

CONCLUSIONS
In imaging it's like in every day's life.If you need to know the details of an object you can rely on the information given by different tools :
1) your eyes tell you its morphology and the colors2) your hand tells you its consistence, the characteristics of its surface and very approximately the temperature, weight and lenght3) your tongue tells you its taste, but also its consistence, the characteristics of its surface and its temperature4) your nose tells you its smell.
So is in imaging. Each modality and technique give us different kind of information.
Shear Wave Elastography is capable to show the mechanical properties of the normal parenchima compared to the two different kind of tumors (seminoma and yolk sac tumor) coexisting in the same testis, like showed in the former slide.

CONCLUSIONS
Shear Wave Elastography adds valuable information to the study of the testis, potentially resulting in
“a virtual biopsy” .
This final aim will be achieved when further improvement of Shear Wave Elastography technology (the only actually capable to quantify elasticity or stiffness) will give us the right consistency of the quantitative measurements of tissue elasticity that up todate is still lacking.
Hence the RSNA initiative of ‘Quantitative Imaging Biomarkers Alliance’ applied to Sono-Elastography too.This means that if the intrinsic elasticity of the testis is 2 kPa all the measurements have to give this value, not depending on the probe’s frequency or on other variables.
When this requirement will be accomplished we’ll can really establish the cutoff value between normal and abnormal tissues both in focal and in diffuse diseases.Therefore we’ll can rely on it at same extent we actually rely on the use a thermometer to check the behavior of the fever during an infection (if it’s responding to the treatment).
Then let’s go on!Lessons need to be drawn from a great man of the past who had the
vision to preparing for the future through imagination.


Thanks for your attention
Antonio Pio MasciotraCampobasso – Molise – Italy
Website www.masciotra.net
YouTube channelhttps://www.youtube.com/channel/UCgCj21nKGAhR997Ia3-QegQ
Clinical caseMale 30 years old with a mass on his left
testisUS and SWE features