CIS 175 LU1 Part 2
-
Upload
eric-macewen -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
0
description
Transcript of CIS 175 LU1 Part 2

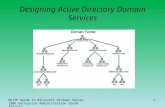
Designing Physical Topology
MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
1

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
2
Learning Objectives
• Plan and implement sites and site links• Design the plan to support a remote branch office• Understand operations master roles• Be able to transfer and seize operations master
roles• Plan and implement read-only domain controllers
(RODCs)

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
3
Implementing Sites
• Site– Well-connected group of hosts or subnets
• Single-location businesses– Local area network (LAN)
• Multi-location businesses– Wide area network (WAN) link
• Expanded site definition– Group of well-connected hosts or subnets– Connected to another group of well-connected hosts
or subnets by a slower WAN link• Represented by a site link object in Active Directory

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
4
Figure 2-1 A two-site business configurationCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
5
Site and Site Link Benefits
• Benefits– Logon optimization– Replication optimization– Access to site data by site-aware applications

Logon Optimization
• Netlogon service used for domain logon– Figure 2-2 user prefers DC2– Not obvious to Active Directory by default
MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
6
Figure 2-2 Netlogon process in two-site enterpriseCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
7
Logon Optimization (cont’d.)
• Steps to allow Netlogon to contact correct DC– Create an Active Directory site object
• Corresponding to each location– Create Active Directory subnet objects
• Representing actual subnets at remote location– Move the domain controller object:
• To the newly created site in Active Directory
• Active Directory used to create objects representing:– Actual location (site), subnet(s), domain controller(s)

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
8
Replication Optimization
• Benefit of configuring sites, subnets, site connectors– Optimizes Active Directory replication between sites
• Replication data: compressed automatically• Replication: scheduled• Replication can be directed

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
9
Figure 2-3 Scheduling site replicationCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
10
Replication Optimization (cont’d.)
• Replication path– Manipulated by controlling site link Cost value
• Default site link cost: 100• Active Directory
– Uses a least-cost algorithm to identify the path it uses• Cost value setting
– Any numbers between 1 and 99999– Choice must reflect environment
• Follow same strategy for future site links

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
11
Figure 2-4 Controlling replication traffic in three-site enterpriseCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
12
Figure 2-5 Controlling replication traffic by adjusting the cost of the linkCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
13
Using Sites for Site-aware Applications
• Site-aware application– Determines its own Active Directory site membership
(and location)– Connects to other servers in the same site
• Examples– Microsoft Exchange e-mail– Distributed File System (DFS)
• DFS namespace• DFS replication
• Can create a separate site to control queries by site-aware applications querying Active Directory

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
14
Using Sites for Site-aware Applications (cont’d.)
• Active Directory applications– Use Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
queries to query domain controllers• Queries add to domain controller load
• Can separate these queries– “Trick” Active Directory into thinking that a separate
site exists• Steps
– Create a separate subnet on the network• Configure TCP/IP so that the domain controller and
application server are located on this subnet

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
15
Using Sites for Site-aware Applications (cont’d.)
• Steps (cont’d.)– Open Active Directory Sites and Services
• Create a site and a subnet corresponding to the first subnet created
– Link the subnet to the site• Move the domain controller to the site in Active
Directory Sites and Services
• Result– All LDAP queries by this application server now
directed at the domain controller in the site created

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
16
Creating Sites and Subnets
• Enterprise physical locations– Include one or more subnets
• Active Directory– Does not know about these locations by default– Must be taught
• Multiple location organizations– Must add the sites, subnets, site links
• Using Active Directory Sites and Services
• Activity 2-1: Creating Sites and Subnets

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
17
Figure 2-6 Active Directory Sites and ServicesCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
18
Creating Site Links
• Site link object– Created in Active Directory Sites and Services– Represents actual WAN links used to connect
different sites• Location often adds more site links• If all WAN links identical
– Use the DEFAULTIPSITELINK to represent each of the WAN links

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
19
Figure 2-7 Adding a subnet and assigning it to a siteCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
20
Creating Site Links (cont’d.)
• Two types of site links– IP and SMTP
• RCP over IP – Uses dynamic port mapping to communicate with
DCs over the IP site link• Starts with TCP port 135 to initiate the connection• Uses different ports to communicate
– May cause trouble going through a firewall• Solution: modify registry to use only a single port
• Activity 2-2: Creating Site Links

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
21
Figure 2-8 Creating a site linkCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
22
Figure 2-9 Changing the cost for a site linkCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
23
Understanding Bridgehead Servers
• Bridgehead server– Domain controller accepting and transferring
replicated data within the site– Replicates data to other domain controllers within the
site (if they exist)– Each site has one
• Inter-Site Topology Generator (ISTG)– Background Active Directory process running on a
site domain controller– Automatically designates the bridgehead server

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
24
Understanding Bridgehead Servers (cont’d.)
• Inter-Site Topology Generator (ISTG) (cont’d.)– If designated bridgehead server fails
• ISTG automatically detects failure• Designates another bridgehead server
• Default: no control over designated bridgehead server– Can designate a preferred bridgehead server
• Confusing and has disadvantages– ISTG will not designate any other DC as bridgehead
servers • Unless DC designated as preferred bridgehead server

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
25
Figure 2-10 Designating a server as a preferred bridgehead serverCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
26
Full Mesh Replication Topology
• Each site can replicate with every other site• Recommended for organizations having 10 or fewer
sites• Site links
– Transitive by default• Can remove the transitive nature of site links
– Disable site link bridging

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
27
Optimizing Replication with Hub and Spoke Sites
• Hub and spoke replication topology used with:– Relatively fast connections between regional sites– Slower connections to outlying sites
• Outlying sites often connected administratively to a regional headquarters
• Regional headquarters typically have the faster connections

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
28
Figure 2-11 Hub and spoke configuration created for replicationCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
29
Figure 2-12 Disabling site link bridgingCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
30
Designing the Branch Office
• For multiple large physical locations:– Create subnet and site objects– Place domain controllers (DCs) in the site– Configure site link properties
• Advantages– Decreases logon time– Ensures resources access if WAN link goes down
• For smaller branch office– Design requires important considerations

Designing the Branch Office (cont’d.)
• Logon process points to consider– Logging with cached credentials– Cached credentials only provide local access– Logon prevented:
• If global catalog server cannot be located
MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
31
Figure 2-13 Reviewing the logon processCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
32
Deciding to Place a DC in a Remote Office
• Benefits– Can log on to a DC in the site without a WAN link– Optimizes site-aware applications
• If DC placed in the remote office:– Users have quicker logon times
• If DC not placed in the remote office– Can control which DCs user accesses
• Create a subnet object for the remote office • Place it in the site object for the main office• Netlogon service uses subnet of client logging on

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
33
Deciding on a Writable DC or an RODC
• RODCs– New feature in Windows Server 2008– Used in a branch office
• When a writable domain controller not feasible
• Before Windows Server 2008– Reasons to not place a DC in a branch office
• Security and manpower
• RODCs overcome both issues– RODC does not hold account passwords by default– RODCs support a local Administrator role

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
34
Including DNS with the DC
• DC should host Domain Name System (DNS) server role when possible
• If DNS server not in the site:– DNS queries have to go over the WAN link
• DNS zone transfers– Included in Active Directory replication
• When DNS server configured with ADI zones
• When DNS server hosted on a domain controller in another site:– Replicated data: compressed and scheduled

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
35
Adding the Global Catalog or Enabling Universal Group Membership Caching
• Site global catalog server choices– Do not make the DC a global catalog server or enable
Universal Group Membership Caching– Make the DC a global catalog server– Enable Universal Group Membership Caching on the
site• Use Active Directory Sites and Services
– To make domain controller a global catalog server

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
36
Adding the Global Catalog or Enabling Universal Group Membership Caching
(cont’d.)• Universal Group Membership cached on a site
– DC in the site caches this data once retrieved• Points about Universal Group Membership Caching
– Enabled on a per-site basis– Cached data automatically renewed every 8 hours by
default– Cached data expires in 7 days
• Activity 2-3: Enabling Universal Group Membership Caching on a Site

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
37
Figure 2-14 Designating a DC as a global catalog serverCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
38
Figure 2-15 Enabling Universal Group Membership CachingCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
39
Understanding Operations Master Roles
• Domain controllers work as multi-masters with loose convergence
• Multi-masters means:– Equal (for most functions)– Each domain controller accepts changes
• Write those changes to the AD DS database
• Loose convergence means:– Given enough time
• All changes made to one domain controller (DC) will eventually make it to all other domain controllers

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
40
Understanding Operations Master Roles (cont’d.)
• Some DCs perform additional roles or functions• Five operations master roles
– Schema master– Domain naming master– RID master– PDC emulator– Infrastructure master
• Identifying role holders for all operations master roles in the forest and a domain– Use the Netdom query fsmo command

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
41
Figure 2-16 Identifying operations master roles in a forestCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
42
The Infrastructure Master and the Global Catalog
• Infrastructure master limitation– Will not work if on a DC designated as a global
catalog server– For name changes
• Infrastructure master only checks for object names from other domains group members in its domain
• Learns change when the global catalog replicated to it– Will never query global catalog server and find
differences– Other DCs in the domain never updated

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
43
The Infrastructure Master and the Global Catalog (cont’d.)
• To get around problem– Designate all domain controllers as global catalog
servers• Infrastructure master not needed
• Challenge with this approach– Replicating the global catalog to all domain controllers
• Can take excessive bandwidth

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
44
Operations Masters and the ADPrep Tool
• Active Directory Preparation (ADPrep) tool– May need to run on domain controllers holding
specific operations master roles– ADPrep /ForestPrep
• Run on DC holding the forest schema master role– ADPrep /DomainPrep (ADPrep /DomainPrep
/GPPrep) • Run on DC holding the infrastructure master role
– ADPrep /RODCPrep• Run on any forest DC

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
45
Transferring Operations Master Roles
• Examples:– Implementing the Active Directory design– Responding to maintenance needs
• Active Directory Users and Computers– Transfers the RID master, PDC emulator,
infrastructure master• From one DC to another
• When transferring roles:– Log on to target DC
• To logically transfer roles– Both DCs must be up and operational

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
46
Figure 2-17 Identifying operations master roles in the domainCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
47
Seizing Operations Master Roles
• Seizing a role:– Occurs when a DC fails while holding a role
• Need to have another DC assume the role
• Drastic action– Last resort after verifying role transfer will not work
• Sometimes possible to wait before seizing the role• Use the NTDSUtil command-line tool
– Log on to target DC– FSMO Maintenance subshell used to connect to the
target server and seize the role

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
48
Seizing Operations Master Roles (cont’d.)
• NTDSUtil– First tries to transfer the role before seizing it
• Only seize it if transfer fails
• Activity 2-4: Removing Active Directory on DC2• Activity 2-5: Creating a Replica Domain Controller• Activity 2-6: Transferring and Seizing the
Infrastructure Master Role

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
49
Figure 2-18 Deleting the last domain controller in the domainCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
50
Figure 2-19 Infrastructure master conflict with global catalog warningCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
51
Figure 2-20 Verifying the role seizure actionCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
52
Figure 2-21 Successful seizure of the role using NTDSUtilCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
53
Using RODCs
• New feature in Windows Server 2008• Writable DC or RODC placed in a remote office
– RODC remote office security• No stored passwords, Administrator role separation
– Most other RODC functions work the same as on a regular DC
• Active Directory still applies Group Policy objects (GPOs)
• Remote office users affected by default domain policy• GPO can be applied to the site hosting the RODC
– Or to an OU containing users and computers in the site

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
54
Using RODCs (cont’d.)
• Section topics:– Requirements for adding RODCs– Installing RODCs from media– Server Core and RODCs– Prestaging an RODC– RODC passwords– RODC filtered attribute set– Local Administrators role on an RODC

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
55
Requirements for Adding RODCs
• RODCs can only be installed on Windows Server 2008 or greater
• Forest functional level must be at least Windows Server 2003
• ADPrep /RODCPrep must be run in the forest• At least one Windows Server 2008 writable domain
controller must exist• DC holding the PDC emulator operations role must
be running Windows Server 2008

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
56
Installing RODCs from Media
• Install from media (IFM) option– Available for server promoted to a DC using the
advanced options– Allows server to get a copy of Active Directory from
media– Used when newly promoted remote site DC
connected via a slow WAN link• Another option to avoid replication over slow link
– Promote server in the same site as another DC– Manually transport it to the remote site

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
57
Installing RODCs from Media
• IFM created using the NTDSUtil command– Ntdsutil– Activate instance ntds– Ifm– Create rodc c:\DCpromo
• Commands create an ntds.dit file in the C:\DCPromo\Active Directory folder– Can then select installation media
• When running DCpromo using the advanced installation options

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
58
Figure 2-22 Selecting advanced options in DCpromoCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
59
Figure 2-23 Specifying the location of the mediaCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
60
Server Core and RODCs
• If considering deploying an RODC into a branch office:– May consider deploying it with Server Core
• Server Core installation of Windows Server 2008– Limited installation including the command prompt– Windows graphical user interface (GUI) not included– All administration
• Performed at the command prompt• Or remotely once remote administration configured

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
61
Server Core and RODCs (cont’d.)
• Basic tenet of hardening a server– Disable or remove all unneeded services, protocols
• Prevents attack on service or protocol
• Server Core in Windows Server 2008– Does not support PowerShell
• PowerShell requires the installation of .NET
• Can promote server running Server Core– To a domain controller and to an RODC
• Create an answer file to do so
• Activity 2-7: Creating an RODC

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
62
Figure 2-24 Exporting settings to an answer file from DCpromoCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
63
Figure 2-25 Selecting RODC as an additional domain controller optionCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
64
Prestaging an RODC
• Can prestage a computer account in Active Directory before RODC added
• Prestaged RODC– Computer account created in Active Directory– Designated as an RODC– Done before the RODC computer added to the
domain and before DCpromo run• When account prestaged it starts the DCpromo
wizard

Prestaging an RODC (cont’d.)
• Can start the wizard by right-clicking the DCs OU– Select Pre-create Read-only Domain Controller
account
MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
65
Figure 2-26 Beginning the prestaging of an RODCCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
66
Prestaging an RODC (cont’d.)
• DCpromo wizard requires two additional details– Not normally used in DCpromo
• Need to provide the name of the computer• Need to provide a user or group that can complete
DCpromo
• Once wizard completes– Anyone in the delegated group can run DCpromo on
the prestaged computer to complete the installation

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
67
Figure 2-27 Specifying the computer name of the prestaged RODCCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
68
Figure 2-28 Identifying the user or group that will complete DCpromoCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
69
RODC Passwords
• Primary benefit of an RODC– Passwords not stored on the server– If the RODC compromised or stolen
• Attacker cannot discover administrator passwords
• Passwords controlled via three methods:– Password Replication Policy– Allowed RODC Password Replication Group– Denied RODC Password Replication Group

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
70
Figure 2-29 The Password Replication Policy for a specific RODCCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
71
Figure 2-30 The Allowed RODC Password Replication group applies to all RODCsCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
72
RODC Filtered Attribute Set
• Can extend schema to accommodate additional data storage within Active Directory
• Example: Application could store encryption keys or passwords as an attribute within a user account– Works well in most instances– Presents a risk when RODCs implemented
• Unless items added to the RODC filtered attribute set to identify attributes that should not be stored on the RODC

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
73
RODC Filtered Attribute Set (cont’d.)
• RODC filtered attribute set: predefined– Includes several attributes marked as confidential
• If organization added any Active Directory attributes that should not be replicated to RODCs– Take the following two steps:
• Add the attributes to the RODC filtered attribute set• Mark the attribute as confidential

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
74
RODC Filtered Attribute Set (cont’d.)
• Attributes modified by using the LDAP Data Interchange Format (LDIF) tool– Modify attribute search flags– When the 10th bit (0x200) set to a 1
• It adds the attribute to the RODC filtered attribute set• No longer replicated to RODCs
– When the 7th bit (0x080) set to a 1• It marks the attribute as confidential

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
75
Local Administrators Role on an RODC
• Can implement Administrator role separation on an RODC
• When server promoted to a domain controller– Local database of users and groups no longer
available in Computer Management• Includes the local Administrators group
– All accounts managed through Active Directory Users and Computers
• Permissions granted apply to the entire domain
• Possible to enable the local Administrators role

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
76
Local Administrators Role on an RODC (cont’d.)
• Compare Server Operators group with the local Administrators role– Server Operators group member can administer any
domain controller in the domain– Members of the local Administrators role can only
administer the single RODC

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
77
Local Administrators Role on an RODC (cont’d.)
• Can identify the delegated group or user for RODC administration when creating the RODC– May also do afterward– Two primary methods used:
• During DCpromo• Using Active Directory Users and Computers
• Activity 2-8: Configuring Administrator Role Separation for an RODC

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
78
Figure 2-31 Adding a group to the local Administrators role on an RODCCourtesy Course Technology/Cengage Learning

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
79
Summary
• Single-site configuration and multi-site configurations– Different considerations for replication, logon, site
awareness, sites, subnets, site links• Bridgehead servers• Full mesh replication topology• Hub and spoke replication topology used when:
– Several key locations connected with faster WAN connections
– Slower connections to outlying sites

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
80
Summary (cont’d.)
• DC in a remote office– Improves logon times, ensures logon in WAN link fails– Should also be a DNS server– Should be designated as a global catalog server or
the site should have Universal Group Membership Caching enabled
• Every forest has one schema master and one domain naming master
• Five master operations roles– Can transfer and seize

MCITP Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Administration (Exam #70-647)
81
Summary (cont’d.)
• Several requirements to support RODCs– Advantages: limit passwords stored on them, can
enable the local Administrators role• Can prevent other attributes from being replicated to
an RODC








![[S. Uludag] CIS / CSC 175 Problem Solving and Programming I Winter 2010 Suleyman Uludag Department of Computer Science, Engineering and Physics (CSEP)](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/56649f145503460f94c28dce/s-uludag-cis-csc-175-problem-solving-and-programming-i-winter-2010-suleyman.jpg)
![HYDRAULIC MOTORS EPM - EIBL- DHT · 2018-10-24 · Max. Oil Flow, cont. 405060 60 60 60 60 60 60 [lpm] int.* 455570 75 75 75 75 75 75 Max. Inlet cont. 175 175 175 175 175 175 175](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5e92874e36e2be41131fa132/hydraulic-motors-epm-eibl-dht-2018-10-24-max-oil-flow-cont-405060-60-60.jpg)








