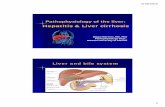
Cirrhosis of the liver (1)
-
Upload
jennifer-amponsah -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
5.809 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Cirrhosis of the liver (1)

Cirrhosis of the LiverBy Jennifer Amponsah, Krystalle Myers, Hayley
Townsend

What is cirrhosis?Cirrhosis is a
condition in which the liver slowly deteriorates and malfunctions due to chronic injury. Scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue, partially blocking the flow of blood through the liver

What causes cirrhosis?heavy alcohol consumptionchronic hepatitis C (the most common)ObesityAutoimmune inflammation of the liverMetabolic disorders

What are the symptoms of cirrhosis?Symptoms are hard to catch in the early stages of the
disease. However, as the disease progresses, a person may experience the following symptoms:
weaknessfatigueloss of appetitenauseavomitingweight lossabdominal pain and bloating itchingspiderlike blood vessels on the skin

DiagnosisDuring a physical examination the doctor may find:Enlarged liver or spleenExpanded abdomen, as a result of too much
fluidAbdominal or chest painRed spider-like blood vesselsJaundice (yellow eyes or skin)AnemiaLiver function problemsLow hormone levels

Population at risk for CirrhosisAlcoholicsWhite men Hispanic womenAges 41-50 StatisticsIn 2007 about 29,000 people died in the US from
cirrhosis, about 10 per 100,000.In 2010 there were about 14,000 deaths in the US
from cirrhosisIn 1997 cirrhosis was that 10th leading cause of
death in the US

What are the complications of cirrhosis?Edema and ascites: fluid collects in the legs, called edema, and
in the abdomen, called ascites..Bruising and bleeding easilyHigh blood pressureEsophageal varices and gastropathy: enlarged blood vessels in
the esophagus and stomachSplenomegaly: spleen enlargesGallstonesSensitivity to medicationsInsulin resistance and type 2 diabetesLiver cancer

Treatment and PreventionPreventionStop drinking alcohol (or don’t start at all)Limit salt in the dietEat a nutritious dietGet vaccinated for influenza, hepatitis A and
B.Practice safe sexTreatmentLiver transplantAntibiotics

Alcohol-related liver disease Heavy alcohol use over
several years can cause chronic injury to the liver.
For women, consuming two to three drinks—including beer and wine—per day and for men, three to four drinks per day, can lead to liver damage and cirrhosis.
Alcohol-related cirrhosis led to more deaths than cirrhosis of any other cause.

Behavioral Change ModelA behavior that you
can change to prevent cirrhosis is to stop alcohol consumption or reduce it quite a bit.

ReferencesNational Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse (NDDIC).(2008).
Cirrhosis. Retrieve from http://digestive.niddk.nih.gov/ddiseases/pubs/cirrhosis/
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000255.htm