chronic myeloid leukemia
-
Upload
srinivas-kinjarapu -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
111 -
download
3
Transcript of chronic myeloid leukemia
CHRONIC MYELOID
LEUKEMIA
K SRINIVAS,DEPT OF GEN
MED
Sunday,
February 1,
2015
1CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
DEFINITION
CML is defined as clonal expansion of a hemotopoietic stemcell possessing a reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22.
Sunday, February 1, 2015
2
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
This translocation results in head to tail fusion of the
breakpoint cluster region (BCR) gene on chr 22q11 with ABL1
gene located on chr 9q34
Sunday, February 1, 2015
3
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
Sunday, February 1, 2015CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
4
CML is myeloproliferative stem cell disorder resulting in
proliferation of all haemotopoetic lineages but manifesting
mostly in the granulocyte series
ETIOLOGY
Cigarette smoking acclerated the progression to blast crisis.
Atomic bomb survivors had increase evidence.
Sunday, February 1, 2015
5
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
INCIDENCE
I.5 per I00,000 population per year
Higher in men than in women(I.9 vs I.I)
Incidence gradually increases with age until in middle forties
when it starts to rise rapidly.
Sunday, February 1, 2015
6
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
The product of fusion gene resulting from the t(9;22) plays a
central role in the development of CML.
This chimeric gene is transcribed in to hybrid BCR-ABLI m RNA
in which exon ABLI is replaced by variable numbers of 5’BCR
exons producing a fusion protein P210BCR ABLI .
A rare brealk point occuring in the region of 3’ exons results in
230kDa,p230 BCR ABLI .
Sunday, February 1, 2015
7
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
Attchments of BCR sequences to ABLI results in 3 functional changes
1. the ABL protein becomes constituviley active as tyrosine
kinase(TK)enzyme
2. The DNA protein binding capacity of ABL is attenuated.
3. The binding of ABL to cytoskeletal action microfilaments is
enhanced.
Sunday, February 1, 2015
8
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
NATURAL HISTORY
Sunday, February 1, 2015CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
9
HAS 3 PHASES
A CHRONIC PHASE in which the disease is responsive to treatment and easily controlled.
AN ACCELERATED PHASE in which the disease control becomes more difficult.
BLAST CRISIS in which the disease transforms in to acute leukemia myeloid (70%) and lymphoblastic(30%),which is relatively refractory to treatment
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
Some patients are diagnosed while asymptomatic, during health
screening tests.
Fatigue
Malaise and wt loss
Symptoms resulting from splenic enlargement .
Infections , thrombosis , bleeding
Sunday, February 1, 2015
10
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
CVA
MI,
venous thrombosis
priapism
visual disturbances
pulmonary in sufficiency
Sunday, February 1, 2015
11
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
PHYSICAL FINDINGS
Pallor
Minimal to moderate splenomegaly
Sternal tenderness
Retinal haemorrhages
Purpura
Lymphadenopathy and myeloid sarcomas are unusual except in the late
stages of the disease
Sunday, February 1, 2015
12
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
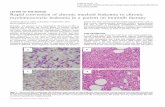
HEMATOLOGIC FINDINGS
PERIPHERAL SMEAR
elevated white blood cell count (>1,00,000)
The circulating cells are predominantly neutrophils,
metamyelocytes, myelocytes
Small portion of myeloblasts < 5%
Platelet count is elevated
Mild degree of normocytic normochromic anemia is seen
Sunday, February 1, 2015
13
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
BONE MARROW
Marrow cellularity is increased,with an increased myeloid to
erythroid ratio
Marrow blast percentage is normal or slightly elevated
Reticulin stain measured fibrosis is seen in half of the patients,
collagen fibrosis is unusualSunday, February 1, 2015
17
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
DISEASE ACCLERATION
Increased degree of anemia
Blood or marrow blasts between 10 and 20%
Marrow basophils >20%
Platelet count lees than 1,00,000
BLAST CRISIS
Blood or marrow blasts >20%
Hyposegmented neutrophils may appear (pegler huet anomaly)
Sunday, February 1, 2015
18
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
Sunday, February 1, 2015CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
19
Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase is low in CML
cells.
Histamine production is increased secondary to
basophilia causing pruritis, diarrhea and flushing.
CHROMOSOMAL FINDINGS
Hall mark of CML is the t(9:22)(q34<q11.2)
Recognised by a presence of shortened chromosome 22(22q)
designated as philadelphia chromosome.
Some patients may have complex translocations involving 3, 4,
5 chromosomes.Sunday, February 1, 2015
20
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
PROGNOSTIC FACTORS
Clinical outcome in cml is variable
Death was expected in 10 % of the patients with in 2 years and
20% thereafter,the median survival time was 4 years
2 important staging systems
Sokal index
Hasford system
Sunday, February 1, 2015
21
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
The prognostic factors are
% of circulating blasts
Spleen size
Plateletcount
Age
Cytogenic clonal evaluation
Developed based on chemotherpy treated patients
The prognostic factors are
% of circulating blasts
Spleen size
Plateletcount
% of eosinophils and basophils
Developed based on IFNtreated patients
SOKAL INDEX HASFORD SYSTEM
Sunday, February 1, 2015
22
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
TREATMENT
IMATINIB MESYLATE
HSCT
CHEMOTHERAPY
INTERFERON
LEUKAPHERISIS
SPLENECTOMY
NEWER AGENTSSunday, February 1, 2015
23
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
TREATMENT
The goal of CML therapy is to achieve prolonged
non durable
non neoplastic,
non clonal haemotopoesis
Sunday, February 1, 2015
24
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
IMATINIB MESYLATE
Acts through competitive inhibition of ATP binding site of
ABL kinase which leads to inhibition of tyrosine
phopsphorylation of proteins involved in BCR ABL signal
transduction
Induces apoptosis in cell expressing BCR ABL
The dosage is 400mg/day Sunday, February 1, 2015
25
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
SIDE EFFECTS
Fluid retention
Nausea
muscle cramps
Diarrhea
Skin rashes
myelosuppression
Sunday, February 1, 2015
28
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
RESISTANCE TO IMATINIB
4 mechanisms of resistance to imatinib
1. Gene amplification
2. Mutations at the kinase site
3. Enhanced expression of multidrug exporter proteins
4. Alternative signalling pathways
Sunday, February 1, 2015
29
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
NOVAL TK INHIBITORS
1. Nilotinib
2. Dasatanib
In patients with resistance to imatinib due to mutation at
kinase domain
IFN ALPHA has been approved by FDA only used if all other
options failed.
Sunday, February 1, 2015
30
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
HSCT
Allogenic hemtopoetic stem cell trans plantation
Autologous hemtopoetic stem cell trans plantation
Sunday, February 1, 2015
31
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
ALLOGENIC HSCT
Outcome depends upon
I. The patients age and phase of the disease
II. The type of donar
III. The preparative regimen
IV. GVHD
V. Post trans plantation treatment
Imatinib
Immunosuppression
Donar leukocyte transfusion
Sunday, February 1, 2015
32
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
AUTOLOGUS HSCT
Could potentially cure if cells are collected at complete
molecular remission.
Ptnts with this degree of response never relapse, so this
treatment modality has been abandoned by many groups
Sunday, February 1, 2015
33
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
CHEMOTHERAPY
Currently reserved for rapid lowering of
1. Wbc
2. Reduction of sym
3. Reversal of sym splenomegaly
HYDROXY UREA
BUSULPHAN
Not recommended mainly because of fatal myelosupression,
pulmonary, cardial fibrosis and addison like wasting syndrome
Sunday, February 1, 2015
34
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
LEUKAPHERISIS
Intensive leukapherisis may control the blood counts in
chronic phase CML
Useful in emergencies such as pulmonary failure and
crebrovascular accidents
Expensive and cumbersomeSunday, February 1, 2015
35
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
SPLENECTOMY
Symptomatic relief of painful splenomegaly.
Significant anemia or thrombocytopenia associated with
hypersplenism.
Splenic radiation is usually used to reduce the size of spleen
Sunday, February 1, 2015
36
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
NEW AGENTS
Several new agents are in development for CML for those patients who fail
with currently available TK inhibitors
OMACETAXINE
XL228
FTY720
AP24534
SARAFENIB
Sunday, February 1, 2015
37
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
TREATMENT OF BLAST
CRISIS
Sunday, February 1, 2015CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
38
Treatment with imatinib is generally ineffective.
Ptnts should be considered for allogenic HSCT.
Other approaches include induction of chemotherapy tailored
to the phenotype of blast cell ,followed by TK inhibitors with
additional chemotherapy and HSCT