Chordate clades & characters · Amphioxus and tunicates as evolutionary model systemsAmphioxus and...
Transcript of Chordate clades & characters · Amphioxus and tunicates as evolutionary model systemsAmphioxus and...

bs148h 27 September 2007Read: Text ch 34
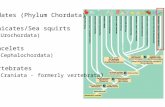
• animal diversity: vertebrates• chordate clades and shared derived characters• notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, post-anal tail• segmentation, shingles• Urochordates: sea squirts • Cephalochordates: amphioxus• Hagfish• Vertebrates
• Gnathostomes• Chondrichthyes• Osteichthyes• Tetrapods• Amniotes• 'Reptiles' & Birds• Mammals
Chordate Chordate cladesclades & characters& characters
induction by Sonic HedgehogSonic Hedgehog !
‘morphogen’{see ch 47}
Sonic Hedgehog expression in the Notocord and Neural Tubefloorplate.- Lance Davidson
http://phylogeny.arizona.edu/tree/eukaryotes/animals/chordata/chordata.html1. The notochordnotochord is an elongate, rod-like, skeletal structure
dorsal to the gut tube and ventral to the nerve cord. ... should not be confused with
the backbone of adult vertebrates.
In most adult chordates the notochord disappears …{remnants become spongy discs between vertebrae}
In some non-vertebrate chordates and fishes the notochord persists as a flexible rod that prevents collapse of the body during swimming.
2nd1st
The notochord appears early in embryogenyand plays an important role in organizing the embryonic development of nearby structures. Human
neural fold closes at 22 days
2. The nerve cordnerve cord develops … as a dorsal hollow tube above the notochord. … it differentiates into the brain & spinal cord.
{HOX genes induce anterior-posterior segments}
http://phylogeny.arizona.edu/tree/eukaryotes/animals/chordata/chordata.html3. visceral (pharyngeal or gill) clefts & arches:visceral (pharyngeal or gill) clefts & arches:The visceralvisceral cleftsclefts … push outward from the lateral walls
of the pharynx … connecting the pharynx to the exterior.… tissues between adjacent clefts are the visceral archesvisceral arches. 2nd
1st
In adult amphibiansamphibians and the amnioteamniote tetrapodstetrapods(= “reptiles,” birds and mammals)
the the anteriormostanteriormost cleftcleft transforms {during ontogeny}… auditory (EustachianEustachian) tubetube & middle ear chambermiddle ear chamber,
The embryonic fate of the clefts & slits varies depending on the taxonomic subgroup.
In many of the nonnon--vertebrate chordatesvertebrate chordates, such as tunicates and cephalochordates, … elaborated as food straining devicesstraining devices
In fishfish and juvenile amphibiansjuvenile amphibiansthe pharyngeal arches develop into gillsgills…. organs of gas exchange between the water and blood.
{ in planktivorous fish ‘rakers’ are straining devices} rakersrakers
filaments filaments (gills)(gills)
archarch

http://phylogeny.arizona.edu/tree/eukaryotes/animals/chordata/chordata.html3. visceral (pharyngeal or gill) clefts & archesvisceral (pharyngeal or gill) clefts & arches
{+4. Muscular postanal tail }
2nd
1st
HumanFetus at 40 days
(in humans)
cleftsclefts
Jaw bones of fish evolved & develop from
anterior arches
Ear bones of mammalsevolved from
posterior jaw bones
Segmentation Segmentation muscle somites & nerves
ShinglesShingles (Herpes varicella-zoster) is a nerve infection caused by the chicken-pox virus. … results from reactivation of the chicken-pox virus that remained in your body since you had chicken pox--perhaps many years ago. {dorsal root nerve ganglia,
organized in segments}
http://phylogeny.arizona.edu/tree/eukaryotes/animals/chordata/chordata.html
The strictly marine UrochordataUrochordata or Tunicataare commonly known as tunicates, sea squirts, and salps.
There are roughly 1,600 species of urochordates; most are small solitary animals but some are colonial organisms.
Morphological traits of chordates are clear in the larval the larval ““tadpoletadpole”” stagestage which showsshows
3. pharyngeal slits and archespharyngeal slits and arches, 2. dorsal hollow nerve corddorsal hollow nerve cord, 1. notochordnotochord and 4. postpost--anal muscular tailanal muscular tail. Adults … with an endostyleendostyle, a mucous food trap in the pharyngeal floor
that is homologous with the thyroid gland of vertebrates.+ molecular phylogenies (later)
Nearly all are sessile as adultsbut they have free-swimming larvae.
The larva swims until it attaches by its head to a surface and undergoes metamorphosis, during which {it becomes sedentary &}most of its chordate characteristics disappear.
(sung to the tune of "It's a Long Way to Tipperary")chorus: It's a long way from amphioxusIt's a long way from amphioxusIt's a long to us…It's a long way from amphioxus To the meanest human cuss. It's good-bye, fins and gill slits, Hello, lungs and hair! It's a long, long way from amphioxus, But we all came from there! …http://www3.pgh.net/~newcomer/amphioxus.htm
http://phylogeny.arizona.edu/tree/eukaryotes/animals/chordata/chordata.html
CephalochordataCephalochordata are also known as amphioxusamphioxusand lanceletslancelets.
The group contains only about 20 species of sand-burrowing marine creatures.
Adult post-dispersal movementsmight have selected forretention of ‘svelte’ juvenile morphology
What is wrong w/ this song?(aside from the obvious!)

Amphioxus and tunicates as evolutionary model systemsAmphioxus and tunicates as evolutionary model systems • Review articleSchubert, et al. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 21, 1 May 2006, Pages 269-277... all extant chordateschordates, at some stage in their life have:
The neural crestneural crest, a component of the ectoderm, is referred to as the fourth germ layer ...
These cells migrate extensively to yield: dorsal root gangliadorsal root ganglia, , sympathetic chain gangliasympathetic chain ganglia, , the four prethe four pre--aortic ganglia ... aortic ganglia ... the the adrenal medullaadrenal medulla, , ssensory gangliaensory ganglia of the fifth, seventh, ninth and tenth of the fifth, seventh, ninth and tenth cranial nervescranial nerves, muscle, bone, and cartilage in the face,, muscle, bone, and cartilage in the face,dentindentin--producingproducing cells of the cells of the teethteeth, , melanocytesmelanocytes, , smooth musclesmooth muscle of of great arteriesgreat arteries ... ... cornea, lens, and cornea, lens, and ciliaryciliary muscle of the eyemuscle of the eye ...
VertebratesVertebrates have acquired several specific characters.{not present in Urochordates or Cephalochordates}
The most important ‘invention’ of vertebrates ... a new head a new head with a full array of sensory organs derived mainly from neural crest ... neural crest ... which enabled vertebrates to shift to an active predatory lifestyle.
Class Myxini: HagfishesHagfishesThere are ~30 species of hagfishes, all marine. They are mainly bottom-dwelling scavengers. The skeleton of a hagfish is entirely cartilage:
- cartilaginous cranium (skull)- a cartilagenous notochord
Hagfishes do not have vertebrae.Hagfishes do not have vertebrae.{“degenerate” sister group to vertebrates}
a headhead - consisting of a brain at the anterior end of the dorsal nerve cord, eyes and other sensory organs, and a skulla skull -opened up a completely new way of feeding for chordates: active predation
Hagfish embryology with reference to Hagfish embryology with reference to the evolution of the neural crest.the evolution of the neural crest.
K.G. Ota et al. 2007 Nature 446, 672-675 ... hagfish neural crest is specified by molecular mechanisms that are general to vertebrates.
HagfishesHagfishes and lampreyslampreysnot only lacklack skeleton-supported jawsjawsbut also lack paired appendageslack paired appendages.
Class Cephalaspidomorphi: There are about 35 species of lampreyslampreysinhabiting marine and freshwater environments.The notochord of lampreys persists as the main
axial skeleton in the adult animal, as it does in hagfishes.
Lampreys also have pairs of cartilaginous projections partially enclosing the nerve cord.
{which pass for vertebrae}
VertebratesVertebrates are craniates that have a backbone
During the late Silurian & early Devonian period, gnathostomesgnathostomes largely replaced the agnathans.
Single-loop circulation - OK for low metab. rate ectotherms
Fishes & vert. descendantscannot synthesize ‘essential’aromatic Amino Acids (ch 41)
The common ancestors of all gnathostomes... an additional duplication of duplication of HoxHox genesgenes,... the single cluster in early chordates → four. Running the length of each side of the body
in aquatic gnathostomes is the lateral line system, a row of microscopic organs sensitive to vibrations ...

Sharks and their relatives, are called cartilaginous fishescartilaginous fishesbecause they have relatively flexible endoskeletons made of cartilage rather than bone.
In most species, parts of the skeleton are strengthened by mineralized granules, and the teeth are bony.
The cartilaginous skeleton of these fishes The cartilaginous skeleton of these fishes is a derived characteristic, not a primitive one; is a derived characteristic, not a primitive one; the ancestors of Chondrichthyes had bony skeletons,
The Shark Research Institute (SRI) is engaged in a worldwide study to locate, tag and document the behavior of whale sharks, Rhincodon typus, the largest fish in the sea.
They have a lateral linelateral line (pressure sensor) but no operculumno operculum (boney gill cover, helps pump water); & no swim bladderno swim bladder to maintain neutral buoyancy.
Unlike most bony fish, sharks have internal fertilizationinternal fertilization.
The boney fishesboney fishes (OsteichthyesOsteichthyes) evolved in fresh water
Bony fishesBony fishes have a lateral line system – like Chondrichthyes… can breathe while stationary by drawing water through the gills
by movement of the operculumoperculum… the transfer of gases between the blood & swim bladderswim bladder
helps control the buoyancy of the fish …… are the most numerous vertebrates (≈ 30,000 species).
Nearly all the families of fishes familiar to us are rayray--finned fishesfinned fishes(class Actinopterygii): bass, trout, perch, tuna, herring etc.
LobeLobe--finned fishesfinned fishes (Sarcopterygii) have muscular pectoral and pelvic fins supported by extensions of the bony skeleton - the coelacanth (Latimeria)
{+ Dipnoi lungfishes}
Zoology: Record-breaking fishProc. R. Soc. Lond. B doi:10.1098/rspb.2005.3419 (2006)Zoologists have unveiled the smallest freethe smallest free--living vertebrate ever foundliving vertebrate ever found. Mature females of the fishfish Paedocypris progenetica (pictured right),
which lives in highly acidic blackwater peat swamps in southeast Asia, average just 7.9 average just 7.9 millimetresmillimetres in lengthin length.
Described by Ralf Britz, of London's Natural History Museum, and his colleagues, the miniature species has a larva-like appearance, with a skull that does not form properly, leaving it with a hole in the top.
But the specimens' gonadal development shows them to be mature adults - and males possess a unique specialized structure near their genitals thought to be used for clasping the female during mating.
AmphibiansAmphibians lack lack the amniotic the amniotic ‘‘landland’’ egg.egg.
TetrapodsTetrapods are gnathostomes that have four legs & feet.The bones of the pelvic girdle are fused to the backbone, permitting forces generated by the hind legs to be transferred to the rest of the body.
... on the origin and phylogeny of living amphibians... on the origin and phylogeny of living amphibiansZhang P et al. 2005. SYSTEMATIC BIOLOGY 54: 391-400 .

The amniotic (land) eggamniotic (land) eggpossesses a unique set of membranes: amnion, chorion, and allantois.
The chorionchorion forms a protective membrane around the egg.
The allantoisallantois performs gas exchange and stores metabolic wastes (and becomes the urinary bladder in the adult).
As in other vertebrates, nutrients … are stored in the yolk sacyolk sac, which is much larger in amniotes than in vertebrates generally.
Placental mammalsPlacental mammals have suppressed the egg shell & yolk sac, and elaborated the amniotic membranes to enable nutrients and wastes to pass between mother and embryo.
The chorionchorion & allantoisallantois fuse, form umbilical cordumbilical cord & most of the placentaplacenta.
The amnionamnion surrounds the embryo and creates a fluid-filled cavity in which the embryo develops.
Reptiles are paraphyletic because of birds,unless we include birds w/ reptiles
Note: phylogeny of turtlesis still unresolved,
rel to other ‘reptiles.’
http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/diapsids/avians.htmlBirdsBirds are theropod dinosaurs w/ feathersfeathers.
Ancestors of the fearsome Tyrannosaurus rexwere clothed in delicate feathers, a fossil discovered in China suggests. …Xu X., et al. Nature, 431. 680 - 684 (2004). | Article |
Almost every part of a bird’s anatomy is modified to enhance flight. The bones are honeycombed – strong but light. The skeleton of a frigate bird
has a wingspan of more than 2 m but weighs only about 113 g (4 oz) {≈a Quarterpounder!}
Origin of avian genome size and structure Origin of avian genome size and structure in nonin non--avian dinosaursavian dinosaurs C.L. Organ et al. 2007. Nature 446, 180-184
Birds have the smallest genomes of all amniotes Birds have the smallest genomes of all amniotes {less non{less non--coding coding ““junkjunk””}}... may have been favoured by the demands of flight ... reducing metabolic costsreducing metabolic costs.... bats possess smaller genomes than do mammalian sister groups. ... there is a well-known positive relationship between cell size and genome size ... it is possible to approximate osteocyte (bone-cell) size from fossilized bones... the small genomes ... evolved in the evolved in the saurischiansaurischian dinosaur lineagedinosaur lineage ...
hair, milk w/o nipples, eggs
hair, milk w/ nipples, w/o placenta
hair, milk w/ nipples, w/ placenta - mom
Data suggests that in humans,mammary glands have been shaped by sexual selection –(possibly as a signal of age & health)
http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/chordata/mammalia.html
All mammalsmammals share three characteristics not found in other animals:
3 middle ear bones3 middle ear bones; hairhair; andthe production of milkmilk
by modified sweat glands called mammary glandsmammary glands.
and/or cosmetic surgery!
+ Mammalshave specialized‘heterodont’ teethteeth