Chapters 10 and 12. 1 st studies of heredity genetics Traits characteristics that are inherited.
-
Upload
karen-willis -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
1
Transcript of Chapters 10 and 12. 1 st studies of heredity genetics Traits characteristics that are inherited.

MENDELIAN GENETICS AND MEIOSIS
Chapters 10 and 12

MENDEL’S LAWS OF HEREDITY

Gregor Mendel 19th century Austrian monk
1st studies of heredity genetics Traits characteristics that are inherited

Studied pea plants
Contrasting traits were easily seen Short generation time Many offspring per generation Sexes on 1 flower control of pollination Mathematical analysis of data

PHENOTYPES AND GENOTYPES

Phenotype
Physical appearance Expressed in words tall, short

Genotype
Genetic makeup Expressed in terms of alleles Allele form of a gene for a trait Dominant allele always expressed (T
tall) Recessive allele if present, may not
be expressed (t short)

More Terminology
Homozygous 2 identical alleles (TT, tt) Heterozygous (hybrid) 2 different
alleles (Tt) Different genotypes can have the same
phenotype Tall TT or Tt

MONOHYBRID CROSSESA single trait

Mendel crossed a tall plant with a short plant
Original parents P generation Offspring F1 generation All F1 were tall

F1 were allowed to self-pollinate
F2 75% were tall, 25% short 3:1 ratio

Mendel’s conclusion
Each organism has 2 factors (alleles) that control each trait

Rule of Dominance
When an individual is hybrid for a pair of contrasting traits, only the dominant trait can be seen
TT x tt Tt **recessive trait is masked**
Crossing 2 hybrids always results in 3:1

Law of Segregation
Pairs of alleles for a trait are separated during the formation of gametes and are recombined during fertilization
Tt T (egg) + t (sperm) Tt (zygote) Explains appearance of recessive traits in
subsequent generations

Dihybrid crosses 2 traits
Height and seed color

Law of Independent Assortment
Genes for different traits are inherited independently of each other
Exception genes on the same chromosome

Punnett squares
Predict the ratio of all possible results for a certain genetic cross
Not what will happen, but what could happen
Exact ratios are not seen in nature due to chance

Monohybrid cross height (Tt x Tt)

Dihybrid cross height, color(TtYy x TtYy)
TY Ty tY ty
TY TTYY TTYy TtYY TtYy
Ty TTYy TTyy TtYy Ttyy
tY TtYY TtYy ttYY ttYy
ty TtYy Ttyy ttYy ttyy

MEIOSIS Type of cell division in which
daughter cells receive only half the # of chromosomes of the
parent cell

GENES, CHROMOSOMES, AND
NUMBERS

Diploid vs. monoploid
Chromosomes occur in pairs 1 allele is on each of the paired chromosomes

DiploidCell with 2 of each kind of chromosome (2n)
Body cells (somatic)

MonoploidCell with 1 of each kind of chromosome (n) also called haploid
Gametes sperm and egg

Homologous chromosomes paired chromosomes
Each of a pair has genes for the same traits
They may carry different alleles

Why meiosis?
Associated with sexual reproduction 2 parents
Allows offspring to have the same number of chromosomes as parents No doubling of chromosome number

PHASES Meiosis I and II
2 separate divisions

Interphase
Replication of the chromosomes Same as in mitosis

Prophase I
Each pair of homologous chromosomes comes together to form a tetrad
This is known as synapsis

Crossing-over may occur at this point
Exchange of genetic material between nonsister chromatids
Results in genetic variation or mutation
Completely random and unpredictable


Metaphase I
Tetrads line up at cell equator metaphase plate


Anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles disjunction
Critical step without disjunction, gametes would have abnormal numbers of chromosomes


Telophase I
Cytokinesis forms 2 daughter cells Each cell has only 1 chromosome from
each homologous pair Each chromosome is still doubled
another division is required


Meiosis II
Identical to mitosis


Results 4 monoploid daughter cells

Meiosis and genetic variation
Crossing-over results in genetic recombination gene shuffling
Almost endless number of different possible chromosomes You are not the exact blend of your parents Explains Mendel’s results

MISTAKES IN MEIOSIS

Nondisjunction
Failure of homologous chromosomes to separate
Both chromosomes move to the same pole
1 cell has an extra chromosome 1 cell is missing a chromosome


Trisomy
A gamete with and extra chromosome fuses with a normal gamete
Zygote has 1 extra chromosome 47 instead of 46 in humans
Trisomy 21 Down syndrome

Monosomy
A gamete with a missing chromosome fuses with a normal gamete
Zygote has 1 missing chromosome 45 instead of 46 in humans
Lethal most of the time Turner syndrome XO

Polyploidy
Total lack of chromosomal separation Lethal in animals Frequent in plants
Larger and healthier fruits and flowers Plant breeders induce polyploidy by using
chemicals that cause nondisjunction

MENDELIAN INHERITANCE OF HUMAN TRAITS
Chapter 12

Pedigree
Graphic representation of genetic inheritance
A chart showing familial relationships and patterns of trait inheritance

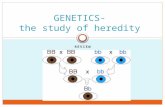
Sample pedigree chart
Squares maleCircles femaleFilled in afflictedBlank not afflictedHalf filled in carrier

RECESSIVE HEREDITY2 copies of allele are needed
(Most genetic disorders)

Cystic fibrosis (CF)
Formation and accumulation of mucus in lungs and pancreas
Due to a defective protein 1 in 25 white Americans carry the allele Resistance against tuberculosis

Tay-Sachs disease
Buildup of lipids in brain cells (lethal) Missing the gene coding for an enzyme Amish and eastern European Jews

Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Accumulation of phenylalanine (amino acid) in brain cells
Causes mental retardation Missing the enzyme needed to break
down the amino acid Standard test for all newborn infants PKU mothers can damage unborn child

Sickle-cell anemia
Abnormally shaped red blood cells Mutation in hemoglobin gene Most afflicted don’t survive childhood Carriers are more resistant to malaria Africans

Dominant heredity
1 allele is needed Tongue rolling Hitchhiker’s thumb Huntington’s chorea
Degeneration of brain cells lethal Onset of symptoms at 30-50 years of age 50% chance of passing on the allele

COMPLEX PATTERNS OF INHERITANCE

Incomplete dominance
Dominant allele is only partially expressed when recessive allele is present
Genetic blending

Four-o’clock flowersRed (RR) x White (RR)

Codominance
Both alleles are expressed equally Cattle red coat and white coat
codominant Hybrid roan (mixture of red and white
hairs)

Multiple alleles
More than 2 possible alleles within a species
Human blood type 3 possible alleles

Sex determination
Sex chromosomes only unmatched pair All other are autosomes 22 pairs
Female XX Male XY It is the male that determines the sex of
the offspring

Sex-linked traits
Controlled by genes on the X chromosome
Males are more likely to be afflicted Females may be carriers Color blindness Hemophilia Male pattern baldness *

Polygenic inheritance
Trait controlled by 2 or more genes Not expressed in 2 contrasting forms, but
varies between the 2 extremes Human height

Gene linkage
Genes located on the same chromosome Inherited together

Environmental influences
External temperature, light, nutrition, infectious agents
Internal hormones, age, sex

INHERITANCE OF HUMAN TRAITS

Human blood typescodominance and multiple alleles
3 possible alleles IA and IB are codominant i is recessive
6 possible genotypes IAIA or IAi type A IBIB or IBi type B IAIB type AB ii type O

Sex-linked traits
Red-green color blindness Most common
Hemophilia Commonly missing clotting factor VIII

Polygenic inheritance
Eye color, skin color, height Almost all human traits

Changes in chromosome number
Autosomes Down syndrome Sex chromosomes
Turner syndrome XO Klinefelter syndrome XXY OY lethal

DETECTING GENETIC DISORDERS

Karyotype
Comparing specimen chromosomes to normal chromosomes


Amniocentesis
Sample of free-floating fetal cells Make a karyotype

Genetic Screening
Compare your genes to known disease markers