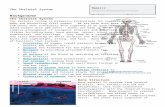
CHAPTER TWENTY FOUR 1. Bone Composed of two different kinds of bony tissue Cancellous or...
58
PHARMACY TECHNICIAN CHAPTER TWENTY FOUR 1
-
Upload
helen-lewis -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of CHAPTER TWENTY FOUR 1. Bone Composed of two different kinds of bony tissue Cancellous or...
- Slide 1
- CHAPTER TWENTY FOUR 1
- Slide 2
- Bone Composed of two different kinds of bony tissue Cancellous or spongy boneporous, inner bone that provides volume Compact bonehard, outer covering that provides strength and shape The rounded end of a bone is covered with smooth, slippery articular cartilage Many bones are hollow, and contain marrow: Red marrow in children Fatty yellow marrow in adults 2
- Slide 3
- Bone and Muscle 3
- Slide 4
- Types of Muscle Skeletal musclesattached to bones; provide body movement Voluntary, striated in shape, contain multiple peripheral nuclei Cardiac muscletissue that composes the heart Contracts rhythmically, coordinated by transmission of electrical impulses from nerve to muscle fibers Smooth or visceral muscleattached to or lines other organs such as the stomach, intestines, lungs, and blood vessels 4
- Slide 5
- Five Categories of Bone: Flat bonesgenerally more flat than round Irregular boneshave no defined shape Sesamoid boneshave cartilage or fibrous tissue mixed in Short bonesgenerally cube-shaped Long bonesthe most common bone Epiphysis (the rounded end of the bone) Diaphysis (the main shaft or central part of the bone) 5
- Slide 6
- Disorders of the Bone Osteomyelitis Bacterial Infection Inside the Bone Destroys bone tissue Original site of infection is frequently in another part of body Infection spreads to the bone via the blood Osteoporosisbone brittleness due to lack of calcium Prevalent in postmenopausal women because of estrogen deficiency Pagets diseasechanges the normal process of bone growth Causes bone to break down more quickly and grow back softer than normal bone 6
- Slide 7
- Musculoskeletal Diseases/Disorders Bursitisinflammation of the small, fluid-filled pouches between bones Tendonitisinflammation of the cords of connective tissue that attach muscle to bone Myalgiamuscle pain 7
- Slide 8
- Skeletal Muscle Relaxants MOA: may block action of calcium in muscles Indications: painful muscle spasms, neurological spinal cord injury Main Side Effects: Drowsiness, weakness GenericBrand CyclobenzaprineFlexeril MethocarbamolRobaxin BaclofenLioresal
- Slide 9
- ArthritisInflammation of a Joint Rheumatoidan autoimmune disorder Osteoarthritiscaused by physical degeneration of connective tissue Goutcaused by crystals of uric acid in blood 9
- Slide 10
- Treatments Osteomyelitis Anti-infective agent is best treatment for osteomyelitis Osteoporosis Vitamin D and mineral calcium replacement therapy Hormone therapy (estrogen, calcitonin) and bisphosphonates SERMs for postmenopausal women Gold compounds used to treat osteoarthritis 10
- Slide 11
- Treatments Gout Colchicine used to alter ability of phagocytes to attack uric acid crystals Anti-inflammatory analgesics can be used to reduce pain and inflammation Inflammation Salicylates relieve inflammation by inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandin Topical corticosteroids treat most causes, including chemical, mechanical, microbiological, and immunological 11
- Slide 12
- Musculoskeletal Pharmaceuticals ASA (acetylsalicylic acid) Relieves inflammation by inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandin Salicylates are also used as analgesics and antipyretics NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) Inhibit or block the enzyme that starts the reaction of inflammation by making prostaglandin COX-2 inhibitors Block only the cyclooxygenase II that makes PGE-2, but not C-1 (PGE-1) Inflammation is inhibited, but not the viscosity of the mucosal linin 12
- Slide 13
- Non Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drugs Called the NSAIDS Excellent drugs for pain relief and reducing fever and inflammation Developed as an alternative to corticosteroids MOA: blocks the COX enzyme to block prostaglandin formation Side effects are: severe GI bleeding (possible), GI upset and gastritis, kidney insufficiency, edema and elevated blood pressure, hyperkalemia risk GenericBrand IbuprofenMotrin, Advil NaproxenNaprosyn KetorolacToradol (IV available) DiclofenacVoltaren CelecoxibCelebrex (COX2 inhibitor)
- Slide 14
- Musculoskeletal Pharmaceuticals Bisphosphonatesindicated for osteoporosis Mimic the natural organic bisphosphonate salts found in the body Inhibit bone resorption and osteoclast activity Restore bone mass and density SERMs (selective estrogen receptor modulators) Indicated for postmenopausal women Protective effect on bones and heart Skeletal muscle relaxantsused to relax specific muscles in the body Relieve pain, stiffness, and discomfort Block muscle contraction at the neuromuscular junctio 14
- Slide 15
- CHAPTER TWENTY FIVE 15
- Slide 16
- The Respiratory System Divided into the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract The upper respiratory tract consists of: Nose or nasal cavity Paranasal sinuses Pharynx and larynx 16
- Slide 17
- The Respiratory System (cont.) The lower respiratory tract consists of: Trachea Two lungs Two main bronchi 17
- Slide 18
- The lower respiratory tract. 18
- Slide 19
- Respiration Diaphragmdome-shaped layer of muscle that lies across bottom of chest cavity Breathing occurs as diaphragm contracts and relaxes Carbon dioxide pushed out of the lungs during relaxation Oxygen pulled into the lungs during contraction 19
- Slide 20
- Structure of Lungs About 10 percent solid tissue Remainder of structure filled with air and blood The functional structure can be divided into two parts: Conducting airways (bronchi and bronchioles)tubes lined by cilia and respiratory mucosa Cartilagesupports and cushions the bronchi 20
- Slide 21
- Common Cold Caused by a viral infection that inflames the membranes in nose and throat Antibiotics will not cure a cold or any other viral infection Treatment is considered symptomatic Cough May be a symptom of a cold, flu, respiratory problems, or nonrespiratory diseases Most likely begins with an irritation of nerves in the respiratory tract Nonproductive cough treated with cough suppressant Productive cough treated with an expectorant 21
- Slide 22
- Allergies and Asthma Allergies Caused by the immune system reacting to a substance that does not cause disease Treatment may be palliative, with antihistamines and antitussives Treatment may be preventive, with mast cell stabilizers Asthma Chronic respiratory disease Characterized by inflammation of airways, tightening of muscles around airways Treatment is palliative with albuterol and other bronchodilators 22
- Slide 23
- Emphysema Chronic destruction of alveoli External exchange interrupted when alveoli become permanently damaged Treatment may be palliative, with stimulant inhalers Treatment may be preventive, with anti-inflammatory corticosteroids 23
- Slide 24
- Nasal Congestion and Rhinitis Nasal Congestion Inflamed, stuffy nose Treatment may be palliative, to promote easier breathing Indications for use of decongestants are nasal and bronchial congestion Rhinitis Inflammation of nasal membranes, and/or runny nose Common component of colds and allergies Treatment is considered symptomatic Drugs to treat include: 24 GenericBrand OxymetazolineAfrin Nasal Spray PhenylephrineNeoSynephrine Nasal Spray FluticasoneFlonase (Nasal Steroid preparation) MometasoneNasonex (Nasal Steroid preparation) Oxymetazoline and Phenylephrine are sympathomimetic and can raise blood pressure. They also should be used with caution in gluacoma patients
- Slide 25
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Umbrella term for emphysema and chronic bronchitis, and asthma Characterized by partially blocked bronchi and bronchioles, mucus plugging and bronchoconstriction Causes shortness of breath Treatment may be palliative, with bronchodilators Drugs 25 GenericBrand AlbuterolProventil PirbuterolMaxair IpratropiumAtrovent Fluticasone/SalmeterolAdvair Diskus Budesonide/FormoterolSymbicort Albuterol and Pirbuterol and Beta 2 agonist but can cause tachycardia in some people. All of the above drugs are available as MDI Advair is a DPI (Dry powder inhaler system) (no CFC propellants) With Advair and Symbicort advise the patient to rinse the mouth with water to prevent candida infection (Trush or moniliasis)
- Slide 26
- CHAPTER TWENTY SIX 26
- Slide 27
- The heart. 27
- Slide 28
- Anatomy of the Heart Composed of four chambers: two upper and two lower Atriatop two chambers Ventriclesbottom two chambers Septumdivides heart into right and left sides 28
- Slide 29
- Valves of the Heart Tricuspid valvelocated between the right atrium and the right ventricle Pulmonary valvelocated between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery Mitral or bicuspid valvelocated between the left atrium and the left ventricle Aortic valvelocated between the left ventricle and the aorta 29
- Slide 30
- Layers of the Heart Pericardiumfluid-filled sac that surrounds and protects the heart Permits free movement of the heart during contraction Endocardiuminnermost wall layer; covers the inside surface of the heart Myocardiumsurrounds heart and causes chamber contractions 30
- Slide 31
- Function of the Heart Provides oxygenated blood throughout the body by a pumping mechanism Oxygenated blood deposits materials necessary for growth and nourishment Receives from tissues the waste products resulting from metabolism 31
- Slide 32
- Hypertension Sustained elevation of systemic arterial blood pressure Symptoms include: Severe headache Chest pain Irregular heartbeat Fatigue Pharmaceutical treatment includes diuretics, vasodilators, ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, and calcium channel blockers 32
- Slide 33
- Congestive Heart Failure Heart pumps out less blood than it receives Results in weakened and enlarged heart Symptoms of CHF include: Upright posture or leaning forward Anxiety and restlessness Cyanotic and clammy skin Persistent cough Rapid breathing Fast heart rate Edema of the lower limbs Pharmaceutical treatment includes cardiac glycosides, diuretics, vasodilators, ACE inhibitors, beta-adrenergic blockers, and phosphodiesterase inhibitors 33
- Slide 34
- Coronary Artery Disease Occurs when there is insufficient blood flow to the heart Can lead to: Angina Heart attack Arrythmias Stroke Pulmonary embolism Heart failure Early CAD is closely monitored and symptomatic relief is given by the use of nitroglycerin and other nitrate drugs. NTG ISDN (isosorbide dinitrate) Once CAD has progressed to the point where a patient has angina at rest. Two procedures can be taken PCI with stents CABG (Coronary artery bypass graft) 34
- Slide 35
- Cardiovascular Pharmaceuticals Antiarrhythmic drugsrestore normal rhythm patterns but do not cure the cause of the irregular heartbeat Cardiac glycosidesused to increase the force of myocardial contraction, without causing an increase in the consumption of oxygen Diureticsused to eliminate excess sodium and water via the urinary tract Vasodilatorsallow more blood to exit the heart, preventing or mitigating congestion; lower blood pressure 35
- Slide 36
- Cardiovascular Pharmaceuticals (cont.) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors)lower high blood pressure; thought to reshape the heart; prevent the body from producing natural vasodilators Angiotensin II receptor blockerssimilar to ACE inhibitors; block the bodys natural vasodilators Beta-adrenergic blockersused to block cells from receiving natural vasoconstrictors Platelet aggregation inhibitorsreduce the ability of the blood to coagulate 36
- Slide 37
- Cardiovascular Pharmaceuticals (cont.) Anticoagulantsprevent clots from forming or existing clots from getting bigger Tissue plasminogen activatorsbreak down blood clots by reversing the clotting order and interfering with the synthesis of various clotting factors Thrombin inhibitorsinactivate bound thrombin by binding to the enzyme and blocking its interaction with its substrates of fibrin Antihyperlipidemicshelp prevent the progression of coronary artery disease by lowering plasma lipid levels 37
- Slide 38
- Anticoagulants Do not thin out the blood Prevent clots from forming Prevent existing clots from getting bigger Cannot dissolve existing blood clots 38
- Slide 39
- Warfarin Oral drug of choice Works by preventing the synthesis of clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X Used in the long-term prevention or management of venous thromboembolic disorders, including: Deep vein thrombosis Pulmonary embolism Clotting associated with atrial fibrillation and prosthetic heart valves Vitamin K may be used as an antidote when too much warfarin has been given 39
- Slide 40
- Heparin Parenterally administered drug of choice Works by inactivating clotting factors IX, X, XI, and XII Used prophylactically to: Prevent and treat deep vein thrombosis Prevent and treat pulmonary embolism Treat thrombophlebitis Prevent clotting during cardiac and vascular surgery The only antidote for heparin overdose is protamine sulfate 40
- Slide 41
- Cholesterol and Triglycerides HDLhigh-density lipoproteins or good cholesterol LDLlow-density lipoproteins or bad cholesterol Triglyceridesa form of energy stored in adipose and muscle tissues Often measured to depict fat ingestion and metabolism Can be used to assess CAD risk factors Statins- drugs used to lower LDL cholesterol 41 GenericBrand AtorvastatinLipitor SimvastatinZocor FluvastatinLescol RosuvastatinCrestor Major: Side effects are nausea, GI and a reaction called Rhabdomyolysis and myopathy where patient experiences muscle pain and at the extreme renal failure and hospitalization Statins are drug interactions with medications that block the livers CYP450 systems: Diltiazem, amiodarone, HIV protease inhibitors, Ketoconazole
- Slide 42
- GenericBrand Simvastatin + EzetimibeVytorin Lovastatin + NiacinAdvicor Simvastatin + NiacinSimcor 42 Above medications are combination products that contain a statin + one other drug. Exetimibe is a drug that block enteral absorption of cholesterol. Niacin is a B vitamin used to high doses to alter metabolism of triglycerides and raise HDL One unique combination product is Caduet, which is a combination of Atorvastatin and Amlodipine (calcium channel blocker ). This product is used to treat metabolic syndrome
- Slide 43
- Non Statin Antilipidemic drugs Other drugs that target lowing VLDL, triglycerides, and raising HDL have a beneficially affect on coronary artery disease 43 GenericBrandIndications GemfibrozilLopidHigh VLDL FenofibrateTricorHigh VLDL, low HDL NiacinNiaspanHigh VLDL, low HDL Omega 3 Fatty acid LovazaHigh VLDL, low HDL
- Slide 44
- Drugs used in the Treatment of MI MI is a myocardial Infarction. Heart attacks occurs because a arterial plaque raptures and triggers the coagulation cascade completely occudding a coronary artery. This cause necrosis of the heart muscle. If not treated MI result in death from cardiogenic shock Even if treat mortality is high from secondary ventricular fibrillation Even if treated, patient will suffer irrevocable heart damage resulting in CHF and/or damage to cardiac conduction system leading to pacemaker or ICD placement The main goal is to relieve the blood vessel of the clot and reestablish coronary blood flow Can use clot busters drugs or have percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) which the femoral artery undergo catherization and a probe is guide to the site of occlusion and a ballon is inflated to push aside the clot 44
- Slide 45
- GenericBrandUse AspirinEcotrinTo stop platelet action at the clot ClopidogrelPlavixTo stop platelet action at the clot NitroglycerinVariousTo vasodilate coronary artery to relieve pain Tissue plasminogen activator TPA Alteplase (Activase) Reteplase (Retavase) Tenecteplase (Tnkase) Activate plasmin, a blood protein that opens blood clots HeparinN/AA potent blood anticoagulant that stop further coagulation MetoprololLopressorA beta blocker that slows heart rate and slows spread of infarction 45
- Slide 46
- Drug used in the treatment of Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation is a heart rate disturbance in which the atrium/ atria are beating extremely rapidly Can lead to cardiogenic shock if the rate reaches the ventricles Therapy is aimed blocking this rate disturbance from reaching the ventricles (called rate control), preventing blood clots in the heart muscle wall from forming embolus (anticoagulation), and eventual cardioversion Rate control Diltiazem Verapamil Beta blockers Amiodarone Anticoagulation Warfarin Apixaban (Eliquis) Cardioversion Ibutilide (Tikosyn) High dose Amiodarone 46
- Slide 47
- Ventricular Fibrillation Ventricular Fibrillation, VF, is a cardiac arrythmia where the ventricles beat extremely rapidly to the point where no coordinated contraction occurs Medical emergency VF lasting more than the 90 seconds leads to asystole, sudden cardiac death and cardiogenic shock. Brain death from cerebral hypoxia Therapy Direct DC shock with ACD: delivery of DC shock with about 360 Joules of electricity to bring about normal sinus rhythm. Best chance at survival but not always successful Drug treatment used in conjunction with ACD if shock initially unsuccessful Amiodarone: 300 mg IV push with 150 mg IV supplemental doses Lidocaine: 100 mg IV push Epinephrine or Atropine can be tried after failed attempts at shock Other drugs include calcium chloride 10%, magnesium sulfate and vasopressin 47
- Slide 48
- Beta Blockers Very useful in extending the life expectancy of patients post MI and in CHF patients Due to evidence from clinical trials like the scandinavian Timolol study and the BHAT (beta block heart attack trial with propranolol) beta blocker are now an important drug in the therapy of post MI patients 48 GenericBrand PropranololInderal MetoprololLopressor TimololBlocadren AtenololTenormin CarvedilolCoreg
- Slide 49
- ACE Inhibitors Used to decrease mortality in post MI and CHF patients Used with beta blockers and often in combination with them 49 GenericBrand CaptoprilCapoten EnalaprilVasotec LisinoprilZestril, Prinivil BenazaprilLotensin RamiprilAltace Potassium levels should be monitored ACE inhibitors are pregnancy category X May cause relentless coughing in some patient requiring discontinuation due to potent edema and closure of the airway
- Slide 50
- CHAPTER TWENTY EIGHT 50
- Slide 51
- The renal system. 51
- Slide 52
- The Renal System Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, one bladder, and the urethra Filtering system of the kidneys is composed of millions of nephrons Waste from food and drug metabolization is filtered through the nephrons Wastes exit the kidneys as urine via the ureters Ureters lead to the bladder, where urine is stored until released The kidneys are located in the posterior abdomen just above the waist 52
- Slide 53
- Nephron Smallest, most basic part of the kidney Filters the blood that passes through the kidneys Produces urine through the processes of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion Enables blood to reabsorb water, electrolytes, and nutrients 53
- Slide 54
- Kidney and Bladder Kidney Built almost entirely of nephrons Organ that filters blood and produces urine Urine produced by the kidneys is conducted to the bladder Bladder Organ used for waste storage Can collect approximately 350 mL to 500mL of urine Allows for discretionary voiding 54
- Slide 55
- Urinary Tract Infections Bacterial infections of the urinary system Symptoms include: Frequent urge to void Burning sensation when voiding Cloudy or strong-smelling urine Blood in the urine 55
- Slide 56
- Treating UTIs Cranberry juice: A substance in cranberry juice keeps infection-causing bacteria from attaching to the walls of the urethra Also makes the urine more acidic Anti-infectives Destroy or inhibit bacterial growth Phenazopyridine (200 mg tid pc) Can be used to manage the symptoms of a burning and itching urethra 56
- Slide 57
- Kidney Stones Common and painful urinary tract disorder Solid mineral deposits accumulate in the urinary tract Treatment is palliative, with pain management Oral analgesics for mild to moderate pain may be used Treatment is preventative, with diet Mineral and vitamin supplements Increased fluid intake 57
- Slide 58
- Edema and Hypertension Consistently elevated blood pressure levels Lead to damage of the kidney arteries Treatment is with diuretics Reduce high blood pressure 58