Chapter 9€¦ · · 2014-07-22Chapter 9 . 9-2 “We Can Make ... design files available for...
Transcript of Chapter 9€¦ · · 2014-07-22Chapter 9 . 9-2 “We Can Make ... design files available for...
9-2
“We Can Make the Bits Produce Any Report You
Want, But You’ve Got to Pay for It.”
• Need to monitor patient workout data.
• Spending too many hours each day looking at patient
workout data.
• Great use for exception reporting.
• Animation & new types of reporting creates innovative and
motivating reports.
• Eliminating silos enables everyone to gain more information
from PRIDE data.
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-3
Study Questions
Q1: How do organizations use business intelligence (BI) systems?
Q2: What are the three primary activities in the BI process?
Q3: How do organizations use data warehouses and data marts to acquire data?
Q4: How do organizations use reporting applications?
Q5: How do organizations use data mining applications?
Q6: How do organizations use BigData applications?
Q7: What is the role of knowledge management systems?
Q8: What are the alternatives for publishing BI?
Q9: 2024?
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-4
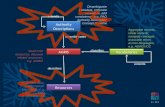
Q1: How Do Organizations Use Business Intelligence
(BI) Systems?
Components of Business
Intelligence System
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-5
Example Uses of Business Intelligence
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-6
What Are Typical Uses for BI?
• Identifying changes in purchasing patterns
– Important life events cause customers to change what they buy.
• BI for entertainment
– Netflix has data on watching, listening, and rental habits, however,
determines what people actually want, not what they say.
• Predictive policing
– Analyze data on past crimes, including location, date, time, day of
week, type of crime, and related data, to predict where crimes are
likely to occur.
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-7
Q2: What Are the Three Primary Activities in the BI
Process?
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-8
Using Business Intelligence to Find Candidate Parts at
AllRoad
• Identified criteria for parts customers might want to print
themselves.
– Provided by vendors who already agree to make part
design files available for sale.
– Purchased by larger customers.
– Frequently ordered parts.
– Ordered in small quantities.
– Simple in design.
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-9
Acquire Data: Extracted Order Data
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-11
Analyze Data: Access Query
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-13
Joining Order Extract and Filtered Parts Tables
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-14
Sample Orders and Parts View Data
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-16
Qualifying Parts Query Design
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-17
Qualifying Parts Query Results Figure
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-18
Publish Results: Sales History for Selected Parts
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-19
Q3: How Do Organizations Use Data Warehouses and
Data Marts to Acquire Data?
Functions of a Data Warehouse
• Extract data from operational, internal and external
databases.
• Cleanse data.
• Organize, relate data warehouse.
• Catalog data using metadata.
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-20
Components of a Data Warehouse
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-21
Examples of Consumer Data That Can Be Purchased
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-22
Possible Problems with Source Data
Curse of
dimensionality
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-23
Data Warehouses Versus Data Marts
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-24
Q4: How Do Organizations Use Reporting
Applications?
• Create meaningful information from disparate data sources.
• Deliver information to user on time.
• Basic operations:
1. Sorting
2. Filtering
3. Grouping
4. Calculating
5. Formatting
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-25
How Does RFM Analysis Classify Customers?
• Recently
• Frequently
• Money
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-26
RFM Analysis Classifies Customers
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-27
Typical OLAP Report
OLAP Product Family by Store Type
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-28
Example of Expanded Grocery Sales OLAP Report
Drill
down into
the data
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-29
OLAP Product Family and Store Location by Store Type,
Showing Sales Data for Four Cities
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-30
Q5: How Do Organizations Use Data Mining
Applications?
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-31
Unsupervised Data Mining
• Analyst does not start with a priori hypothesis or model.
• Hypothesized model created based on analytical results to
explain patterns found.
• Example: Cluster analysis.
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-32
Supervised Data Mining
• Uses a priori model to compute outcome of model
• Prediction, such as regression analysis
• Ex: CellPhoneWeekendMinutes
= (12 + (17.5*CustomerAge)+(23.7*NumberMonthsOfAccount)
= 12 + 17.5*21 + 23.7*6 = 521.7
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-33
Market-Basket Analysis
• Market-basket analysis – a data-mining technique for determining sales patterns. – Statistical methods to identify sales patterns in large
volumes of data. – Products customers tend to buy together. – Probabilities of customer purchases. – Identify cross-selling opportunities.
Customers who bought fins also bought a mask.
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-34
Market-Basket Example: Dive Shop
Transactions = 400
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-35
Decision Trees
• Hierarchical arrangement of criteria to predict a classification
or value.
• Unsupervised data mining technique.
• Basic idea of a decision tree
– Select attributes most useful for classifying something
on some criteria to create “pure groups”.
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-36
Credit Score Decision Tree
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-37
Decision Rules for Accepting or Rejecting Offer to
Purchase Loans
If percent past due is less than 50 percent, then accept loan.
• If percent past due is greater than 50 percent and
• If CreditScore is greater than 572.6 and
• If CurrentLTV is less than .94, then accept loan.
• Otherwise, reject loan.
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-38
Using MIS InClass Exercise 9: What Singularity Have
We Wrought?
Trends in the Computing Industry
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-39
Q6: How Do Organizations Use BigData Applications?
• Huge volume – petabyte and larger.
• Rapid velocity – generated rapidly.
• Great variety
– Structured data, free-form text, log files, possibly
graphics, audio, and video.
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-40
MapReduce Processing Summary
Google search
log broken into
pieces
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-41
Google Trends on the Term Web 2.0
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-42
Hadoop
• Open-source program supported by Apache Foundation2.
• Manages thousands of computers.
• Implements MapReduce
– Written in Java
• Amazon.com supports Hadoop as part of EC3 cloud offering.
• Query language entitled Pig.
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-43
Q7: What Is the Role of Knowledge Management
Systems?
• Knowledge Management
– Creating value from intellectual capital and sharing that
knowledge with those who need that capital.
– Preserving organizational memory by capturing and
storing lessons learned and best practices of key
employees.
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-44
Benefits of Knowledge Management
• Improve process quality.
• Increase team strength.
• Goal:
– Enable employees to use organization’s collective
knowledge.
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-45
What Are Expert Systems?
Expert systems
Rule-based IF/THEN
Encode human knowledge
Process IF side of rules
Report values of all variables
Knowledge gathered from human experts
Expert systems shells
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-47
Drawbacks of Expert Systems
1. Difficult and expensive to develop
– Labor intensive
– Ties up domain experts
2. Difficult to maintain
– Changes cause unpredictable outcomes
– Constantly need expensive changes
3. Don’t live up to expectations
– Can’t duplicate diagnostic abilities of humans
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-48
What Are Content Management Systems (CMS)?
• Support management and delivery of documents, other expressions of
employee knowledge
• Challenges of Content Management
– Databases are huge
– Content dynamic
– Documents do not exist in isolation
– Contents are perishable
– In many languages
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-49
What are CMS Application Alternatives?
• In-house custom
– Customer support department develops in-house database
applications to track customer problems
• Off-the-shelf – Horizontal market products (SharePoint)
– Vertical market applications
• Public search engine
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-50
How Do Hyper-Social Organizations Manage
Knowledge?
• Hyper-social knowledge management
– Application of social media and related applications for
management and delivery of organizational knowledge
resources.
• Hyper-organization theory
– Framework for understanding this new direction in KM.
– Focus moves from knowledge and content per se to fostering
authentic relationships among creators and users of
knowledge.
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-51
Hyper-Social KM
Alternative Media
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-52
Q8: What Are the Alternatives for Publishing BI?
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-54
Q9: 2024?
• World generating and storing exponentially more information.
• Information about customers, and data mining techniques going
to get better.
• Companies will know more about your purchasing habits and
psyche.
• Social singularity – Machines will build their own information
systems.
• Will machines possess and create information for themselves?
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-55
Guide: Semantic Security
1. Unauthorized access to protected data and information
– Physical security
Passwords and permissions
Delivery system must be secure
2. Unintended release of protected information through reports and documents.
3. What, if anything, can be done to prevent what Megan did?
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-56
Guide: Data Mining in the Real World
• Problems:
– Dirty data
– Missing values
– Lack of knowledge at start of project
– Over fitting
– Probabilistic
– Seasonality
– High risk – unknown outcome
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-57
Active Review
Q1: How do organizations use business intelligence (BI) systems?
Q2: What are the three primary activities in the BI process?
Q3: How do organizations use data warehouses and data marts to acquire data?
Q4: How do organizations use reporting applications?
Q5: How do organizations use data mining applications?
Q6: How do organizations use BigData applications?
Q7: What is the role of knowledge management systems?
Q8: What are the alternatives for publishing BI?
Q9: 2024?
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-58
Case Study 9: Hadoop the Cookie Cutter
• Third-party cookie created by a site other than one you visited.
• Generated in several ways, most common occurs when a Web
page includes content from multiple sources.
• DoubleClick
– IP address where content was delivered.
– Records data in cookie log.
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-59
Case Study 9: Hadoop the Cookie Cutter (cont'd)
• Third-party cookie owner has history of what was shown,
what ads clicked, and intervals between interactions.
• Cookie log contains data to show how you respond to ads
and your pattern of visiting various Web sites where ads
placed.
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .
9-61
Ghostery in Use (ghostery.com)
C o p y r i g h t © 2 0 1 5 P e a r s o n E d u c a t i o n , I n c .