Chapter 7 Notes - Maroon scienceSomatosensation Description receives impulses from the body’s...
Transcript of Chapter 7 Notes - Maroon scienceSomatosensation Description receives impulses from the body’s...

Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Slides 8.1 – 8.19
Seventh Edition
Elaine N. Marieb
Chapter 8
Special Senses
Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook

Special Senses
Title
• Somatosensation
Essential Question
• Describe the structures and functions of somatosensation.

Somatosensation Description
receives impulses from the body’s somatosensory receptors
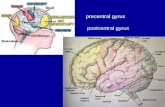
Location in the Brain
Found in the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe
Posterior to the central sulcus, and anterior portion of the parietal lobe.
Body Regions with the Most
Sensory Receptors:
Lips and fingertips

Sensory and Motor Areas of the
Cerebral Cortex
Slide 7.31Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 7.14


Sensory pathways are crossed pathways.
• The left side of the sensory cortex receives impulses from the right side of the body, and vice versa.
Right Hand

Pathways for Sensory System
• Pain
DRG (dorsal root ganglion) spinal cord thalamus SS cortex

DRG – Dorsal Root Ganglion

Pathways for Sensory System
• Touch/Temp
DRG spinal cord medulla thalamus SS cortex

What is a Penfield Homunculus?
• “little man” is a drawing that indicates the density of neurons in the somatosensory cortex
• The more dense the neurons are, the greater the volume that is taken up in the brain.


Special Senses
Title
• Vision
Essential Question
• Describe the structures and functions of vision.

Meibomian
Glands

Accessory Structures of the Eye
Slide 8.3bCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Meibomian glands –modified sebaceous glands produce an oily secretion to lubricate the eye

Accessory Structures of the Eye
Slide 8.3cCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Ciliary glands (no label) –modified sweat glands between the eyelashes
Figure 8.1b

Conjunctiva

Accessory Structures of the Eye
Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Conjunctiva
Membrane that lines the eyelids
Connects to the surface of the eye
Secretes mucus to lubricate the eye

Lacrimal Apparatus
Slide 8.5Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Function
Protects, moistens, and lubricates the eye by producing lacrimal fluid (tears)

Lacrimal Apparatus
Slide 8.5Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
StructuresLacrimal
Gland
Lacrimal
Canal
Lacrimal
Sac
Nasolacrimal Duct

Flow of Tears

Structure of the Eye
Slide 8.7Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
The wall is composed of three tunics
Fibrous tunic –outside layer
Choroid –middle layer
Sensory tunic –inside layer
Figure 8.3a
Sclera
Cornea

The Fibrous Tunic
Slide 8.8Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Sclera
White connective tissue layer

The Fibrous Tunic
Cornea
Allows for light to pass through
Repairs itself easily
The only human tissue that can be transplanted without fear of rejection
YouTube - Cornea
Transplant

Structure of the Eye
Slide 8.7Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
The wall is composed of three tunics
Fibrous tunic –outside layer
Choroid –middle layer
Sensory tunic –inside layer
Figure 8.3a
Lens
Ciliary
Body
Iris
Pupil

Choroid Layer
Slide 8.9Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Ciliary body
smooth muscle that attaches to and controls the lens

Choroid Layer
Slide 8.9Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Lens
Biconvex crystal-like structure
Can change shape to allow light to properly focus on the retina

Choroid Layer
Slide 8.9Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Iris
Pigmented layer that gives the eye color
Prevents light from scattering

Choroid Layer
Slide 8.9Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Pupil
Rounded opening of the iris that controls the amount of light to pass through

Structure of the Eye
Slide 8.7Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
The wall is composed of three tunics
Fibrous tunic –outside layer
Choroid –middle layer
Sensory tunic –inside layer
Figure 8.3a
Fovea
Centralis
Retina
Optic
DiscOptic
Nerve

Sensory Tunic
Slide 8.10Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Retina
Contains millions of receptor cells, the rods and cones

Neurons of the Retina
Slide 8.11Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 8.4

Sensory Tunic
Slide 8.10Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Optic Nerve
Receives information from the retina and sends it to the brain

Sensory Tunic
Slide 8.10Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Optic Disc
The site where the optic nerve leaves the eyeball
The “blind-spot”

Sensory Tunic
Slide 8.10Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Fovea Centralis
Portion of the retina that contains only cones
Area of greatest visual acuity (sharpest vision)

Structure of the Eye
Slide 8.7Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
The wall is composed of three tunics
Fibrous tunic –outside layer
Choroid –middle layer
Sensory tunic –inside layer
Figure 8.3aVitreous
Humor
Canal of
Schlemm
Aqueous
Humor

Internal Eye Chamber Fluids
Slide 8.15aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Aqueous humor
Watery fluid found in chamber between the lens and cornea
Helps maintain intraocular pressure
Provides nutrients for the lens and cornea

Internal Eye Chamber Fluids
Slide 8.15aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Canal of Schlem
Located at the junction of the sclera and cornea
Reabsorbs aqueous humor into the venous blood

Aqueous humor

Internal Eye Chamber Fluids
Slide 8.15bCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Vitreous humor
Gel-like substance behind the lens
Keeps the eye from collapsing
Lasts a lifetime and is not replaced

Aqueous & Vitreous humor


Neurons of the Retina and Vision
Slide 8.12aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Rods
Allow dim light vision and peripheral vision
Perception is all in gray tones

Neurons of the Retina and Vision
Slide 8.12bCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Cones
Allow for detailed color vision
Function in bright light to help with discriminatory vision

Image formation on the Retina
Slide 8.16Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
The image formed on the retina as a result of the light-bending activity of the lens is a real image – that is , it is reversed from left to right, upside down, and smaller than the object
Figure 8.9

Eye Reflexes
Slide 8.19Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Convergence Reflex
Moving both eyes to view close up objects
Controlled by extrinsic eye muscles

Eye Reflexes
Slide 8.19Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Pupillary Reflexes
Pupils constrict due to viewing close objects or exposure to bright light
Controlled by internal eye muscles and the autonomic nervous system
Prevents excessively bright light from damaging the photoreceptors

Visual Pathway to the optic cortex
Slide 8.18aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Photoreceptors of the retina
Optic nerve
Optic nerve crosses at the optic chiasma
Figure 8.11
Optic tracts
Thalamus (axons form optic radiation)
Visual cortex of the occipital lobe


Special Senses
Title
• Audition
Essential Question
• Describe the structures and functions of hearing.

Anatomy of the Ear
Slide 8.21Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
The ear is divided into three areas
Outer (external) ear
Middle ear
Inner ear
Figure 8.12

The External Ear
Slide 8.22Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Pinna (auricle)
collects, funnels, and amplifies sound
Figure 8.12

The External Ear
Slide 8.23Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
External auditory canal
Narrow chamber in the temporal bone
Has Ceruminous (wax) glands

The External Ear
Slide 8.24aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Tympanic Membrane
Separates the outer and middle ear
Vibrates when hit by sound waves

Tympanic Membrane

Bones of the Tympanic Cavity

Middle Ear
Slide 8.25bCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Ossicles
Vibrations from eardrum move the malleus
These bones transfer sound to the inner ear
Figure 8.12

Middle Ear
Slide 8.25bCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Oval Window
Opening at the head of the cochlea
Sound vibrations from the stapes is transmitted to inner ear
Figure 8.12

The Middle Ear or Tympanic Cavity
Slide 8.24bCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Auditory Tube
connects the middle ear with the throat
Allows for equalizing pressure during yawning or swallowing

Auditory Tube

Inner Ear or Bony Labyrinth
Slide 8.26aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Cochlea
Contains the organ of Corti where the hearing receptors are found
Figure 8.12

Inner Ear or Bony Labyrinth
Slide 8.26aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Vestibule
Contains muculae which are involved in static equilibrium
Reports on the position of the head
Figure 8.12

Inner Ear or Bony Labyrinth
Slide 8.26aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Semicircular Canals
Involved in dynamic equilibrium
Responds to angular or rotary movements of the head
Figure 8.12


Pathways for Sensory System
• Audition
– Receptors: Mechanoreceptors
– Stimulus Energy: Sound
– Pathway
• Ear: hair cells Ear: vestibulochochlear nerve medulla midbrain thalamus auditory cortex (temporal lobe)

Organs of Hearing
Slide 8.27aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Organ of Corti
Contains the hearing receptors or the hair cells.

Organs of Hearing
Slide 8.27aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
The receptors are positioned on the basilar membrane, and the hairs are embedded in the tectorial membrane

Organs of Hearing
Slide 8.27aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
When the tectorial membrane is disturbed, this stimulates the hair cells which send information to the cochlear nerve.

Sensorineural Deafness
Slide 8.27aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Deafness that is caused by damage to neural structures (cochlear nerve or auditory cortex cells)
Can be caused by stroke or trauma

Conduction Deafness
Slide 8.27aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Deafness that is caused by any interference with the conduction of vibrations from the outer to the inner ear
Can be caused by wax accumulations, otitis media, fusion of the ossicles, or pressure imbalance between the middle and outer ear


Organs of Equilibrium
Slide 8.30aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Receptor cells are in two structures
Vestibule
Semicircular canals
Figure 8.16a, b

Static Equilibrium
Slide 8.31Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
The vestibule helps us with static equilibrium or the position of the head with respect to the pull of gravity when the body is not moving.

Static Equilibrium
Slide 8.32Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 8.15

Dynamic Equilibrium
Slide 8.33aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
The semicircular canal helps with dynamic equilibrium, which responds to angular or rotary movements of the head, rather than straight-line movements.

Dynamic Equilibrium
Slide 8.33aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 8.16c


OLFACTION

Olfactory Epithelium
Slide 8.36Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 8.17

Olfaction – The Sense of Smell
Slide 8.35Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Olfactory Bulb
Contains the receptors for the sense of smell

Olfaction – The Sense of Smell
Slide 8.35Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Cribiform Plate
Portion of the ethmoid bone where the olfactory bulb sits

Olfaction – The Sense of Smell
Slide 8.35Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Olfactory Tract
The neural pathway from the olfactory bulb to the olfactory cortex in the brain

Olfaction – The Sense of Smell
Slide 8.35Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
receptors are in the roof of the nasal cavity
Neurons with long cilia
Chemicals must be dissolved in mucus for detection

Pathways for Sensory System
• Olfaction– Receptors: Chemoreceptors
– Stimulus Energy: Chemical
– Pathway• Olfactory sensory neurons Olfactory bulb
neurons olfactory cortex (in temporal lobe)



Anatomy of the Tongue
Slide 8.40Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 8.18

Taste Buds
Slide 8.37Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
house the receptor organs
Location
Tongue
Soft palate
Cheeks
Figure 8.18a, b


Anatomy of the Tongue
Slide 8.40Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 8.18

The Tongue and Taste
Slide 8.38Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Papillae
Small peglike projections that house the taste buds


Anatomy of the Tongue
Slide 8.40Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 8.18

Structure of Taste Buds
Slide 8.39aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Gustatory cells
Specific epithelial cells that respond to chemicals dissolved in saliva

Anatomy of the Tongue
Slide 8.40Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 8.18

Structure of Taste Buds
Slide 8.39bCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Gustatory Hairs
Taste receptors that emerge from the taste pores

Gustation

Pathways for Sensory System• Gustation
– Receptors: Chemoreceptors
– Stimulus Energy: chemical (sweet, sour, bitter, salty)
– Pathway
• Taste bud Facial nerve (VII) or glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) or vagus nerve (X) medulla thalamus cortex (parietal lobe)

Taste Sensations
Slide 8.41Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Sweet receptors
Sugars
Saccharine
Some amino acids
Sour receptors
Acids

Taste Sensations
Slide 8.41Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Bitter receptors
Alkaloids
Salty receptors
Metal ions

Factors that affect Taste Sensations
Slide 8.41Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Stimulation of our olfactory aromas
Temperature and texture of food
Spicy foods can excite pain receptors in
our mouth