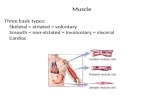
Chapter 7 Muscular System. Functions and Types of Muscle Has three types –Smooth –Cardiac...
-
Upload
augusta-mathews -
Category
Documents
-
view
229 -
download
3
Transcript of Chapter 7 Muscular System. Functions and Types of Muscle Has three types –Smooth –Cardiac...

Chapter 7Chapter 7
Muscular SystemMuscular System

Functions and Types of Muscle
Functions and Types of Muscle
• Has three types– Smooth– Cardiac– Skeletal
• Has three types– Smooth– Cardiac– Skeletal

Functions and Types of Muscle
Functions and Types of Muscle
• Smooth Muscle:– Wall of hollow internal organs– Involuntary contractions– Moves materials– Single nucleus– Parallel lines, forming sheets– No striations– Sustain prolonged contraction, doesn’t fatigue
easy
• Smooth Muscle:– Wall of hollow internal organs– Involuntary contractions– Moves materials– Single nucleus– Parallel lines, forming sheets– No striations– Sustain prolonged contraction, doesn’t fatigue
easy

Functions and Types of Muscle
Functions and Types of Muscle
• Smooth Muscle:• Smooth Muscle:

Functions and Types of Muscle
Functions and Types of Muscle
• Smooth Muscle:• Smooth Muscle:

Functions and Types of Muscle
Functions and Types of Muscle
• Cardiac Muscle:– Wall of heart– Uninucleiated– Striated, tubular, and branched– Intercalated disks = quick contractions– Involuntary and rhythmic
• Cardiac Muscle:– Wall of heart– Uninucleiated– Striated, tubular, and branched– Intercalated disks = quick contractions– Involuntary and rhythmic

Functions and Types of Muscle
Functions and Types of Muscle
• Cardiac Muscle:• Cardiac Muscle:

Functions and Types of Muscle
Functions and Types of Muscle
• Cardiac Muscle:• Cardiac Muscle:

Functions and Types of Muscle
Functions and Types of Muscle
• Skeletal Muscle:– Multinucleated– Striated– Voluntary
• Skeletal Muscle:– Multinucleated– Striated– Voluntary

Functions and Types of Muscle
Functions and Types of Muscle
• Skeletal Muscle:• Skeletal Muscle:

Functions and Types of Muscle
Functions and Types of Muscle
• Skeletal Muscle:• Skeletal Muscle:

Functions and Types of Muscle
Functions and Types of Muscle
• Connective Tissue Coverings:– Endomysium: each muscle fiber is
surrounded by – Fascicles: groups of muscle fibers– Perimysium: Connective tissue covering of
fascicles– Epimysium: Covers the entire muscle
• Connective Tissue Coverings:– Endomysium: each muscle fiber is
surrounded by – Fascicles: groups of muscle fibers– Perimysium: Connective tissue covering of
fascicles– Epimysium: Covers the entire muscle

Functions and Types of Muscle
Functions and Types of Muscle
• Connective Tissue Coverings:• Connective Tissue Coverings:

Functions and Types of Muscle
Functions and Types of Muscle
• Skeletal muscle:– Supports the body– Makes bones and other body parts move– Helps maintain a constant body temperature– Contraction assists movement in
cardiovascular and lymphatic vessels– Protects internal organs and stabilizes joints
• Skeletal muscle:– Supports the body– Makes bones and other body parts move– Helps maintain a constant body temperature– Contraction assists movement in
cardiovascular and lymphatic vessels– Protects internal organs and stabilizes joints

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Sarcolemma: plasma membrane
• Sarcoplasm: cytoplasm– Contains glycogen for energy– Contains myoglobin that binds oxygen
• Sarcoplasmic reticulum: endoplasmic reticulum– Encases myofibrils- contractile portion of
muscle fibers
• Sarcolemma: plasma membrane
• Sarcoplasm: cytoplasm– Contains glycogen for energy– Contains myoglobin that binds oxygen
• Sarcoplasmic reticulum: endoplasmic reticulum– Encases myofibrils- contractile portion of
muscle fibers

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Sarcomeres- units of myofibrils– Contain myosin: thick protein filament– Contain actin: thin protein filament
• Sarcomeres- units of myofibrils– Contain myosin: thick protein filament– Contain actin: thin protein filament

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Thick filaments– Made of hundreds of protein myosin
• Thick filaments– Made of hundreds of protein myosin

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Thin filaments– Made of two intertwining strands of protein
actin
• Thin filaments– Made of two intertwining strands of protein
actin

Actin and MyosinActin and Myosin

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Neuromuscular junction: the area between the axon terminal and the sarcolemma
• Neuromuscular junction: the area between the axon terminal and the sarcolemma

Neuromuscular JunctionNeuromuscular Junction

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Actin- surrounded by threads of tropomyosin and troponin
• Calcium ions bind with troponin and expose myosin binding sites
• ATP binds to myosin and is broken down to ADP and P
• Energy is released, contraction occurs
• Actin- surrounded by threads of tropomyosin and troponin
• Calcium ions bind with troponin and expose myosin binding sites
• ATP binds to myosin and is broken down to ADP and P
• Energy is released, contraction occurs

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Muscles acquire ATP in 3 ways– Creatine phosphate breakdown– Cellular respiration– Fermentation
• Muscles acquire ATP in 3 ways– Creatine phosphate breakdown– Cellular respiration– Fermentation

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Creatine Phosphate Breakdown– Creatine Phosphate builds up when muscle is
at rest– Speediest way to make ATP available– 8 seconds of intense energy
• Creatine Phosphate Breakdown– Creatine Phosphate builds up when muscle is
at rest– Speediest way to make ATP available– 8 seconds of intense energy

Creatine Phosphate Breakdown
Creatine Phosphate Breakdown

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Cellular Respiration:– Completed in mitochondria– Only when oxygen is available– From glycogen and fatty acids– End products are carbon dioxide, water, and
heat
• Cellular Respiration:– Completed in mitochondria– Only when oxygen is available– From glycogen and fatty acids– End products are carbon dioxide, water, and
heat

Cellular RespirationCellular Respiration

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Fermentation:– Anaerobic– Glucose breaksdown into lactic acid– Build up of lactic acid leads to cramping
• Fermentation:– Anaerobic– Glucose breaksdown into lactic acid– Build up of lactic acid leads to cramping

FermentationFermentation

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• All or nothing law
• A single fiber either contracts or rest
• However, a group of fibers some contract and other will not to appear to have the ability for partial contractions
• All or nothing law
• A single fiber either contracts or rest
• However, a group of fibers some contract and other will not to appear to have the ability for partial contractions

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Muscle twitch- single contraction that last for a fraction of a second– Latent period: time between stimulation and
initiation of contraction– Contraction period: muscle shortens– Relaxation period: muscle returns to its former
length
• Muscle twitch- single contraction that last for a fraction of a second– Latent period: time between stimulation and
initiation of contraction– Contraction period: muscle shortens– Relaxation period: muscle returns to its former
length

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Summation – increase in muscle contraction until maximal sustained contraction is achieved
• Tetanic contraction- maximum contraction
• Summation – increase in muscle contraction until maximal sustained contraction is achieved
• Tetanic contraction- maximum contraction

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Innervated- muscle fibers are innervated with nerve fibers called a motor unit
• Motor units either contract or do not contract
• Recruitment- stronger and stronger muscle contractions
• Innervated- muscle fibers are innervated with nerve fibers called a motor unit
• Motor units either contract or do not contract
• Recruitment- stronger and stronger muscle contractions

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• While some muscles are contracting others are resting, this helps prevent fatigue
• Tone: some fibers are always contracting– Helps maintain posture
• While some muscles are contracting others are resting, this helps prevent fatigue
• Tone: some fibers are always contracting– Helps maintain posture

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Atrophy- loss of muscle tone due to inactivity or nerve damage– Muscle will eventually be replaced by adipose
and fibrous tissue– Muscles will shorten, leaving parts contracted
• Atrophy- loss of muscle tone due to inactivity or nerve damage– Muscle will eventually be replaced by adipose
and fibrous tissue– Muscles will shorten, leaving parts contracted

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Pertrophy- increase in muscle size– Prolonged period of forceful muscular activity
increases myofibrils
• Pertrophy- increase in muscle size– Prolonged period of forceful muscular activity
increases myofibrils

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Slow-twitch muscles– Steadier and more endurance– Highly resistant to fatigue– Substantial reserve of glycogen and fat– Abundant mitochondria, few fibers– Aerobic
• Slow-twitch muscles– Steadier and more endurance– Highly resistant to fatigue– Substantial reserve of glycogen and fat– Abundant mitochondria, few fibers– Aerobic

Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
• Fast-twitch muscles– Anaerobic– Designed for strength– Many fibers, few mitochondria– Little or no myoglobin– Few blood vessels– Vulernable to cramping
• Fast-twitch muscles– Anaerobic– Designed for strength– Many fibers, few mitochondria– Little or no myoglobin– Few blood vessels– Vulernable to cramping

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Origin – of a muscle is on the stationary bone
• Insertion- of a muscle in on the bone that moves
• Origin – of a muscle is on the stationary bone
• Insertion- of a muscle in on the bone that moves

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Prime mover- the muscle that does most of the work
• Synergists- the assisting muscles
• Prime mover- the muscle that does most of the work
• Synergists- the assisting muscles

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Antagonist- pair of muscles working against the synergist
• Antagonist- pair of muscles working against the synergist

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Naming muscles– Size
• Example: gluteus maximus, largest butt muscle
– Shape• Deltoid, shaped like a delta
– Direction of fiber• Rectus abominis, rectus = straight
– Location• Frontalis, overlies the frontal bone
• Naming muscles– Size
• Example: gluteus maximus, largest butt muscle
– Shape• Deltoid, shaped like a delta
– Direction of fiber• Rectus abominis, rectus = straight
– Location• Frontalis, overlies the frontal bone

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Naming muscles– Attachment
• Ex. Brachioradialis, brachium and the radius
– Number of attachments• Ex. Bicep = two attachments
– Action• Extensor digitorum – extends fingers
• Naming muscles– Attachment
• Ex. Brachioradialis, brachium and the radius
– Number of attachments• Ex. Bicep = two attachments
– Action• Extensor digitorum – extends fingers

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Muscles of the Head– Frontalis: frontal bone
• Raising eyebrows, wrinkle brow
– Orbicularis oculi: encircles eye• blinking
– Orbiularis oris: encircles mouth• Pucker lips
• Muscles of the Head– Frontalis: frontal bone
• Raising eyebrows, wrinkle brow
– Orbicularis oculi: encircles eye• blinking
– Orbiularis oris: encircles mouth• Pucker lips

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Muscles of the Head– Buccinator: cheek
• Compresses to whistle
– Zygomaticus: cheekbone to corner of mouth• Smile
• Muscles of the Head– Buccinator: cheek
• Compresses to whistle
– Zygomaticus: cheekbone to corner of mouth• Smile

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Muscles of Mastication– Masseter: zygomatic arch to mandible
• Ex. chewing
– Temporalis: overlies temporal bone• Ex. Elevates mandible
• Muscles of Mastication– Masseter: zygomatic arch to mandible
• Ex. chewing
– Temporalis: overlies temporal bone• Ex. Elevates mandible

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Muscles of the Neck– Deep neck muscles are responsible for
chewing– Superficial muscles are responsible for
moving the head
• Muscles of the Neck– Deep neck muscles are responsible for
chewing– Superficial muscles are responsible for
moving the head

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Muscles of the Neck– Sternocleidomastoid
• Turns head from right to left
– Trapezius• Triangular• Shrug shoulders
• Muscles of the Neck– Sternocleidomastoid
• Turns head from right to left
– Trapezius• Triangular• Shrug shoulders

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Muscles of the Trunk– External intercostal: between ribs
• Ex. Elevate rib cage during inspiration
– Diaphragm• Ex. Assists in inspirations
– Internal intercostal• Ex. Normally no muscular contraction, only with
forced expiration
• Muscles of the Trunk– External intercostal: between ribs
• Ex. Elevate rib cage during inspiration
– Diaphragm• Ex. Assists in inspirations
– Internal intercostal• Ex. Normally no muscular contraction, only with
forced expiration

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Muscles of the Abdominal Wall– External and internal obliques: Lower ribs and
pelvic girdle• Ex. Trunk rotation and lateral flexion
– Transversus abdomininis: horizontal across abdomen
• Synergist muscles
– Rectus abdominis: from pubic bones to the ribs and strernum
• Ex. Flex and rotate lumbar region
• Muscles of the Abdominal Wall– External and internal obliques: Lower ribs and
pelvic girdle• Ex. Trunk rotation and lateral flexion
– Transversus abdomininis: horizontal across abdomen
• Synergist muscles
– Rectus abdominis: from pubic bones to the ribs and strernum
• Ex. Flex and rotate lumbar region

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Muscles of the Shoulder– Serratus anterior: from armpit to chest
• Ex. Helps elevate arm above head
• Muscles of the Shoulder– Serratus anterior: from armpit to chest
• Ex. Helps elevate arm above head

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Muscles of the Arm– Deltoid
• Abducts arm to horizontal position
– Pectoralis major– Latissimus dorsi: from lower spine to humerus
• Ex. Swimming, rowing and climbing rope
– Rotator cuff: muscles over proximal humerus
• Muscles of the Arm– Deltoid
• Abducts arm to horizontal position
– Pectoralis major– Latissimus dorsi: from lower spine to humerus
• Ex. Swimming, rowing and climbing rope
– Rotator cuff: muscles over proximal humerus

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Muscles of the Arm– Biceps brachii: muscles of the forearm
• Turn a doorknob unscrew a jar
– Brachilais: humerus to ulna• Ex. Flexing the forearm
– Triceps brachii: scapula to humerus• Ex. To punch and in tennis
• Muscles of the Arm– Biceps brachii: muscles of the forearm
• Turn a doorknob unscrew a jar
– Brachilais: humerus to ulna• Ex. Flexing the forearm
– Triceps brachii: scapula to humerus• Ex. To punch and in tennis

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Muscles of the Arm– Flexor carpi and extensor carpi
• Flexes and extends wrist
– Flexor digitorum and extensor digitorum• Flexes or extends fingers
• Muscles of the Arm– Flexor carpi and extensor carpi
• Flexes and extends wrist
– Flexor digitorum and extensor digitorum• Flexes or extends fingers

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Muscles of the Hip and Leg– Iliopsoas: ilium to lumbar vertebrae
• Ex. walking, bowing, standing erect
– Gluteus maximus: large buttocks muscle• Ex. Walking, jumping, climbing stairs
– Gluteus medius: small buttocks muscle– Adductor group
• Ex. Thighs inward
• Muscles of the Hip and Leg– Iliopsoas: ilium to lumbar vertebrae
• Ex. walking, bowing, standing erect
– Gluteus maximus: large buttocks muscle• Ex. Walking, jumping, climbing stairs
– Gluteus medius: small buttocks muscle– Adductor group
• Ex. Thighs inward

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Muscles of the Leg– Quadricep femoris: thigh
• Ex. Extends leg
– Sartorius: thigh to knee• Ex. Sit cross legged
– Hamstring:Back of thigh• Ex. Antagonist muscle group
• Muscles of the Leg– Quadricep femoris: thigh
• Ex. Extends leg
– Sartorius: thigh to knee• Ex. Sit cross legged
– Hamstring:Back of thigh• Ex. Antagonist muscle group

Skeletal MusclesSkeletal Muscles
• Muscles of the Ankle and Foot– Gastrocnemius
• Ex. Pushing forward while walking, dancing
– Tibialis anterior• Ex. Inversion of foot
– Peroneus• Ex. Plantar flexion
– Flexor and extensor digitorum longus• Ex. Flexes and extends toes
• Muscles of the Ankle and Foot– Gastrocnemius
• Ex. Pushing forward while walking, dancing
– Tibialis anterior• Ex. Inversion of foot
– Peroneus• Ex. Plantar flexion
– Flexor and extensor digitorum longus• Ex. Flexes and extends toes

Effects of AgingEffects of Aging
• Mass and strength decrease
• Muscle tissue initially replaced by connective tissue then eventually fat
• Mass and strength decrease
• Muscle tissue initially replaced by connective tissue then eventually fat

HomeostasisHomeostasis
• Heartbeat and movement of blood
• Protect internal organs
• Moves bones and allows daily activities
• Heartbeat and movement of blood
• Protect internal organs
• Moves bones and allows daily activities