Chapter 6 Lesson 1 Notes. Geography of India I. Indian Subcontinent A. Located on the continent of...
-
Upload
derek-white -
Category
Documents
-
view
228 -
download
0
Transcript of Chapter 6 Lesson 1 Notes. Geography of India I. Indian Subcontinent A. Located on the continent of...

Chapter 6 Lesson 1 Notes

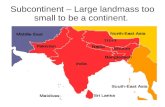
Geography of India I. Indian Subcontinent
A. Located on the continent of AsiaB. has three main land regions
1. Himalayas separate the subcontinent from the rest of Asia
a. The Himalayas are the highest mountains in the world
b. Mt. Everest is the highest mountain peak in the world
2. the Northern Plains lie between the Himalayas and the southern peninsula stretches over 1,500 miles and contains the valleys of the Ganges and
Indus rivers and their branches
3. Deccan Plateaua. forms most of the southern peninsula b. lies between the Eastern and Western
Ghats (mountain ranges)




Geography of India C. seven countries are found on the Indian
subcontinent1. India, Pakistan, & Bangladesh
parts of Afghanistan, Nepal, Bhutan, and Myanmar or Burma
Islands considered part of are Maldives & Sri Lanka


Geography of India
II. Indus RiverA. flows from Tibet, through the Himalayas
and Hindu Kish into the Arabian Sea. B. flows through what is today China, India,
and Pakistan.C. begins in the Himalayan Mountains. D. overflows its bank and leaves fertile soilE. Formed a delta region where it empties into the Arabian SeaF. allows farming to take place in a very dry area.
1. The Indus Valley was one of the first places were farming developed.
2. Farming communities found date back to 6000 B.C.


Chapter 6 lesson 2 Notes

Early Indian Civilization I. Indus River valley civilization A. We do not know a lot about the Indus River valley
civilization. B. Experts have not learned how to read the writing of the
people.II. HarappaA. Located within the Indus River valley.
1. named after an Indian goddo not know what the people called themselves
2. The entire ancient Indus River valley is called Harappan civilization
3. It lasted about 1,000 years, from c. 2500 B.C. to c. 1600 B.C.

Early Indian Civilization

Early Indian Civilization III. Mohenjo-DaroA. 400 miles south of Harappa, in the Indus River civilization is
called Mohenjo-Daro B. Mohenjo-Daro means “Mound of the Dead” in Sanskrit
1. Sanskrit is an ancient Indian language
C. about 40,000 people lived in this cityD. the city had grid streets, the same size bricks were used to
pave the roads and build housesE. city had wells throughout it and sewer systems complete with
manholes F. a citadel stood at the west end of the city
1. a citadel is a massive fort2. remains on top of the citadel may have been a city hall3. surrounding the citadel were thick walls to protect
against floods and enemies

Early Indian Civilization


Early Indian Civilization G. around 1600 B.C. the city of Mohenjo-Daro was abandoned H. an earthquake may have caused the river to change course
and disrupted peoples way of life (drought or floods)I. Both cities were laid out the same. It’s believed the area
had a strong central government. J. Workers of Mohenjo-Daro were highly skilled
remains found of workshops along city avenues beautiful figures were carved into small squares of stone
(see page 136) stone squares may have been used as seals for marking
belongings things created by craft workers include water jars, cooking
bowls, and other containers farmers produced a surplus of food; grain may have been
used to pay city workers
K. Harappan merchants traded with people in Mesopotamia sailors probably went to Mesopotamia by sailboat from the
Indus delta along the coast into the Persian GulfL. c. 1500 B.C. people from central Asia migrated into the Indus
Valley

Early Indian Civilization The medieval walls and revetments of the ancient city of Harappa

Early Indian Civilization

Early Indian Civilization Review1. We don’t know a lot about the Harappan
civilization because-Answer:We haven’t learned to read their writing.

Early Indian Civilization2. What evidence suggest the Harappan
civilization had a strong central government?Answer:Both cities were laid out the same suggesting a strong central government.