Chapter 4 and 5: The Amazing Carbon Atom and Function of Macromolecules Estimated time: 5 days
description
Transcript of Chapter 4 and 5: The Amazing Carbon Atom and Function of Macromolecules Estimated time: 5 days

Chapter 4 and 5: The Chapter 4 and 5: The Amazing Carbon Amazing Carbon Atom Atom and Function of and Function of MacromoleculesMacromolecules
Estimated time: 5 daysEstimated time: 5 daysLearning Goals:
1. Understand why carbon is the basis of living things
2. Organic Chemistry is carbon based chemistry
3. Recognize the functional groups
4. Understand the basics of macromolecule chemistry
1. Carbohydrates
2. Proteins
3. Nucleic Acid
4. Lipids

Why Carbon?Why Carbon?
-Organic Chemistry is the study of carbon based compounds
-At some point in Earth’s history organic compounds were created (Miller Experiment)
-Hydrocarbons contain only hydrogen and carbon (Fatty acid chains (non polar)
Carbon AnatomyCarbon Anatomy-Four valence electrons
- Can bond with four other atoms
-Can create single, double, and triple bonds (Rings and Resonance)

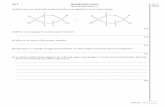
What are IsomersWhat are Isomers
-Carbon has the ability to be the backbone of isomers due to it’s four potential bonds.
-Isomers have the same molecular formula but different shapes
Structural differ in covalent arrangement of atoms
Geometric differ in spacial arrangement
-Across double bonds
-Trans and Cis
Enatomers are mirror images of each other
**Look at page 63 for other samples

Functional Groups: There are seven major groups that have specific chemical properties
1. Hydroxyl
2. Carbonyl
3. Carbonxyl
4. Amino
5. Sulfhydryl
6. Phosphate
7. Methyl
** You will need to make a foldable with all the functional groups on it. P. 64-65 will help.

Macromolecules…. Macromolecules…. What?What?
- “Macromolecules are the molecules of life”
-”Macro cause their big”
-Types:
-Proteins
-Lipids
-DNA
-Carbohydrates

Macromolecule polymer Macromolecule polymer chemistrychemistry
- Polymers: long chains of monomers
- Monomers: Similar units (building blocks)
Carbohydrates Monomers = various sugars
Protein Monomers = Amino Acids
Nucleic Acid Monomers = Nucleotides
**Lipids don’t consist of polymers.
Hydrolysis = breaks a monomer off the polymer
Dehydration = adds monomers to a polymer

CarbohydratesCarbohydrates
-Monosaccarides = one sugar molecule (Follow (CH2O)n formula)
-Open chain or ring forms -Open chain or ring forms www.stolaf.edu/people/.../biological%20anamations.htmlwww.stolaf.edu/people/.../biological%20anamations.html - Classified by- Classified by:
1. Number of Carbons2. Aldoses or Ketoses3. Chiral Carbons

CarbohydratesCarbohydrates
- Polysaccharides = Polymers made up of monosaccarides (different monomers make up different polymers
- 1-4 glycosidic bond = Bonds between monosaccharides are between the 1carbon and the four carbon

Carbohydrates: Energy Carbohydrates: Energy Storage Storage --Glycogen –Glycogen – Branched Glucose polymer Branched Glucose polymer
-Stores glucose in animals -Stores glucose in animals -Hydrolysis releases glucose for -Hydrolysis releases glucose for
metabolismmetabolism
--StarchStarch – Branched and Unbranched plant – Branched and Unbranched plant glucose polymers.glucose polymers.
-Stores glucose in plants-Stores glucose in plants-hydrolysis releases glucose for -hydrolysis releases glucose for
metabolismmetabolism-Animals can hydrolyze starch-Animals can hydrolyze starch
Carbohydrates: StructureCellulose – Long linear chains
- Can hydrogen bond with parallel chains
Starch vs Cellulose
-Structural difference in Glucose (Alpha or Beta)
- Starch can be digested by humans
-Cellulose can’t be digested by humans
http://pslc.ws/macrog/kidsmac/starlose.htm

Lipids are …Lipids are … -Non polar-Non polar-Not considered polymers-Not considered polymers-Mostly hydrocarbon chains-Mostly hydrocarbon chains
-Fats are considered lipids
-Three fatty acids connected to a glycerol molecule
-Energy Storage (adipose cells) 1 g has twice as much storage as 1 g of starch
-Saturated (solid) vs unsaturated (liquids) contain double bonds p. 75
-Fat is an adaptation
-Phospholipids contain a polar (hydrophilic) head and two hydrocarbon, non polar (hydrophobic) tails
-Form the lipid bilayers of cells and organelles
-Cells wouldn’t exist without phospholipids
Steriods
- lipids characterized by four carbon rings fused together
-Cholesterol found in cell membranes
-Hormones like testosterone and estrogen

Protein FunctionProtein Function-50% of dry mass of most -50% of dry mass of most cells is proteinscells is proteins-Extremely large molecules-Extremely large molecules-Act as enzymes p. 78-Act as enzymes p. 78--Enzymes Enzymes are biological are biological catalysts that speed up catalysts that speed up chemical reactionschemical reactions This 3-D model shows the enzyme
integrase which is responsible for inserting HIV into the DNA of humans
http://www.cbc.ca/technology/story/2010/02/01/tech-aids-enzyme-structure.html
Active Site

Protein Protein CompositionComposition-Proteins are polypeptide -Proteins are polypeptide chainschains
-Made up of monomers -Made up of monomers called amino acidscalled amino acids
-Amino acids have -Amino acids have various propertiesvarious properties
-Properties determine -Properties determine folding and overall folding and overall protein functionprotein function
-Proteins are made in -Proteins are made in the ribosomes and the ribosomes and coded for in DNAcoded for in DNA

Protein Protein StructureStructure
Primary Structure
-Amino Acid Sequence
-Can be thought of as a book
Secondary Structure is dictated by amino acid sequence (polar amino acids) that form hydrogen bonds
Alpha Helix and Beta pleated sheets
Tertiary Structure
Uses all the molecular attractions to hold the protein together.
Quaternary Structure
-Bonding of more then one protein sequence.
-Can use units like iron to hold together.

Sickle Cell ExampleSickle Cell Example-Read p. 84.
-Example of how a single error in the primary structure can effect the rest of the structures

Protein CrazinessProtein Craziness-Proteins will fold the correct way provided a proper environment
-Temperature and pH have an affect on pH.
-Protein Chaperones can create a proper environment for other protein folding
-Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s are associated with misfolded proteins

Nucleic Acid FunctionNucleic Acid Function
1. Store and transfer genetic information
2. Can exist as DNA (double stranded)
3. Can exist as various types of RNA (single stranded)
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA

Nucleic Acid CompositionNucleic Acid Composition -Monomers are nucleotides made up of one sugar, one phosphate group and one nitrogenous base
-Bases differ in structure
-Sugars differ depending on if RNA or DNA

Nucleic Acid StructureNucleic Acid Structure
-Double Helix Structure
-Anti-parallel (5’ – 3’)
-Bases are bound by hydrogen bonds
-Sugars and phosphate groups alternate on the backbone.