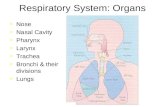
Chapter 15 Respiratory System. 1. Components ---nose ---pharynx ---larynx ---trachea ---bronchi...
-
Upload
antonia-baldwin -
Category
Documents
-
view
231 -
download
3
Transcript of Chapter 15 Respiratory System. 1. Components ---nose ---pharynx ---larynx ---trachea ---bronchi...
2. Trachea and main bronchi
three layers 1) Mucosa: ---epithelium: pseudostratified ciliated columnar ep
ithelium---lamina propria: CT, contain LC, PC, MC, BV, LV
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epi. ciliated cell: columnar, cilia goblet cell basal cell:
-pyramidal, basally-located
-undifferentiated cell→ciliated cell or goblet cell
brush cell:
-columnar, microvilli,
-EM: RER, no g.
-function: not very clear, may be
i. become into ciliated cell
ii.receive sensory stimuli-epitheliodendritic synapse
diffuse neuroendocrine cell:
-less, pyramidal
-EM: dense-core g.-small granule cell
neuroepithelial body: cell + NF
-Function: secret hormones to regulate contract of SM and secretion of gland
i. 5-hydroxytryptamine(serotonin)
ii. calcitonin
iii. enkephalin
* clear basement membrane
2) Submucosa:
LCT, with BV, LV and N
tracheal gland: mixed
diffuse LT and LN
* S Ig A = secretory component (secreted by epi. cell) + Ig A ( produced by plasma cell)
3) Adventitia:
cartilage ring: 16-20 “C ” shaped
circular ligament: elastic F
SM- posterior part( membrane part): SM, elastic F, tracheal gland
1) General structure:
---capsule: visceral layer of pleura- serous membrane-CT + mesothelium
---parenchyma: all branches of bronchi and alveoli( right 3, left 2)
---interstitia: CT, BV, LV, N
* branchi →intrapulmonary bronchial tree( lobar bronchial tree, segmental bronchi and small bronchi)
D < 1mm D < 0.5 mm →bronchioles →terminal bronchioles →respiratory
bronchioles →alveolar duct →alveolar sac → alveoli
* pulmonary lobule: one bronchioles and its all branches and all alveoli cone or pyramidal-shaped: apex pointed toward the hilum and basal(1.0 cm in D) faced the surface more CT between them
2) Conducting portion ① from lobar bronchi to small bronchi
---Regulation of simplification: (gradually)
mucosa: -epi. : become thinner -goblet cell ↓ -lamina propria: thinner, SM ↑
submucosa: gland ↓ adventitia: cartilage→cartilage →decreasing
② bronchiole: D < 1mm
---continuous to change
goblet cell, Gland, cartilage ↓ or disappear
smooth muscle ↑,circular mucosa plica ↑
③ terminal bronchiole: D < 0.5 mm
---goblet cell, gland, cartilage disappear
---SM: form a whole layer of circumferential SM
---Wall:simple columnar epi.: two types of cellsA layer of SM
i. ciliated cell ii. secreting cell: Clara cell EM:
dome-shaped apicalSERSecreting G: contains proteolytase and oxidase
function: dissolve the mucus biological thansformation undifferentiated cell → ciliated cell
3) respiratory portion ① respiratory bronchiole
---similar to terminal bronchioles: simple ciliated columnar epi.smooth muscle
---place where connect with alveoli: gradual changingsimple cuboidal epi. →simple squamous epi.less SM, elastic F
② alveolar duct: 20-60 alveoli connect with it
---wall: hard to see- opening part between two alveoli
simple cuboidal epi. or squamous epi.
SM: single, EF- knob-liked structure
④ alveoli:---polygonal, with opening sac- 0.2mm in
D, 300-400 million/per lung, total area: 70-80mm2
---wall:
epi. and basal lamina alveolar septum: CT with BV, EF
a. alveolur epi: ---type I alveolar cell: LM: flattened, 0.2um, N: round EM:
plasmalemmal vesicles tight junction
Function: constitute the blood-air barrier
---type II alveolar cell: scattered, 5-8/per alveoles
LM:
cuboidal or round, with round N
paler- stained, foamy cytoplasm
EM:
secreting granules: Osmiophilic multilamellar body
-0.1-1.0 um
-contains: phospholipid, glycosaminoglycan and protein
microvilli, mito, lysosome, RER, Golgi
Function:
i. secreting surfactant
ii. differentiated into type I alveolar cell
b. alveolar septum: CT• EF
Fibroblast, macrophage, plasma cell, mast cell
LV, N
capillary: endothelium + basement membrane
* Blood-air barrier: the structure through which the gaseous exchange takes place
---0.2-0.5 um---components:
a layer of liquid type I alveolar cell and basement M CT capillary endothelial cell and BM
c. alveolar pore: 10-15 um
---equalize( balance) the air-pressure between alveoli
---lober pneumonia- bacteria or inflammatory spread through the pore