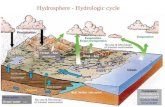
Chapter 14 Water: A Limited Resource Overview of Chapter 14 o Importance of Water Hydrologic Cycle...
-
Upload
hector-ray -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
2
Transcript of Chapter 14 Water: A Limited Resource Overview of Chapter 14 o Importance of Water Hydrologic Cycle...
Importance of WaterImportance of Water
o CookingCookingo WashingWashingo Use large Use large
amounts for:amounts for:• AgricultureAgriculture• ManufacturingManufacturing• MiningMining• Energy productionEnergy production• Waste disposalWaste disposal
o Use of freshwater Use of freshwater is increasingis increasing
Properties of WaterProperties of Water
o Composed of 2 Hydrogen Composed of 2 Hydrogen and 1 oxygenand 1 oxygen
o Exists as solid, liquid or gasExists as solid, liquid or gaso High heat capacityHigh heat capacityo PolarPolar
• One end has (+) charge, one One end has (+) charge, one end has (-) chargeend has (-) charge
o Forms Hydrogen bond Forms Hydrogen bond between 2 water moleculesbetween 2 water molecules• H-bonds define water’s H-bonds define water’s
physical propertiesphysical properties
Properties of Properties of WaterWater
o Water is never Water is never completely completely pure in naturepure in nature
o Content of Content of seawater (left)seawater (left)
o Many Many substances substances water dissolves water dissolves cause water cause water pollutionpollution
Distribution of Distribution of WaterWater
o Only 2.5% of Only 2.5% of water on earth is water on earth is freshwaterfreshwater
o 2% is in the form 2% is in the form of ice!of ice!
o Only ~0.5% of Only ~0.5% of water on earth is water on earth is available available freshwaterfreshwater
Freshwater TerminologyFreshwater Terminology
o Surface waterSurface water• Precipitation that remains on the surface and does Precipitation that remains on the surface and does
not seep into soilnot seep into soilo RunoffRunoff
• Movement of surface water to lakes, rivers, etc.Movement of surface water to lakes, rivers, etc.o Watershed (drainage basin)Watershed (drainage basin)
• Land area that delivers water into a stream or river Land area that delivers water into a stream or river systemsystem
o GroundwaterGroundwater• Freshwater under the earth’s surface stored in Freshwater under the earth’s surface stored in
aquifersaquiferso AquiferAquifer
• Underground caverns and porous layers of sand, Underground caverns and porous layers of sand, gravel and rock in which groundwater is storedgravel and rock in which groundwater is stored
Water Use and Resource Water Use and Resource ProblemsProblems
o Fall into Three CategoriesFall into Three Categories• Too much waterToo much water• Too little waterToo little water• Poor quality/contamination (discussed in Poor quality/contamination (discussed in
Chapter 22)Chapter 22)
Too Much WaterToo Much Water
o FloodingFlooding• Both natural and human-inducedBoth natural and human-induced
o Modern floods are highly destructive Modern floods are highly destructive because humans:because humans:• Remove water-absorbing plant cover from Remove water-absorbing plant cover from
soilsoil• Construct buildings on floodplainsConstruct buildings on floodplains
o FloodplainFloodplain• Area bordering a river channel that has the Area bordering a river channel that has the
potential to floodpotential to flood
FloodplainFloodplain
o Government restrictions on buildingGovernment restrictions on building• Levees can failLevees can fail
o Rather than rebuild Rather than rebuild levees adjacent to levees adjacent to rivers, experts rivers, experts suggest allowing suggest allowing some flooding of some flooding of floodplains during floodplains during floodsfloods• (next slide)(next slide)
Left: Left: Traditional Traditional levees levees adjacent to adjacent to riverriver
Right: Right: Suggested Suggested levee style, set levee style, set back from back from riverriver
Too Little WaterToo Little Water
o Typically found in arid landTypically found in arid lando ProblemsProblems
• DroughtDrought• Overdrawing water Overdrawing water
for irrigation for irrigation
purposespurposes• Aquifer depletionAquifer depletion
• SubsidenceSubsidence• SinkholesSinkholes
Too Little WaterToo Little Water
o Problems (continued)Problems (continued)• Saltwater IntrusionSaltwater Intrusion
Water Water Problems In Problems In
US and US and CanadaCanada
o US has a US has a plentiful supply plentiful supply of freshwaterof freshwater
o Many areas Many areas have a severe have a severe shortagesshortages• Geographical Geographical
variationsvariations• Seasonal Seasonal
variationsvariations
Water Problems in US and Water Problems in US and CanadaCanada
o Water shortages in West and SouthwestWater shortages in West and Southwest• Water is diverted and transported via Water is diverted and transported via
aqueductsaqueducts
Water Problems in US and Canada- Water Problems in US and Canada- Surface WaterSurface Water
o Mono Lake (Eastern CA)Mono Lake (Eastern CA)• Rivers and streams that once fed this lake Rivers and streams that once fed this lake
are diverted to Los Angeles (275mi away)are diverted to Los Angeles (275mi away)• Becoming highly salineBecoming highly saline• Court ordered water diversion reductionCourt ordered water diversion reduction
o Colorado River BasinColorado River Basin• Provides water for 27-million peopleProvides water for 27-million people• Numerous dams for HydropowerNumerous dams for Hydropower• Colorado River no longer reaches oceanColorado River no longer reaches ocean
Water Problems in US and Canada-Water Problems in US and Canada-GroundwaterGroundwater
o Aquifer DepletionAquifer Depletion Ogallala Aquifer
Global Water ProblemsGlobal Water Problems
o Amount of freshwater on planet CAN Amount of freshwater on planet CAN meet human needsmeet human needs• BUT, it is unevenly distributed and some BUT, it is unevenly distributed and some
places lack stable runoffplaces lack stable runoff
o Problems:Problems:• Climate ChangeClimate Change• Drinking WaterDrinking Water• Population GrowthPopulation Growth• Sharing Water Resources Among CountriesSharing Water Resources Among Countries
Global Water ProblemsGlobal Water Problems
o Water and Climate ChangeWater and Climate Change• Climate change affects the type and Climate change affects the type and
distribution of precipitationdistribution of precipitation• Potential issues:Potential issues:
• Reduced snowfall will impact water resources Reduced snowfall will impact water resources downstreamdownstream
• Sea level rise will cause saltwater intrusion into Sea level rise will cause saltwater intrusion into drinking water suppliesdrinking water supplies
Global Water ProblemsGlobal Water Problems
o Drinking Water ProblemsDrinking Water Problems• Many developing countries have Many developing countries have
insufficient water to meet drinking and insufficient water to meet drinking and household needshousehold needs
o Population GrowthPopulation Growth• Increase in population means an increase Increase in population means an increase
in freshwater requirementsin freshwater requirements• Limits drinking water availableLimits drinking water available• Limits water available for agriculture (food)Limits water available for agriculture (food)
Global Water ProblemsGlobal Water Problems
o Sharing Water Resources Sharing Water Resources Among CountriesAmong Countries• Rhine River Basin (right)Rhine River Basin (right)
• Countries upstream Countries upstream discharged pollutants into discharged pollutants into riverriver
• Countries downstream had to Countries downstream had to pay to clean the water before pay to clean the water before they could drink itthey could drink it
• Aral Sea (next slide)Aral Sea (next slide)• Water diversion for irrigation Water diversion for irrigation
has caused sea to become has caused sea to become too salinetoo saline
Global Water ProblemsGlobal Water Problems
o Potentially Volatile International Water Potentially Volatile International Water SituationsSituations• Jordan RiverJordan River• Nile RiverNile River
Water ManagementWater Management
o Main Goal: Provide sustainable supply Main Goal: Provide sustainable supply of high-quality waterof high-quality water• Requires humans to use resource carefullyRequires humans to use resource carefully
o Dams and ReservoirsDams and Reservoirso Water Diversion ProjectsWater Diversion Projectso DesalinizationDesalinization
Dams and ReservoirsDams and Reservoirs
o Benefits:Benefits:• Ensure year-round Ensure year-round
supply of water with supply of water with regulated flowregulated flow
• Generate electricityGenerate electricity• Provide recreational Provide recreational
activitiesactivities
o DisadvantagesDisadvantages• Alter the ecosystemAlter the ecosystem• Reduce sediment loadReduce sediment load
Dams and ReservoirsDams and Reservoirso Glen Canyon DamGlen Canyon Dam
• Regulated flow has changed ecosystemRegulated flow has changed ecosystemo To rectify situationTo rectify situation
• Canyon has been flooded several timesCanyon has been flooded several times• Small floods compared to natural floodsSmall floods compared to natural floods• Still helps rebuild habitatStill helps rebuild habitat
Dams and ReservoirsDams and Reservoirs
o Salmon Population Salmon Population in Columbia R. in Columbia R. very low due to very low due to dams that impede dams that impede migrationmigration
o Fish ladders help, Fish ladders help, but are not but are not effective enougheffective enough
Water Diversion ProjectsWater Diversion Projects
o Requires diverting Requires diverting water to areas that water to areas that are deficient by are deficient by pumping through a pumping through a system of aqueductssystem of aqueducts
o Much of CA’s Much of CA’s receives its water receives its water supply from diverted supply from diverted water from Northern water from Northern CACA
o Controversial and Controversial and expensiveexpensive
DesalinizationDesalinization
o Removal of salt from ocean or brackish Removal of salt from ocean or brackish waterwater
o Two methods: Two methods: • Distillation- salt water is evaporated, and Distillation- salt water is evaporated, and
water vapor is condensed into freshwater water vapor is condensed into freshwater (salt left behind)(salt left behind)
• Reverse Osmosis- involves forcing salt Reverse Osmosis- involves forcing salt water through a membrane permeable to water through a membrane permeable to water, but not saltwater, but not salt
o Very expensiveVery expensive
Water ConservationWater Conservation
o Reducing Agricultural Water WasteReducing Agricultural Water Waste• Agriculture is very inefficient with waterAgriculture is very inefficient with water• Microirrigation- irrigation that conserves Microirrigation- irrigation that conserves
waster by piping to waster by piping to
crops through sealed crops through sealed
systemssystems• Also called drip or Also called drip or
trickle irrigationtrickle irrigation
Water ConservationWater Conservation
o Reducing Industrial Water WasteReducing Industrial Water Waste• Stricter laws provide incentive to conserve Stricter laws provide incentive to conserve
waterwater• Recycling water within the plantRecycling water within the plant
• Water scarcity (in addition to stricter Water scarcity (in addition to stricter pollution control requirements) will pollution control requirements) will encourage further industrial recyclingencourage further industrial recycling
• Potential to conserve water is huge!Potential to conserve water is huge!
Water ConservationWater Conservation
o Reducing Municipal Reducing Municipal Water WasteWater Waste
o Gray WaterGray Water• Can be used to flush Can be used to flush
toilets, wash car or toilets, wash car or water lawnwater lawn
o Water saving Water saving household fixtureshousehold fixtures
o Government Government incentivesincentives
Population Increases (1990-Population Increases (1990-2000)2000)
Population increases from 1990-2000 in %
Annual electricity consumption growth rates from 1988 to 1998 (%)
Source: California Energy Commission, Electricity Analysis Office
Population ProjectionsPopulation Projections
Population Projections
(2000-2030)
Greatest increases expected in the driest states.
Source: U.S. Census Bureau
NEEDS: FRESH WATER!
Snow Survey and Water Supply Snow Survey and Water Supply Forecasting ProgramForecasting Program
o 12 western states 12 western states including Alaskaincluding Alaska
o 60 FTE60 FTE(36 Field, 24 NWCC)(36 Field, 24 NWCC)
o 25.5M acres of 25.5M acres of irrigated agricultureirrigated agriculture
o $51.1B in annual $51.1B in annual market valuemarket value(Ag. Census, 2002)(Ag. Census, 2002)
NRCS SNOTEL NetworkNRCS SNOTEL Network
o SNOTEL networkSNOTEL network• 12 western states12 western states• 730+ sites730+ sites• 16 million observations 16 million observations
(2005)(2005)• 16.1 million downloads16.1 million downloads
o 920 manual snow courses920 manual snow courses
SNOTEL Site Augmented Data Array
o Snow water contentSnow water contento PrecipitationPrecipitationo TemperatureTemperatureo Snow depthSnow deptho Relative humidityRelative humidityo Wind speed/directionWind speed/directiono Solar radiationSolar radiationo Soil moisture / Soil moisture /
temperaturetemperature
Water Supply ForecastsWater Supply Forecasts
o Water Year 2006Water Year 2006• 740 locations 740 locations
forecast Jan-Jun forecast Jan-Jun with NWSwith NWS
• Over 11,534 Over 11,534 forecasts issued forecasts issued by states to usersby states to users
• Over 1.9M visits to Over 1.9M visits to WSF pagesWSF pages
New Products - WSFNew Products - WSF
Rapid changes in snowpack affect water supply forecastsRapid changes in snowpack affect water supply forecasts