CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
-
Upload
riyan-saputra -
Category
Documents
-
view
258 -
download
4
Transcript of CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 1/29
1
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
LocationVentricular system
Subarachnoid space (including cysternal system)
Function Protect the CNS from mechanical insult (as a cushion)
Maintain the equilibrium of neuronal and glial
Remove the waste products of neuronal metabolism
Determine pulmonary ventilation andCBF according to its acidity

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 2/29
2
CSF
Aim of its examination
Diagnostic
Treatment evaluation or follow up
Prognostic
Formation
Rate – 0.35 mL/minute ~ 500 mL/day
Formed by :Choroid plexuses at :
Floor of each lateral ventricles (largest and
most important)
Roofs of the third and fourth ventricles (smaller)Capillary beds that supply the pia and
arachnoid (smaller)
Ependyma and adjacent glial elements (smaller)

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 3/29
3

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 4/29
4

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 5/29
5

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 6/29
6

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 7/297
CSF
Formation (ctnd)
A complex process : Active transport (expenditure of energy)
Passive diffusion
Active transport
Cuboid epithelial cells (in choroid pelxus) secrete Na ion
Positive potential attracts negative ion especially Cl
Many of ionic solutes increase osmotic pressure
Water and other solutes follow in
maintaining osmotic equilibrium
Passive diffusion
Continual diffusion occurs at :
Ependyma and vascular beds

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 8/298

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 9/299
CSF
DynamicTotal volume of CSF : 75 – 100 mL
( 15-40 mL at ventricular system)
Rate of production 0.35 mL/min ~ 500 mL/day
Daily turn over 4-5 times
CirculationLateral ventricles Monro foramenThird ventricle
Sylvii aqueductFourth ventricle
Luschka and Magendie foramina
Subarachnoid space (cysternal system)superior and lateral convexity of brain hemispheres
Arachnoid villi
venous sinuses
(venous blood flow)

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 10/2910
CSF
AbsorptionMainly at Arachnoid villi (Arachnoid granulation or
Pacchionian bodies)
Others (smaller) : veins and capillary of piamatter
Unidirectional (valve)
Mechanism - Depends on :
Hydrostatic pressure (high to low)
Colloid osmotic pressure (low to high)
Active transport by cells formingthe walls of the arachnoid villi

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 11/2911

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 12/2912
CSF
Composition
Water
Small amount of protein
Gases in solution (O2 and CO2)Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl-, Glucose
A few white cell
Organic constituents

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 13/29
13
CSF
Normal values
Color Clear, colorlessPressure 70-200 mmH2O
Cell 0-5/mm3 (lymphocyte or mononuclear cell)
Glucose 45-80 mg%
Protein 5-15 mg% (ventricles)
10-25 mg% (cysternal)15-45 mg% (lumbar)
-globulin 5-22 % total protein
Osmolaritas 295 mOsmol/L
pH 7.31
Natrium 142-150 mEq/LKalium 2.2-3.3 mEq/L
Chloride 120-130 mEq/L
Magnesium 2.7 mEq/L
CO2 25

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 14/29
14
CSF
Color
Clear, colorlessChange in color : Cell > 200 / mm3 (RBC > 1000 red color)
Traumatic puncture : 3-tubes test
More pale
clear
blood
xantho-
chrom
bloodUnchange

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 15/29
15
CSF
Pressure
Depends on :Rate of formation and absorption
Flow disturbance
Measurement :
Manometer while Lumbar or Cysternal puncture
Position :
Lateral decubitus : Normal pressure 70-200 mmH2O
Sitting : 280 mmH2O
Normally slight increase in case of
Coughing or straining
Change in heart beat and respiratory cycle
Pressure on abdomen

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 16/29
16
CSFPressure
Change in flow disturbance
Queckenstedt Test – press on jugular veins result in
normally increase CSF pressure and return to normal limit in10 “
CSF obstruction nothing or slightly increase CSF pressure
Cell : Leucocytes or PMN means pathologic I.e infection of
bacterial, fungal, viral, chemical agents, tumor
Protein : higher than normal limit means pathologic condition
Glucose : two third of blood glucose; below 40 mg% abnormal (i.e in pyogenic infection,
tuberculous/fungal meningitis)
Electrolytes : low chloride concentration meningitis (but
not specific)

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 17/29
17
CSF
Osmolality : similar to blood plasma
Acidity (pH) : Lower than blood
pCO2 : Higher than blood
In subacute or chronic metabolic acidosis :
CSF acidity relatively un-changed

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 18/29
18
CSF
Disorders of CSF
Flow disurbance Accompany other diseases
Flow disturbance
Obstruction occurs in CSF flow in ventricular system or subarachnoid space
Result in Hydrocephalus
Non-communicating :Common in children
Caused by aqueduct stenosis, over-growth of foramina
Luschka and Magendie

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 19/29
19
CSF
Disorders of CSF
Communicating hydrocephalus
Common in adultFree communicating between ventricles and subarachnoid space
Obstruction at subarachnoid space
Caused by inflammation, subarachnoid bleeding, tumor growth

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 20/29
20
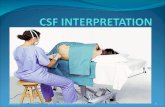
CSF|LP
LUMBAL PUNCTURE
Indication :Measure CSF pressureObtain sample for cell count, chemical work-up,
bacteriology
Intrathecal treatment/procedure :spinal anesthesia,antitumors, antibiotics
Diagnostic procedure : pneumoencephalography,myelography, scintigraphic cysternography

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 21/29
21
CSF|LP
Indications:
•Suspect meningitis
•Suspect encephalitis•Diagnose meningeal carcinomatosis
•Diagnose tertiary syphilis
•Diagnose meningeal leukemia
•Staging of lymphomas;•Follow up therapy for meningitis
•Evaluation of dementia
•Evaluation for Guillain-Barre
•Treat pseudotumor cerebri
•Evaluation for multiple sclerosis
•R/O subarachnoid hemorrhage (after neg. head CT)
•Instillation of drugs, anesthetics, or radiographic media
into CNS

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 22/29
22
CSF|LP
Technique
Preparation :Take blood sample for glucose 15’ before LP Explain the procedure to patientObtain informed consent
Exclude possibility of increased ICP or CNS mass lesion (eye exam/ head CT).
Position :Lateral decubitus in full flexion posture
At the bed sideSmall cushion on head or knee (if needed)

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 23/29
23
CSF|LP
Technique
Site of punctureInter-vertebral space at vertebra L3 – L4Imaginary line connecting iliac crestsOther site (if failed) : L2-L3 or L4-L5
Infant/children at L4-L5
CSF|LP

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 24/29
24
CSF|LP
Technique
Sitting position if failed in recumbent (2-3 times)Measure (opening) pressure
Patient preparationAseptic technique :Clean the area using iodine 10%
application in round movestarting from the center
Change glove onceUse sterile covering/towel
CSF|LP

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 25/29
25
CSF|LP
Technique
Insertion :All tools available : spinal needle (18,19,20),
manometer, sterile bottles (3)Local anesthetic (lidocaine 1-2%) :
0.1-0.2 mL subcutaneous and0.2-0.5 mL deeperIntroduce spinal needle, with bevel turned up,
into interspace, in a horizontal direction,
with slightly cephalad inclination
("aim for the belly button"). Always have stylish in place when
maneuvering needle in interspace.
CSF|LP

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 26/29
26
CSF|LP
•Measure opening pressure (normal is 100-250 mmHg): If
pressure elevated, ask pt to relax and ensure that there isno abdominal compression or breath holding (straining
and abdominal pressure can increase ICP).
•If pressure markedly elevated, remove only 5 cc of spinal
fluid and remove needle immediately.
•Else, collect 15-20 cc in four collection tubes (2 cc per
tube), and remove needle (with styled in place). Can send
extra fluid in tube #3, or in extra red-top (#5).
•Instruct pt to lie flat for approx. 4 hrs to minimize post LP
headache (caused by CSF leakage).
CSF|LP

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 27/29
27
CSF|LP
Contraindications:
•Infection at intended site of LP
• Anticoagulation;•Increased intra-cranial pressure
•Severe hemorrhagic diathesis
•CNS mass lesion in posterior fossa
•Suspect venous sinus occlusion
CSF|LP

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 28/29
28
CSF|LP
Complication
Headache
BackacheIntracranial subdural hematoma
Infection
CSF leak
Herniation

7/27/2019 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.PPT
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/cerebrospinal-fluidppt 29/29