Jual Load Cell, Load Cell Murah, Jual Load Cell , Teori Load Cell, Load Cell Murah, Jual Load Cell
Cell
-
Upload
jason-raquin-roque -
Category
Documents
-
view
12 -
download
0
Transcript of Cell

Roque, Jason R. HUB32
CELL
Parts Functions
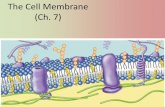
Cell Membrane
The outermost covering of a cell, lipid bilayer containing intrinsic proteins and with and external coat of carbohydrate.
The cell membrane acts like a traffic police man, that regulates entry and exit of substances, that is, ions and solutes. This helps in regulating the internal cell balance.
Centrioles A barrel shape cell structure.
The centrioles are a part of the animal cell. An animal cell may contain one or two centrioles that help in mitosis.
Cytoplasm
The mixture of water and soluble organic and inorganic compounds is called the cytoplasm.
Most of the parts of a cell are suspended in the cytoplasm. All the metabolic functions and activities of an animal cell takes place here. You can read more on cytoplasm function in a cell
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The tubular structures that are found near the nucleus and help provide support to both plant and animal cells are called the endoplasmic reticulum.
There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum, the smooth reticulum without the attached ribosomes and rough endoplasmic reticulum with the attached ribosomes.
Golgi Bodies The golgi apparatus or bodies are flat vesicular structures that are stacked one above the other.
They secrete and store hormones and enzymes that help in transportation out of the cell.
Lysosome
This part of an animal cell that is a membranous sac.
It is part of the golgi apparatus that contains different enzymes. It helps in intracellular digestion and in the elimination of foreign substances. They are also known as the 'suicide sacs' as, if one of them bursts, the entire cell will be destroyed.
Mitochondria
The mitochondria has two layers of membrane of which the inner membrane is folded to form cristae.
It is the powerhouse of the cell where ATP is generated by cellular respiration.
Nuclear Membrane
The covering of the nucleus is the nuclear membrane.
It has many pores that aid in the transport of substances.
Nucleolus Dense non‐membrane‐bound structure in nucleus.
The nucleolus contains the RNA and sends out the RNS to ribosomes along with the blueprints of the protein to be synthesized.
Nucleoplasm
The dense fluid that contains chromatin fibres made up of DNA is called nucleoplasm.
The chromatin fibers undergo a change in structure after cell division and are called chromosomes. This chromosome contains the hereditary information of genes.

Nucleus Double membrane‐bound large structure containing chromatin
The brain of a cell the cell nucleus controls all the functions occurring in the cell. It contains the blueprint of life, that is, DNA.
Ribosomes Small structure free in cytoplasm or bound to endoplasmic reticulum.
The part of a cell that contains RNA that helps in protein synthesis.
Vacuole The large and abundant vesicle of a plant cell is called a vacuole.
It contains fluids and helps in storage of substances, building material and water.
Cytoskeleton
Microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules.
Maintain cell shape and orientation, cell movement, movement of organelles around the cell, movement of chromosome during cell division.
Transport / Secretory Vesicles
Membrane‐bound vesicle often with a protein coat.
Transport materials between different cell compartments and to plasma membrane for export.
Phagosomes
Membrane‐bound vesicles containing material imported into cell.
Phagocytosis / endocytosis and transport of cargo to intracellular destination
Peroxisomes Membrane‐bound vesicles containing oxidases and catalase
Killing of pathogenic organism (in phagocytic cells) and degradation of waste products
Glycogen granules
Non‐membrane‐bound granules and aggregates of granules (rosettes)
Energy storage
Lipid droplets Non‐membrane‐bound spherical aggregates of lipid of variable size
Energy storage
Lipofuscin Brown pigment in cytoplasm Waste product
Reference:
‐ Retrieved from http://www.buzzle.com/articles/parts‐of‐a‐cell.html on June 20, 2011
‐ Young, B., Lowe, J.S., Stevens, A. & Heath, J.W. 2006. Wheather’s Functional Histology A Text and Color Atlas. C & E Publlishing, Inc.