Cell Transport Vocabulary - Susquehanna Township School District · 2019-08-28 · Active Transport...
Transcript of Cell Transport Vocabulary - Susquehanna Township School District · 2019-08-28 · Active Transport...
Solution – Solute - Solvent • Solute – The substance that dissolves to form
a solution
• Solvent – The substance in which a solute dissolves
• Solution – A mixture of one or more solutes dissolved in a solvent
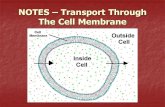
Semi-permeable membrane
• This membrane lets certain molecules pass through and prevents others from crossing
Passive transport
• the movement of substances across the plasma membrane from areas of high concentration to low concentration; does not require cellular energy.
• EX: – Diffusion
– Facilitated diffusion
– Osmosis
Diffusion
• the movement of particles from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration.
Facilitated Diffusion
• A process where a substance passes through a membrane with a aid of an protein carrier, no energy required Protein Carrier
Osmosis • diffusion of water through a semi-permeable
membrane
• Water will move in the direction where there is a high concentration of solute (and hence a lower concentration of water)
Osmotic Pressure
• The pressure exerted by the flow of water through a semipermeable membrane separating two solutions with different concentrations of solute.
• EX:
– Hypotonic solution
– Hypertonic solution
– Isotonic solution
Osmotic Solutions • Hypotonic solution (“POW”)
– If concentrations of dissolved solutes are less outside the cell than inside, the concentration of water outside is correspondingly greater.
• When a cell is exposed to such hypotonic conditions, there is net water movement into the cell causing cell to burst.
Osmotic Solutions
• Hypertonic solution – If concentrations of dissolved solutes are greater outside the cell, the concentration of water outside is correspondingly lower.
• As a result, water inside the cell will flow outwards to attain equilibrium, causing the cell to shrink.
Osmotic Solutions • Isotonic solution - When cells are in isotonic
solution, movement of water out of the cell is exactly balanced by movement of water into the cell.
Active transport • the movement of substances across the plasma
membrane from areas of Low concentration to high concentration; requires cellular energy.
• The movement of macromolecules(large molecules such as proteins or polysaccharides into or out of the cell is called bulk transport.
• 2 types of bulk transport
– Exocytosis
– Endocytosis
Active Transport
• Endocytosis - the process by which materials move into the cell.
• Phagocytosis - “cellular eating,” the cell’s plasma membrane surrounds a macromolecule
• Pinocytosis - “cellular drinking,” the cell engulfs drops of fluid by pinching in and forming vesicles
Active Transport
• Exocytosis - materials are exported out of the cell via secretory vesicles
– Golgi complex packages macromolecules into transport vesicles that travel to and fuse with the plasma membrane.
Equilibrium
• a state of equilibrium is reached when the concentrations of solutes and water is the same inside and outside the cell.