Cell Structure and Function. OBJECTIVE Today we will talk about the difference between prokaryotic...
-
Upload
anthony-greene -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Cell Structure and Function. OBJECTIVE Today we will talk about the difference between prokaryotic...
OBJECTIVE
Today we will talk about the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. We will also review for the quiz tomorrow by playing a game!
The Cell Theory
All living things are composed of cells.
Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things.
New cells are produced from existing cells.
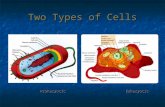
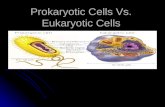
Types of Cells
Two kinds of cells depending on whether they have a nucleus
Prokaryote
Eukaryote
Genetic material
Prokaryotes
Usually small and simple
Genetic material (DNA) is not contained in a nucleus
The ONLY prokaryotes in the world are BACTERIA.
Eukaryotes
Usually larger and more complex than prokaryotes.
May be unicellular like an amoeba or multicellular like a plant
Contain dozens of specialized structures called organelles.
Includes protists, fungi, plants and animals.
Lysosomes-The Clean Up Crew
Function: Breakdown of lipids,
carbohydrates and proteins into small molecules to be used by the rest of the cell
Breakdown used up organelles
Get rid of all “stuff” in the cell
Structure: Small, filled with
enzymes
Vacuoles - Storage
Function:Stores water, salts,
proteins and carbohydrates
Structure:Sac-likePlant cells have one
large central vacuoleAnimal cells have
many small vacuoles
Chloroplasts – Energy in Plants
Function: Captures energy from the
sun (solar energy) and changes it into food (chemical energy) for plants (photosynthesis)
Structure: Surrounded by two
membranes Contains own genetic
information like mitochondria
Contains green pigment called chlorophyll
Not found in animal cells!
CILIA/FLAGELLA
Cilia are short hair-like structures that help the cell move around.
Flagella are long whip-like structures that also assist the cell in moving.