Cell Structure and Function Go to Section: Prokaryotic Cells 1. Prokaryotes: Do not have nucleus but...
-
Upload
rolf-alexander -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of Cell Structure and Function Go to Section: Prokaryotic Cells 1. Prokaryotes: Do not have nucleus but...

Cell Structure and Function
Go to Section:

Prokaryotic Cells
1. Prokaryotes: Do not have nucleus but they DO have DNAa. Smallest and simplest cellsb. DNA located in cytoplasm
(nucleoid region)c. Have cell wallsd. Have ribosomese. Many have flagella for
movementf. NEVER multicellular
2. Bacteria have prokaryotic cells
Slide # 3
Bacteria are the only organisms that have
prokaryotic cells.
DNACytoplasm
Cell wall
Cell membrane
ribosomesflagellum

Eukaryotic Cells
1.Eukaryotic: cells that have nucleus
2. Have specialized structuresa.Larger & more complex
than prokaryotic cells3. Unicellular & multicellular
organisms have eukaryotic cells
Slide # 3 nucleus
mitochondria
nucleoluschloroplast
vacuole
Cell membrane
Cell wall

Cellular Structures

Structure and Functions of the Nucleus
1. Nuclear membrane is a double membrane (each is a lipid bi-layer) pourous (controls what enters / exits nucleus
2. Nucleolus produces ribosomes
3. DNA is organized into distinct units called chromosomes that carries the genetic material
Nucleus controls cell’s activities because it contains the cell’s DNA

Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
1. A network of membranous tubules and sacs (cisternae)
2. ER membrane is continuous with the nuclear membrane
3. Transports substances throughout the cell
4. Rough ER
* has ribosomes
* produces proteins (pancreas produces insulin)
*makes membrane proteins
Smooth ER * no ribosomes * makes lipids & steroid hormones * breaks down toxins in liver cells * controls release of calcium in muscle cells

Golgi Apparatus (Body) (Complex)1. Single membrane
2. Membrane covered sacs (5-8 layers)
3. Receives products from ER
4. Modifies products from ER
5. Packages products into vesicles
6. Sorts and targets products to different parts of the cell or to be exported from the cell
Hydrolytic enzymes & lysosomal membranes that are made by the rough ER are packaged into lysosomes by the Golgi

Ribosomes (Free & Attached)
1. NOT membrane bound
* found in prokaryotes & eukaryotes
2. Proteins are synthesized (made) here
3. Free Ribosomes:
* found throughout the cytoplasm
* make proteins that function in the cytoplasm
4. Attached ribosomes (on ER) make proteins that are:
* destined for insertion into membranes
* put into lysosomes * many are exported
from the cell

Lysosomes1. Single membrane
2. Contain hydrolytic enzymes that break down cell waste & “junk” from outside the cell into simple compounds
* simple compounds transferred to cytoplasm as new cell building materials
3. Lysosomes originate in the Golgi
but enzymes are made in rough ER
4. Most numerous in disease fighting
cells (white blood cells) that engulf bacteria by phagocytosis
Tay Sachs is a genetic disorder that prevents the formation of the enzyme that breaks down ganglioside (a lipid). Result is damage to nervous system, mental retardation, and death in early childhood.

Mitochondria
1. Found in cytoplasm of ALL eukaryotic cells
* number of mitochondria in the celldepends on the cell & its function
2. convert oxygen and nutrients into ATP (adenosine triphosphate) through aerobic respiration (metabolism)
* ATP is the energy that cells use
3. Has its own DNA
4. Can reproduce independently of the cell

Cytoskeleton
1. Made up almost entirely of protein filaments
2. Functions:
* give cell shape
* provides mechanical strength
* aids in locomotion (especially in Amoeba and white blood cells -- pseudopods)
* helps in separating chromosomes during mitosis
* anchors organelles in cytoplasm

Vacuoles
1. Both plant and animal cells have vacuoles
* Temporary structure in animal cells
* Large, permanent structure in plant cells
2. Function: Stores water
3. When filled with water:
* helps cell maintain shape by exerting pressure on cell membrane & thus cell wall
* When plants wilt, they have lost water from vacuole
Large, central vacuole

Plastids1. Found in plant cells
2. Have a double membrane
3. Many different types
* chromoplasts
-- found in brightly colored flowers & fruits & leaves
-- have accessory pigments involved in photosynthesis
* amyloplasts
-- found in root cells; store starch
* leukoplasts (colorless)
-- contain oils and lipids
Chromoplasts
Amyloplasts

Chloroplasts1. Double membrane2. Plastids that convert light energy into
chemical energy (photosynthesis) * found in leaves & green stems3. Addition membrane system inside
the chloroplast * Thylakoids; flattened sacs * Grana; stacks of thylakoids * thylakoids are surrounded by fluid
called stroma4. Stroma contains circular DNA,
ribosomes, and enzymes5. Can replicate on own by binary
fission
Chlorophyll is found inside the thylakoids

Plasma (Cell) MembraneThe Boundary
1. Described as a lipid bi-layer fluid mosaic model2. Fatty acid tails face each other (hydrophobic)3. Phosphate heads (hydrophilic) are on the inside and outside of the membrane4. Lipid portion: isolates hydrophilic
substances from entering / exiting the cell
5. Protein portion: allows hydrophilic molecules and ions (charged) in / out of cell & communicates with other cells
Phosphate headhydrophilic
Fatty Acid tailshydrophobic
proteins

Membrane Structures / Functions
1. Transport: provides a hydrophilic channel across the membrane that is selective to a particular particle (salt, sugars, water, etc)
2. Some transport proteins change their shape to move substances from one side to another
hydrophilic
Changes shape

Cell Wall
1. Found in plant cells (NOT animals)
2. Protects cell, maintains cell shape, & prevents excessive uptake of water
3. Cellulose in cell wall – cross linked structure (like a chain linked fence) – makes cell wall very strong

Theory of Endosymbiosis
1. Theory that Eukaryotes arose from symbiotic relationship between prokaryotes and aerobic bacteria that they took in
2. 2 organelles involved: mitochondria & chloroplasts
3. Evidence that supports theory:
* bacteria, mitochondria, & chloroplasts all have circular DNA
* bacteria, mitochondria, & chloroplasts all about the same size
* bacteria, mitochondria, & chloroplasts can self replicate by binary fission
Prokaryote takes in aerobic bacterium
Prokaryote takes in cyano bacterium (capable of photosynthesis)

Contractile Vacuoles
1. Found in animal-like PROTISTS, not plants or animals
2. Pump excess water out of cell; keeps them from bursting open

Diffusion through phospholipid bilayer
What molecules can get through directly?
– fats & other lipids
inside cell
outside cell
lipid
salt
aa H2Osugar
NH3
What molecules can NOT get through directly?
– polar molecules
• H2O
– ions (charged)• salts, ammonia
– large molecules• starches, proteins

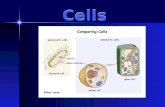
Animal Cells Plant Cells
Several small vacuoles scattered throughout the cell
Cell membraneRibosomesNucleusEndoplasmic reticulumGolgi apparatusVacuolesMitochondria
Cell WallChloroplast1 Large central vacuole
Slide # 10
Go to Section:
Structures in Animal verses Plant Cells