Cell and tissues - excerpts.numilog.comexcerpts.numilog.com/books/9782764409008.pdfCell and tissues...
Transcript of Cell and tissues - excerpts.numilog.comexcerpts.numilog.com/books/9782764409008.pdfCell and tissues...

Cell and tissues
The human body is formed of hierarchically organized components (tissues, organs, and systems), of which the basic unit is the cell. Cells are the site of intense activity: they accumulate and transmit energy, make proteins that are essential to the body’s functioning, and constantly reproduce by cellular division. They also contain all of the genes belonging to each individual.

8
structure of a cell
estructura F de la célula F All human cells have a similar structure: they are formed of a nucleus surrounded by cytoplasm and encased in a membrane.
CE
LL A
ND
TIS
SU
ES
human cell célula F humana Basic unit of the human body, whose size and shape vary depending on the functions that it performs.
centriole centríolo M
Cell structure playing a key role during mitosis.
vacuole vacuola F
Spherical cavity in which water, waste and various substances required by the
cell are stored.
mitochondrion mitocondria F
Structure associated with cell breathing; it produces and stores
energy in the cell.
endoplasmic reticulum retículo M endoplásmico
Cell structure consisting of a network of pockets surrounding the nucleus; it is
involved in protein synthesis.
cell nucleus núcleo M celular
Central core of the cell containing genetic information in the form of DNA
and guiding protein synthesis.
cytoplasm citoplasma M
Liquid substance forming the inside of the cell, around the nucleus, in which
cellular organelles bathe.
Golgi apparatus aparato M de Golgi Cell structure consisting of a group of membrane sacs; it is involved in the transport and maturation of proteins in the cell.
microfilament microfilamento M
Rod-shaped structure supporting the cell and giving it its shape.
microtubule microtúbulo M Cylindrical structure supporting the cell and allowing organelles and substances in the cell to move about.
pseudopod pseudópodo M
Extension of the cytoplasm of certain cells, serving mainly in cell
displacement.
ribosome ribosoma M
Organelle, floating free or bound to the endoplasmic reticulum, producing proteins essential to the formation and
functioning of the human body. cell membrane
membrana F celular Bilayer of lipid molecules forming the outer surface of the cell.
lipids lípidos M Molecules containing fatty acids, making up the cell membrane.
protein proteína F Organic compound formed of amino acids; in the cell membrane, proteins form channels allowing the exchange of substances with the outside environment.
Each human being is composed of more than 50 trillion cells. Hundreds of millions of them die every minute, and just as many are born through cellular division. Some, such as certain white blood cells, die after only a few hours, while others, such as neurons, may survive throughout a human being's life.
The Life of Cells

9
CE
LL AN
D TIS
SU
ES
cell nucleus
núcleo M celular Central core of the cell containing genetic
information in the form of DNA and guiding protein synthesis.
human cell
nuclear envelope envoltura F nuclear Membrane surrounding the nucleus.
chromatin cromatina F
Substance consisting of proteins and DNA contained in the nucleus; it is
compressed into chromosomes during mitosis.
nucleoplasm nucleoplasma M
Liquid substance forming the inside of the nucleus of a cell and in which
especially chromatin and nucleoli bathe.
nucleolus nucléolo M Spherical body located inside the nucleus and playing a role in the synthesis of ribosomes.
fat cell
adipocito M Cell forming the essential component
of adipose tissue and ensuring the synthesis, storage and release of lipids.
spermatozoon
espermatozoide M Mature and mobile male reproductive cell produced by the testis; the main
constituent of sperm, its purpose is to fertilize the ovum.
chondrocyte
condrocito M Cell, constituent element of cartilage.
white blood cell
glóbulo M blanco Blood cell belonging to the immune
system, thus playing an essential role in the body’s defenses.
photoreceptor
fotorreceptor M Cell found in the retina capable of
capturing light rays and translating them into nerve signals.
osteocyte
osteocito M Mature cell, constituent element of bone
tissue.
red blood cell
glóbulo M rojo Blood cell that carries oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and carbon dioxide
from the tissues to the lungs.
ovum
óvulo M Mature female reproductive cell
produced by the ovary; after fertilization by a spermatozoon, it enables an embryo
to develop.
neuron
neurona F Cell of the nervous system allowing
information to be carried in the form of electrical and chemical signals.
muscle fiber
fibra F muscular Contractile cell, constituent element of
muscles.
examples of cells ejemplos M de células F
The human body has about 200 types of cells, having very different characteristics and appearance depending on the functions that they perform in the organism.

10
epithelium
tejido M epitelial Tissue formed of cells organized in layers; it serves covering, secretory and protective functions.
CE
LL A
ND
TIS
SU
ES
tissue tejido M All the cells that have a similar structure and perform similar or complementary functions. Four main cell types make up the frame of the organism: epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous.
epithelial cell célula F epitelial
Cell component of epithelial tissue.
microvillus microvellosidad F Protrusion of the cell membrane that increases its surface.
basal lamina lámina F basal Extracellular matrix anchoring epithelial cells to adjacent tissue.
mucous cell célula F calciforme Epithelial cell that secretes mucus.
epithelium tejido M epitelial
Tissue formed of cells organized in layers; it serves covering, secretory and
protective functions.
mucous gland glándula F mucosa
Exocrine gland that secretes mainly mucus.
chorion corion M Loose connective tissue beneath the epithelial tissue of the mucous membrane.
muscularis mucosae mucosa F muscular Fine layer of smooth tissue beneath the chorion.
submucosa submucosa F Connective tissue beneath the mucous membrane.
mucus mucosidad F
Translucent viscous substance secreted by the mucous membrane and that
plays a protective role.
secretory cell célula F secretora Epithelial cell specialized in the secretion of various substances useful to the body.
excretory duct canal M excretor Duct carrying secretions from the exocrine gland.
examples of epithelia ejemplos M de tejidos M epiteliales They include tissues that form the covering of all body surfaces and line inner cavities (mucous membranes, endothelia, epidermis), and glandular tissues that have secretory functions.
exocrine gland
glándula F exocrina All secretory cells producing secretions released outside the body; they consist especially of salivary and sweat glands.
mucous membrane
mucosa F Damp epithelial tissue lining an open cavity of the body; the mucous membrane plays a role in absorption and secretion (mucus).

11
CE
LL AN
D TIS
SU
ES
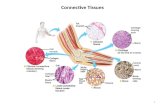
examples of connective tissues ejemplos M de tejidos M conjuntivos
Connective tissue: tissue made up of relatively few cells and fibers bathed in a more or less abundant fluid; its functions are to support, protect and
fill in spaces.
tissue
cartilage tejido M cartilaginoso Connective tissue consisting of cells encased in a rigid substance; it covers the articular surfaces of bones and forms certain soft parts of the body.
adipose tissue tejido M adiposo
Connective tissue made up essentially of adipocytes; it is the body’s energy reserve.
fibrous tissue tejido M fibroso
Connective tissue characterized by an abundance of collagen fibers; it forms especially the tendons and ligaments.
elastic tissue tejido M elástico Connective tissue made up predominantly of elastic fibers; it is found especially in certain ligaments and in the walls of the arteries, trachea and vocal chords.
Connective tissue, present in all organs, is the most abundant tissue in the human body: it accounts for two thirds of the total volume of tissue.
The Most Abundant

12
interphase
interfase F Period between two successive cell
divisions, during which the cell grows.
CE
LL A
ND
TIS
SU
ES
mitosis mitosis F All the mechanisms of cell division that allow the formation of two identical daughter cells from a mother cell.
centrioles centriolos M Double cellular structures that duplicate during interphase.
chromosomes cromosomas M
Elements of the nucleus of a cell, made up of DNA and proteins and carrying genetic
information; they are observed only during cell division.
mitotic spindle huso M mitótico
Ephemeral cellular structure joining the two pairs of centrioles during mitosis.
chromatid cromátida F
One of the two strands of a chromosome.
cytoplasm citoplasma M
Gel-like substance forming the inside of the cell, around the cell nucleus.
prophase
profase F First stage of mitosis, during which the
chromatin condenses into chromosomes; the two pairs of centrioles move toward
opposite poles.
metaphase
metafase F Second stage of mitosis, during which the
chromosomes align in the middle of the cell, guided by the mitotic spindle; the
nuclear membrane disaggregates.
anaphase
anafase F Third stage of mitosis, during which the chromosomes separate into chromatids
and move to either of the cell’s poles.
telophase
telofase F Fourth stage of mitosis, during which the chromosomes reassume the appearance of the chromatin; a new nuclear envelope
appears to cordon off the two nuclei.
cytokinesis
citocinesis F Stage of mitosis during which the
cytoplasm separates in two; the original cell (or mother cell) is replaced by two
identical daughter cells.

13
CE
LL AN
D TIS
SU
ES
DNA ADN M
Complex molecule containing the genetic characteristics (genes) of every person.
DNA molecule
molécula F de ADN M The DNA molecule appears in the shape
of a double helix made up of billions of nucleotides; it is the largest molecule in
the human body.
The human genetic heritage is included in 46 chromosomes (22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes). Each cell in the body has its own copy: for example, a skin cell contains the instruction for eye color.
Billions of Copies
adenine adenina F
Complementary nitrogenous base of thymine.
cytosine citosina F
Complementary nitrogenous base of guanine.
thymine timina F Complementary nitrogenous base of adenine.
guanine guanina F
Complementary nitrogenous base of cytosine.
nitrogenous base base F nitrogenada
Small constituent molecule of a nucleotide; there are four types that assemble in the DNA molecule to form a sequence specific to each
individual.
nucleotide
nucleótido M Basic unit of DNA molecules, consisting
of a nitrogenous base.
chromatid cromátida F One of two strands of a chromosome, consisting of a short arm and a long arm; during cell division, the two chromatids separate at the centromere.
centromere centrómero M Short section of a chromosome that holds the two chromatids together.
X chromosome cromosoma M X
Sex chromosome present in both men and women.
Y chromosome cromosoma M Y
Sex chromosome present only in men.
autosome
autosoma M Chromosome that carries hereditary characteristics unrelated to sex. sex chromosomes
cromosomas M sexuales Chromosomes responsible for
determining sex.
chromosomes cromosomas M
Elements of the nucleus of a cell, made up of DNA and proteins and carrying genetic
information; they are observed only during cell division.