Case report - · PDF filethe mandible. Mental nerve and ves ... Case report During the...
Transcript of Case report - · PDF filethe mandible. Mental nerve and ves ... Case report During the...

Case report
Page 1 of 3
Licensee OA Publishing London 2013. Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY)
For citation purposes: Verma M, Soni S, Saxena A, Das AR. Unilateral variation of the mental foramen. OA Case Reports 2013 Sep 10;2(11):102. Co
mpe
ting
inte
rest
s: n
one
decl
ared
. Con
flict
of i
nter
ests
: non
e de
clar
ed.
All a
utho
rs c
ontr
ibut
ed to
the
conc
eptio
n, d
esig
n, a
nd p
repa
ratio
n of
the
man
uscr
ipt,
as w
ell a
s rea
d an
d ap
prov
ed th
e fin
al m
anus
crip
t.Al
l aut
hors
abi
de b
y th
e As
soci
ation
for M
edic
al E
thic
s (AM
E) e
thic
al ru
les o
f disc
losu
re.
*Corresponding authorEmail: [email protected]
Department of Anatomy, Veer Chandra Singh Garhwali Government Medical Science and Research Institute, Srinagar, Uttarakhand, India
AbstractIntroductionMental foramen is present on the anterolateral aspect of the body of the mandible. Mental nerve and vessels pass through it and supply the area from canine to first molar. The mental nerve is the neurosensory nerve. Foramen present on the body of the mandible other than the mental foramen is considered as accessory foramen. This study reports a case of unilateral variation of the mental foramen. Case report During the anatomical teaching curriculum, we observed an accessory mental foramen on the right side of dried mandible. Morphometric analysis of mental foramen and accessory mental foramen from various anatomical landmarks was done and results were tabulated.Discussion Variations in the number of mental foramen are important when the premolar region is targeted for surgical intervention like osteotomy, root canal treatment and maxillo facial surgeries. Determination of implantation site and achievement of complete nerve block in that region depends upon the anatomical position and possible variation of mental foramen.Conclusion Variations in number of mental foramen is not uncommon. The knowledge of accurate position of MF is important to avoid damage
to neurovascular bundles passing through it and also to achieve absolute anaesthetic effect at the anterolateral mandibular region.
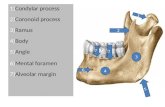
IntroductionMental foramen (MF) is present bilaterally on the anterolateral aspect of the mandible. It is present below the alveolar margin. The MF is an important anatomical landmark for dental surgeons planning for peri epical surgery in the mental region as well as for the local anaesthesia in the anterolateral mandibular region. The neurovascular bundle (mental nerve and vessels) emerges out through the MF. The mental nerve is the sensory nerve supplying the chin, lower lip and gingiva. The mental nerve is coming out from the MF and divides in to four branches named as angular, medial and lateral inferior labial and mental branch1.
Up to the 12th gestation week, the MF remains incomplete. When the mental nerves ramify in to various fascicules before the formation of MF, an accessory foramen is formed to provide an exit to these fascicules2. Accessory MF (AMF) carries the
mental branch and the medial inferior labial branch. It is also important to differentiate the AMF from nutritious foramen. Nutritious foramen is not related with the mandibular canal but AMF always takes origin from the mandibular canal1. Incidence of AMF varies between ethnic groups3. A previous study reported by Balcipoglu and Kocaelli 4 revealed no gender differences in the variations of number of MF. This study reports a case of unilateral variation of the MF.
Case report During osteology demonstration curriculum for undergraduate medical students in the department of anatomy, we came across of dried mandible of unknown sex having double foramina on the right side of the mandible (Figure 1). No accessory foramen was observed on the left side of mandible (Figure 2). Digital calliper was used to measure the dimensions and position of MF and AMF. The relation of MF with lower teeth and its position in relation to symphysis menti, the posterior border of the ramus of the mandible and lower border of the body of the
Unilateral variation of the mental foramenM Verma, S Soni, A Saxena*, AR DasA
nato
my
Figure 1: Showing MF and AMF on right side of mandible.

Case report
Page 2 of 3
Licensee OA Publishing London 2013. Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY)
Com
petin
g in
tere
sts:
non
e de
clar
ed. C
onfli
ct o
f int
eres
ts: n
one
decl
ared
.Al
l aut
hors
con
trib
uted
to th
e co
ncep
tion,
des
ign,
and
pre
para
tion
of th
e m
anus
crip
t, as
wel
l as r
ead
and
appr
oved
the
final
man
uscr
ipt.
All a
utho
rs a
bide
by
the
Asso
ciati
on fo
r Med
ical
Eth
ics (
AME)
eth
ical
rule
s of d
isclo
sure
.
For citation purposes: Verma M, Soni S, Saxena A, Das AR. Unilateral variation of the mental foramen. OA Case Reports 2013 Sep 10;2(11):102.
mandible was observed. The distance between AMF and MF was also measured (Table 1).
DiscussionPrevalence of AMF is variable among ethnic groups and is reported as follows: 2.6% in French, 1.4% in American white, 5.6% in American black, 3.3% in Greek, 1.5% in Russians and 9.7% in Melanesians. Among Japanese it was slightly higher; 6.7–12.5%5.
Three AMF were observed in a study conducted on 100 dried mandibles of the South Gujarat population6.
Triple MF was also reported by Ramadhan et al.7 in 2010 during surgical treatment of mandibular fracture. Gershenson et al.8 observed 0.67% incidence of triple foramina in 525 dried mandibles. Katakami et al.9 examined 150 patients retrospectively using limited cone beam computed tomography and found 16 dual foramina, one triple MF unilaterally. V De Freitas et al.10 examined 1435 mandibles i.e. 2470 sides and found three sides of Mandible devoid of MF.
Thus, the variations in the number of openings in the mental
region also varied. Most of the time a single foramen is present on both sides of the body of the mandible but it may double or triple or rarely be absent.
Clinical significanceMental injection or mental nerve block is given to achieve complete anaesthesia in the region of the anterior teeth including premolars and canines. It is important to consider the position of the MF and its morphological variations for the effectiveness of anaesthesia11.
While performing surgical procedures below the second premolar tooth it has to be kept in mind that there could be two mental nerves as observed by Sahin et al.12 during maxillofacial surgery in a trauma patient.
Before coming out of the MF, the nerve loops in to the body of the mandible so the extent of the loop can affect the position of the implant, therefore, panoramic radiograph should be taken to assess the proper location for the implant placement2. Wang et al.13 observed the average distance between the upper border of the MF and the bottom of the lower second premolar is about 2.50 mm. While performing root canal treatment in this region, the mental nerve could be injured due to close proximity to the lower part of the premolars .
ConclusionAfter reviewing the literatures, it can be concluded that variations in number of MF is not uncommon. If any surgery is planned in the area of canine to first molar tooth, one should always keep in mind these variations. Precise identification of these variations could be done by using advanced diagnostic techniques like Qspeed prospiral computed tomography (CT) scanner, 3D-CT and spiral CT. The knowledge of accurate position of MF is
Table 1 Positions and dimensions of MF and AMF
Parameters MF (Right side)
mm.
MF (Left side)
mm.
AMFmm.
Distance from symphysis menti 30 28 31Distance from posterior border of ramus of mandible
57 60 53
Distance from lower border of mandible
17 14 13
Size: Vertical diameter 1.5 1.8 1.2Horizontal diameter 1.5 1.8 1.0
Shape Round Round OvalDistance of AMF from MF - - 4Position of foramina with respect to lower teeth
Between 1st and 2nd premolar
Below 2nd premolar
Between 1st and 2nd premolar
Figure 2: Front view of mandible showing AMF unilaterally and MF bilaterally.

Case report
Page 3 of 3
Licensee OA Publishing London 2013. Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY)
Com
petin
g in
tere
sts:
non
e de
clar
ed. C
onfli
ct o
f int
eres
ts: n
one
decl
ared
.Al
l aut
hors
con
trib
uted
to th
e co
ncep
tion,
des
ign,
and
pre
para
tion
of th
e m
anus
crip
t, as
wel
l as r
ead
and
appr
oved
the
final
man
uscr
ipt.
All a
utho
rs a
bide
by
the
Asso
ciati
on fo
r Med
ical
Eth
ics (
AME)
eth
ical
rule
s of d
isclo
sure
.
For citation purposes: Verma M, Soni S, Saxena A, Das AR. Unilateral variation of the mental foramen. OA Case Reports 2013 Sep 10;2(11):102.
important to avoid damage to neurovascular bundles passing through it and also to achieve absolute anaesthetic effect at the anterolateral mandibular region.
References1. Neves FS, Soares L, Freitas DEA, Guanaes M, Torres G, Oliveira C. Accessory mental foramen: case report. RPG Rev. posgrad. 2010 Jul;17(3):173–6.2. Aher V, Pillai P, Ali FM, Mustafa M, Ahire M, Kadri M, et al. Anatomical position of mental foramen: a review. GJMPH. 2012 Jan–Feb;1(1):61–4. 3. Singh R, Srivastav AK. Study of position, shape, size and incidence of mental foramen and accessory mental foramen in Indian adult human skulls. Int J Morphol. 2010 Dec;28(4):1141–6.
4. Balcioglu HA, Kocaelli H. Accessory mental foramen. N AM J Med Sci. 2009 Nov;1(6):314–15.5. Sawyer DR, Kiely ML, Pyle MA. The frequency of accessory mental foramina in four ethnic groups. Arch Oral Biol. 1998 May;43(5):417–20.6. Agarwal DR, Gupta SB. Morphome-tric analysis of mental foramen in human mandibles of South Gujarat. People’s J Sci Res. 2011 Jan;4(1):15–8.7. Ramadhan A, Messo E, Hirsch JM. Anatomical variation of mental foramen. A case report. Stomatologija. 2010; 12(3):93–6.8. Gershenson A, Nathan H, Luchansky E. Mental foramen and mental nerve: changes with age. Aeta Anatomica (Basel). 1986;126(1):21–8.9. Katakami K, Mishima A, Shiozaki K, Shimoda S, Hamada Y, Kobayashi K.
Characteristics of accessory mental foramina observed on limited conebeam computed tomography images. J Endod. 2008 Dec;34(12):1441–5.10. V De Friestas, Madeira MC, Tolledofillo IL, Chagas FV. Absence of the mental foramen in dry human mandibles. Acta Anat (Basel). 1979;104(3):353–5.11. Prabodha LBL, Nanayakkara BG. The position, dimensions and morphological variations of mental foramen in mandibles. Galle Med J. 2006;2(1):65–7. 12. Sahin B, Selman H, Gorgu M. An anatomical variation of mental nerve and foramen in a traumatic patient. IJAV. 2010 Jan;3:165–6.13. Wang TM, Shin C, Lin JC, Kuo KJ. A clinical and anatomical study of the location of the mental foramen in adult Chinese mandibles. Acta Anat (Basel). 1986;126(1):29–33.