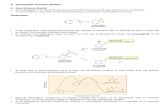
Carbon Reduction Hierarchy Reduce Demand Reduce ‘in- use’ Emissions Substitution and Innovation...
-
Upload
amanda-mills -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
2
Transcript of Carbon Reduction Hierarchy Reduce Demand Reduce ‘in- use’ Emissions Substitution and Innovation...
Carbon Reduction Hierarchy
The most effective way to reduce carbon emissions is to reduce the amount of goods or services consumed/procured. The need has to be challenged as well as identifying unnecessary waste as a result of overstocking, poor storage and handling, lack of operational management control or poor custom and practice.
Carbon Reduction Hierarchy
Focussing on the energy performance (and associated carbon emissions) of infrastructure, equipment or services at the procurement stage can help to reduce the whole life costs of ownership for the end user as well as the carbon footprint.Procurers will be able to exert a good degree of influence over this aspect of the footprint in many cases and realised financial savings can help to justify the investment of resource or higher upfront costs.
Carbon Reduction Hierarchy
If the need is established then it may be possible to meet that need in a different way that effectively reduces the carbon footprint. Substitution may deliver reduced carbon emissions by utilising materials or approaches with a lower carbon footprint while the introduction of innovation or disruptive technologies can radically change the way a need can be met (e.g. telecare).
Carbon Reduction Hierarchy
Ultimately a large proportion of the carbon footprint of goods and services procured is related to the practice and performance of suppliers in the supply chain. There are regulatory and competitive drivers for suppliers at all stages of the chain to improve energy efficiency and reduce relative carbon emissions however, additional client influence can provide a powerful further incentive to improve.Influencing carbon emissions in the supply chain relies on an informed client, should be based on a strategic approach which realises mutual benefits and can require long term commitment on both sides.
Intervention contributions
Contributions from interventions to absolute carbon reductionsContributions from interventions to absolute carbon reductions
Intervention contributions
Contributions from interventions to absolute carbon reductions
2010 2015 2020 2030 2050