CA Sanjeev Maheshwari 5 th September, 2015 Chamber of Tax Consultants Commonly Observed Non...
-
Upload
kenneth-hopkins -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of CA Sanjeev Maheshwari 5 th September, 2015 Chamber of Tax Consultants Commonly Observed Non...

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari
5th September, 2015
Chamber of Tax Consultants
Commonly Observed Non
Compliances in Financial
Statements

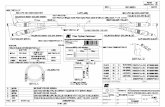
QRB - Number and Percentage of reviews completed and their outcome
Sl. No. Reviews Initiated in the year
Total 2012-13 2013-14 2014-15
1 Number of reviews initiated 37 56 123 216
2 Number of reviews completed till date 37 56 82 175
3Number of reviews where advisories were issued to concerned Audit firm/s 05 26 43 74
4
Number of reviews recommended to the ICAI Council for consideration and action 04 10 11 25
5
Total number of review cases indicating need for improvement [3 + 4] 09 36 54 99
6
Percentage of review cases indicating need for improvement [5/2 x 100] 24.32% 64.29% 65.85% 56.57%
2 CA Sanjeev Maheshwari

3 CA Sanjeev Maheshwari

4Accounting Standards for
Small and Medium Enterprises - Issues
Smaller Entities (SMC or SME)
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari4
AS are mandatory for GPFS - where such statements are statutorily required to be audited under any law (Sept’ 1993 Council’s Decision)
AS not to apply to entities which are not of Commercial, Industrial or Business nature — e.g. Trust having only donation income & spending for objects like poverty alleviation, education, etc.
In case of Companies, refer to Companies (Accounting Standards) Rules, 2006 and not to Accounting Standards of ICAI (AS)
Disclosure not made regarding “SMC” status / availability of certain exemptions to the entity( Para 1.1 of General Instructions)

General
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari5
Contracts without payment in cashSubscription against bonafide debt payable Conversion of loan in event of default Equivalent to cash
Where a company borrows against security of promoter – secured / unsecured?
Such security does not make it a secured advance
Creditors not bifurcated in to dues towards MSME and others.

Current Tax
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari6
Interest is finance cost and not Current Tax
Penalty which are compensatory in nature as ‘Interest Cost’
Other Tax Penalties – Other ExpensesWealth Tax – Rates & Taxes (Not current tax)

AS-1 Significant Accounting Policies
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari7
• All significant accounting Policies not disclosed at one place
• Timing of recognition of Revenue from Interest , Royalty and Dividend not disclosed.
• Policy on Borrowing costs, Inventories, Investments, Employee Benefits, Impairment, Contingent Liabilities etc, are observed to have been missed
• Dividend accounted for as and when received instead of when the right to receive is established.
• Change in accounting policies not appropriately disclosed with quantitative impact
• Failure to test “Going Concern” concept

AS – 2: Valuation of Inventory
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari8
• The Schedule for Inventories includes the following statement below the heading Inventories: “ As taken Valued and certified by the management”
• Finished Goods are Valued “At Cost or Market Value” (instead of NRV)
• Raw material, Work in progress, stores, spares, packaging material, etc. valued at ‘Cost’ - No reference to NRV
• Cost formula employed is not mentioned i.e. FIFO or WAC or SI
• Components of Cost not clearly disclosed(Prime cost [Purchase Cost, Cost of Labour, Other Direct Costs] + Direct Overheads etc.)
• No Separate disclosure of Stock in Transit in the Inventory Schedule
• No provisions for Excise Duty on Finished Goods.
• No provision for Customs Duty for goods lying at Warehouse

AS ‐3 Cash Flow Statement Now mandated under Companies Act,2013,very limited
exemption
Generally Observed Discrepancies: A significant difference has been noted in the amount of Cash
and Cash equivalents and Cash and Bank Balances as reported in the CFSs and schedule of Cash and Bank Balances respectively
Dividends paid are required to be disclosed as cash flow from financing activities. Even tax on dividend should be disclosed along with the dividends paid
Unrealized foreign exchange difference recognised in P&L, but not disclosed in CFSs
Schedule of Cash and Bank Balances include “The balances of Unclaimed Dividend Account, Margin money account and fixed deposit which is under lien with banks.”
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari9

AS ‐3 Cash Flow Statement Cash & Cash Equivalents include deposits with maturity over
twelve months
Purchase/Sales of Investments and Advance given to Subsidiaries disclosed on a net basis in Cash Flow Statement
Investments in Bank fixed deposit and Mutual Fund disclosed as Cash Flow from “Operating Activities” in the Cash Flow Statement
Postal franking machine balances were included as a part of cash and cash equivalents.
Investments in subsidiaries are not shown separately. Further, loan and advances provided to it are reported on net basis.
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari10

AS – 4: Contingencies & Events Occurring After Balance Sheet Date
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari11
Disputed Taxes (though paid) or claim which is not yet settled not disclosed as Contingent Liabilities
• No provision is made as amounts are considered as “unascertainable”(ex. Provision- Doubtful Debts)
• Recognition of expenses / income is often postponed till final “settlement” - instead of evaluating contingencies( ex. Provision-Warranties)

AS – 5: Net Profit or Loss for the Period, Prior Period Items and changes in Accounting Policies
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari12
Difference between ‘exceptional’ items and ‘extra-ordinary items
• Ordinary Activity Disclosure:When items of income or expense within the profit or loss from Ordinary Activities are of such size, nature or incidence that their disclosure is relevant to explain the performance of the enterprise for the period, nature and amount of such items should be disclosed separatelyEx:
Disposal of Fixed Assets/ Long term Investments Litigations settled Reversal of provisions Change of depreciation method Loss on sale of business Service tax/ excise claim
Write down of inventories to NRV and reversals of such write downs

AS – 5: Net Profit or Loss for the Period, Prior Period Items and changes in Accounting Policies
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari13
Extraordinary Activities are income or expenses that arise from events or transactions that are clearly distinct from the ordinary activities of the enterprise and, therefore, are not expected to recur frequently
Ex: Earthquake Attachment of property
In US the 9/11 Attacks were not considered as extraordinary

AS – 5: Net Profit or Loss for the Period, Prior Period Items and changes in Accounting Policies
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari14
Prior period items are income or expenses which arise in current period as a result of errors or omissions in the preparation of the financial statements of one or more prior periods
Adjustments related to previous period but determined in current period are not prior period items e.g. wage settlement arrears
Materiality is to be considered in prior period items
Nature and amount be separately disclosed so that their impact on the current profit or loss can be perceived

AS – 5: Net Profit or Loss for the Period, Prior Period Items and changes in Accounting Policies
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari15
Changes in Accounting Policies vs. Change in Estimates
- Change in Accounting Policy should be made only if it is o Required by statute or for compliance with an ASo Change would result in a more appropriate presentation of financial
statement
• Estimate may be revised if changes occur regarding the circumstances on which the estimate was based, or as a result of new information, more experience or subsequent developments ( e.g. useful life of asset, inventory obsolescence, bad debts, etc.)
Change of estimate is not a prior period or extraordinary item
Disclose effect of change in Accounting Estimate, if material

Depreciation- Companies Act,2013
Background - Global Practice Rates V/s Useful life SLM & WDV Companies Act, 2013, Notifications of 31.3.14 and 29.8.14 Useful life Residual Value Different Useful life & Residual life- Disclosures Technical Advice
16 CA Sanjeev Maheshwari

Depreciation- Companies Act,2013
Intangible Assets Regulatory Authority Revaluation Component Accounting Multiple Shift Transitional Provisions Continuous Process plant Unit of Production Low Value items Rates- Plant & Machinery - Other Assets
17 CA Sanjeev Maheshwari

AS – 6: Depreciation Accounting
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari18
Income Tax ‘Block of Assets’ concept is followed by some SMC. Profit / loss on sale of Assets not recognized, resulting to incorrect amount of depreciation
• Whenever method of depreciation is changed, recalculate depreciation from the date assets are put to use. Surplus / Deficit of depreciation of earlier years to be charged to Current Years Profit and Loss Statement
• However when only useful life is revised, the balance unamortized depreciable amount is charged over revised remaining useful life.
• Assets temporarily not in use- e.g. factory shut down, depreciation to be provided

AS – 6: Depreciation Accounting
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari19
Lower rate of depreciation than prescribed under Schedule XIV couldn't be charged, but now can be charged under Schedule II of Co. Act 2013
Depreciation policy mentions rates as per Schedule XIV or rates as per useful life which ever is higher. No further details given about actual depreciation rates.
- para 29 – if rates are different from the rates specified in in the statute governing the enterprise, they should be disclosed.
• In respect of specified assets, depreciation rates used provided in policy with no further disclosure
• - MCA cir 2/89 read with GN on Acctg for Depreciation requires that if higher rates of depreciation are justified , they may be provided with proper disclosure by way of a note forming part of annual accounts.
• Do not club Depreciation and Impairment

AS – 7 Construction Contract
It was observed from the accounting policy regarding construction contracts of a company that “revenue has been recognised based on bills raised and cost has been accounted, as and when incurred”, whereas paragraph 21 of AS 7 requires to recognise revenue and costs based on the stage of completion of the contract activity as on the reporting date
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari20

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari21
• Revenue recognition from services provided need careful consideration (e.g. completed service contract vs. Proportionate Completion Method) for
a. Coaching or Tuition Fees b. Courier Services
Dividend is to be accounted when right to receive payment is established (e.g. passing of resolution in AGM) and not on cash basis
AS – 9: Revenue Recognition

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari22
• Captive consumption of internally generated product added to sales
• Accounting policy states “ Sales are inclusive of VAT”
• As per para 10 following to be disclosed
Turnover (Gross) XXXLess: Excise Duty (XXX)
Turnover (Net) XXX(Not for VAT/ Sales Tax)
AS – 9: Revenue Recognition

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari23
Classification of fixed assets – often ‘Intangible assets’ not shown separately
Assets held for disposal to be shown separately and to be valued at NRV if lesser than cost
Revaluation of Fixed Assets
Entire class of assets should be revalued on a systematic basis
Revaluation should not be more than recoverable amount Accumulated depreciation should not be written back to
P/L.The method of revaluation should be specifically
mentioned ( for example, by registered valuers using the current reinstatement cost /the market price etc.)
AS – 10: Accounting for Fixed Assets

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari24
Subsequent expenditure related to an item of fixed asset should be added to its book value only if they increase the future benefits from the existing asset beyond its previously assessed standard of performance
Leasehold Properties need to be shown separately and not merged with similar other assets.
Disclosures for gross and net book values of fixed assets at the beginning and end of an accounting period showing additions, disposals, acquisitions and other movements
AS – 10: Accounting for Fixed Assets (Cont..)

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari25
Record Foreign Currency Transactions on the date of transaction i.e. date of sale / purchase or expenses and not on date of realization / payment
Year end balances of monetary items e.g. Debtors, Creditors, Advances, etc. to be translated at year end at closing rate.
Difference between date of transaction & date of settlement / transaction is to be taken to Foreign Exchange Difference Account (& not to Sales / Purchase / Expenditure account)
Accounting policy in relation to foreign currency transaction should state ---monetary assets and monetary liabilities denominated in foreign currency as at the balance sheet date are translated at the rate of exchange prevailing as on that date rather than referring to current assets and current liabilities
Forward Contracts for Hedging Purpose Premium or discount at inception to be amortized over period of
contact (Difference between rate on date of transaction and forward rate)
AS – 11: The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari26
Disclosure whether Investment is Long Term or Current Investments not made.
Disclosure whether Trade and Other than Trade” not made Current Investments are to be Stated “At lower of Cost or Fair Value” Long term Investments “ At Cost” Current Investments to be carried at lower of cost or Fair Value on
individual /Category basis & not on global basis Long term investment to be valued at cost less provision for
diminution (other than temporary), in value of investments Provision for diminution in value of Investments stated under
“Provisions” instead of reduction in the carrying amount. Often there are Prima Facie cases of diminution in value in Investment
but no diminution is recognized.
AS – 13: Accounting For Investments

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari27
Income (interest or dividend) to be disclosed separately on Long term & short term investments.
The Cost is to be considered on Average Cost Basis and not on FIFO or LIFO
AS – 13: Accounting For Investments

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari28
Borrowing cost cannot be capitalized unless such inventories take a substantial period of time to get ready for sale.
Failure to disclose the amount of borrowing cost capitalized.
AS – 16: Borrowing Costs

AS-18- Related Party Disclosures
• The disclosure requirement of this AS are mandatorily applicable to all companies but often noticed to be observed in breach
• Description of the relationship between the parties not stated
• Disclosure do not bring out the nature of transactions
• Details of transactions with related party in excess of 10% of aggregate value is not provided.
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari29

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari30
Lease payments under an operating lease should be recognized as an expense in Profit & Loss statement on a straight line basis over the lease term.
Example – ABC Pvt. Ltd has entered into leave and license agreement with XYZ Pvt. Ltd for 3 years (36 months) for monthly rent of Rs 10,000 per month and increase of 10% in monthly rent after end of every one year.
Total Rent payable during 36 months comes to Rs. 3,97,200 (Rs 10,000 p.m for 1st year, Rs 11,000 p.m. for 2nd Year and Rs 12,100 p.m. for 3rd year)
Hence monthly rent to charged to Profit & Loss Statement is Rs 11,033/-
AS – 19: Leases

AS – 19: Leases
31
Disclosures Made
• Leases– No disclosures made in case of
cancelable operating leases.
– Sometimes operating lease assets are reflected as Investments
– Accounting policy for assets given on lease (finance or operating) is disclosed. However no policy is disclosed for initial direct costs.
Requirement
– For cancelable operating leases also, disclosure of the amounts recognized in the profit and loss statement, contingent rent paid and a general description of the leasing arrangements (SMC exempted from general description) is required as per Para 25 of AS 19.
– As per para 39 of AS 19 lessor should present an asset given under operating lease in its balance sheet under fixed assets.
– As per para 37 and/or 46 in case of Lessor (finance or operating lease) the policy for accounting of initial direct costs should be disclosed.
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari32
Failure to disclose EPS on the face of Profit & Loss Statement
For Level II & III Enterprises and SMC there is no need to disclose Diluted EPS.
Nominal Value of the shares not disclosed on the face of the P/L or note.
Reconciliation of Weighted average nos of shares to be disclosed.
For diluted EPS all potential equity shares are to be considered and not only the existing nos of shares.
AS – 20: Earnings Per Share

AS-21, AS-23, AS-27
Consolidation/ Associate/ Joint VentureNow Mandatory under Companies Act,2013
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari33

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari34
Provision for Tax and Advance Taxes to be netted off.
DTA & DTL are to be set off & disclosed Net.
DTA to be created against b/f losses and unabsorbed depreciation against tax losses and not book loss.
DTA against b/f losses and unabsorbed depreciation in Tax to be created only when there is Virtual Certainty.
Convincing evidence for virtual certainty need to be disclosed.
Rates for DT should be substantive effect of actual enactment.
AS – 22: Accounting For Taxes on Income

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari35
DTA arising from b/f loss or unabsorbed depreciation were tested for virtual certainty but DTA arising from other components were tested for reasonable certainty. (para 17 – all DTA for Virtual Certainty)
DTA on Capital losses are recognized and evidence as required by para 32 not given(only if Virtual certainty)
Break up of major components of DTA/ DTL to be disclosed.
AS – 22: Accounting For Taxes on Income

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari36
Accounting Policy for Intangibles states “depreciation rates” rather than “Amortization Rates”.
Intangible Asset amortized over a period of 10 years needs disclosures of factors playing significant role in determining useful life to be more than 10 years.
No asset like Preliminary expenses, DRE, advertisement expenses, training expenses, etc allowed to be recognized as Intangible asset
Intangible Assets to be recognized only if the same meets criteria of AS i.e. ability to use or sale such assets and generate future economic benefits which are measurable & cost incurred/to be incurred for that is determinable
Internally generated Goodwill, Brands, Mastheads, Publishing Titles, Customer Lists and items similar in substance should not be recognized as intangible assets
AS – 26: Intangible Assets

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari37
AS – 28: Impairment of Assets
At each Balance Sheet date an enterprise should assess whether there is any indication that an asset may be impaired
Disclosure to be made for ‘each class of assets’. Impairment loss should be presented separately in the fixed assets schedule as per requirement of AS 28
AS – 29: Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets
Provision for Warranty, Restoration of Sites, Marketing & Sales Schemes (Reward Points, Future Sales at Discount, etc)
Provision of Book Debt/ Advances identified as Doubtful Provision of Interest on a Bank Settlement which is processed Excess utilization / Accounting of Sales Tax Incentive to be provided as liability Discounts, claims, rebates payable, warranties to be provided for & not
accounted for when settled/paid
AS – 28 & AS – 29:

AS – 29: Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets
• Failure to disclose in case of Contingent liability:o Brief description of the nature of contingent liab.o Estimate of financial effecto Indication of the uncertainties relating to outflowo Possibility of reimbursement
• Failure to disclose in case of Provision:o Carrying amount at the beginning and endo Additional provisions / including increase to existing
provisionso Amounts used and charged against provisiono Reversalo Description / uncertainties relating to outflow / Possibility
of reimbursement
CA Sanjeev Maheshwari38

AS-17 Segment Reporting• Segment Reporting
– No disclosure made in case of single primary and secondary segment.
– Segment assets and additions to segment assets not disclosed in case of secondary segment (geographical segment).
– Inter-segment sales are reported but basis of pricing is not disclosed
– Notes mention more than one segment but no further disclosure made since the other segment is below threshold level
– Requirement
– Where there are no reportable segments, such fact should be clearly disclosed in the financial statements.
– As per para 48 of AS 17, segment assets and additions to segments should be disclosed for geographical segments.
– As per para 53 of AS 17, basis of pricing intersegment transfers and any change therein should be disclosed in the financial statements.
– As per para 28 of AS 17, if a segment (below threshold level) is not disclosed as a Reportable Segment, then the same should be disclosed as Unallocated reconciling item39 CA Sanjeev Maheshwari

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari40
The AS is applicable to all entities but often overlooked i.e. whenever Interim Financials are prepared (say for giving to Bank for renewal/revision of facilities or for any other purpose) – the same has to comply with and reported upon in accordance with provisions of AS 25.
AS – 25: Interim Financial Reporting

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari41
In the Explanatory statements pursuant to section 173(2) of the Companies Act, 1956, states as follows;“As you are aware that we exited the business of manufacturing fertilizers and has taken up real estate activities with the consent of shareholders…”
Failed to disclose the information as required by Paragraph 20 and 32 of AS 24, Discontinuing Operations.
AS – 24: Discontinuing Operations

CA Sanjeev Maheshwari42
?
?? ?
?
??
?
??
?
?
??
QUESTIONS