By: Omar AL-Rawajfjf , ,ah, RN, PhD...Incidence Case- Mortality (Cases per 1,000 admissions)...
Transcript of By: Omar AL-Rawajfjf , ,ah, RN, PhD...Incidence Case- Mortality (Cases per 1,000 admissions)...

By: Omar AL-Rawajfah, RN, PhDy jf , ,

Findings can be presented in a narrative, tables, or figures forms.◦ Example of narrative format: “There were 185,824
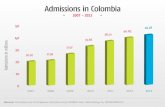
bloodstream infections cases during the full year of the study period. The overall incidence of bloodstreamthe study period. The overall incidence of bloodstream infections in this study was 34.3 cases per 1,000 admissions. Out of the total bloodstream infection cases were 113 436 (61%) nosocomial and 72 388cases were 113,436 (61%) nosocomial and 72,388 (39%) community acquired BSIs. The incidence rate for nosocomial BSIs was 21.7 cases per 1,000 admissions. Whereas the incidence rate for community acquiredWhereas, the incidence rate for community acquired BSIs was13.3 cases per 1,000 admissions”.

Incidence Case- MortalityIncidence(Cases per 1,000
admissions)
Case-Fatality
(%)
Mortality(Deaths per 1,000
admissions)
NBSIs 21.7 20.6 4.5
CBSIs 13.3 13.6 1.8

All admitted patientsN ≈ 8 M
Adult patientsN ≈ 7M
Adult patients hospitalized ≥ 48 hrsN ≈ 5.5M
Patients with at least one BSI coden = 185,824n 185,824
CBSIsn = 72 388 (39%)
NBSIsn = 113 436 (61%)n = 72,388 (39%) n = 113,436 (61%)
Incidence = 21 7 cases per 1 000Incidence = 13 3 cases per 1 000 Incidence = 21.7 cases per 1,000Incidence = 13.3 cases per 1,000

Much more subjective section of a researchMuch more subjective section of a research reportAllows the researcher to make interpretationAllows the researcher to make interpretation of the findingsDiscussion of aspects of the results that are pin agreement and those that are not in agreement with previous research and the
ibl l ti f h fi dipossible explanation of such findingsStudy strengths & limitations

Statistical significance means that nullStatistical significance means that null hypothesis has been rejectedClinical significance means the findings mayClinical significance means the findings may be used in the clinical settingsSome of the findings may be clinicallySome of the findings may be clinically significant but not statistically or the opposite

The incidence rate reported in this study was congruent with other studies (e.g., A l l l 2003 Ed h lApostolopolou et al., 2003; Edgeworth et al., 1999; Orsi et al., 2002; Pittet & Wenzel, 1995; Warren et al., 2001), 00 )
Wisplinghoff et al., (2003) reported an d f dincidence rate of 6 cases per 1,000 admissions.
However, patients with nosocomial BSIs were identified based on report of infection controlidentified based on report of infection control practitioners of the hospitals that participated in the study, which was highly likely to underestimate the number of casesunderestimate the number of cases.

Strengths:Strengths:◦ Design◦ Sample techniques◦ Sample techniques◦ FindingsLimitationsLimitations◦ Alteration in the sample◦ Alteration in the instrumentAlteration in the instrument◦ Control over the variable◦ Methodological alterationsMethodological alterations

Researcher’s attempt to show whatResearcher s attempt to show what knowledge had been gained by the studyAn attempt to generalize the findingsAn attempt to generalize the findings◦ Results from this study demonstrated that age
and gender are not among the main influentialand gender are not among the main influential risk factors for developing nosocomial BSIs. In fact, this study has shown that factors such as , yCVC, mechanical ventilation, the presence of other infections, trauma, and hemodialysis are h i i k f f i lthe most important risk factors of nosocomial
BSIs.

Give researcher opportunity to be creativeGive researcher opportunity to be creative.◦ Based on your conclusions what changes would
you suggestyou suggest◦ Changes may be suggested for research,
education, policy & practice, p y p“Awareness of risk factors can be used to reduce the incidence of these infections and improve the monitoring of these infections as well as the use of the preventionof these infections, as well as the use of the prevention strategies Figures generated by the study can be used to increase the
f th h lth li k i th t iawareness of the healthcare policy makers in these countries about the expected greater negative influences of these infections on their healthcare systems.


By: Omar AL-Rawajfah, RN, PhD

Talk about them
Write about themWrite about them

Ch i h iChoice the appropriate journalP h hPresents the research process
hPresents the major findingsShould be clear, concise

May be localMay be local, regional, or internationalinternationalOral or poster presentationpresentation◦ Call for abstracts
6-12 months before the presentationpresentation200 – 300 words

Results are very recentResults are very recentAudiovisual aidsSame format of journalSame format of journal articleUsually takes about 20Usually takes about 20 – 30 minutes

Many audiencesMany audiences can be reachedInformationInformation should be clear and conciseand conciseText should be big enoughbig enough

Preparing the ArticlePreparing the Article◦ Information for author
Length of the articleLength of the articleHow many tables Format of writing the article
Selecting the journal◦ Refereed journals
Peer review◦ Non refereed journals

Barriers to UtilizationBarriers to Utilization◦ Nurses lack of knowledge of nursing research◦ Negative attitudes toward researchNegative attitudes toward research◦ Lack of institutional support◦ Result are not ready for practicey pInstrumental utilizationConceptual utilizationConceptual utilization

Strategies for researchersStrategies for researchers◦ Do high quality research◦ ReplicateReplicate◦ Collaborate with practitioner◦ Disseminate aggressivelygg y◦ Communicate clearly◦ Suggest clinical implication

Strategies for Practicing NursingStrategies for Practicing Nursing◦ Read widely◦ Attend professional conferencesAttend professional conferences◦ Learn about evidence based practice◦ Involve in journal clubj◦ Collaborate with researchers

Strategies for AdministratorStrategies for Administrator◦ Foster a research climate◦ Offer emotional and moral supportOffer emotional and moral support◦ Offer financial support

Polit, D., & Hungler, B. (1997). Essentials of nursingPolit, D., & Hungler, B. (1997). Essentials of nursing research: Methods, appraisal, and utilization (4th
ed.). Philadelphia: LippincottNieswiadomy R Foundations of nursing researchNieswiadomy, R. Foundations of nursing research(4th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.Burns, N. and Grove, S. (2001). The practice of Nursing Research (4thed) Philadelphia: W BNursing Research (4thed). Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders.Macnee, C. (2004) Understanding Nursing
h d d hg g
Research: Reading and Using Research in Practice. Philadelphia: Lippincott.Polit, D., & Beck, C. (2004). Nursing research:Polit, D., & Beck, C. (2004). Nursing research: principles and methods (7th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott.