BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES PPT Notes wDiagrams.pdf · PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES &...
Transcript of BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES PPT Notes wDiagrams.pdf · PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES &...

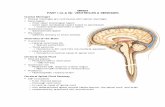
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES
Cranial Meninges • Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges • Dura mater:
– inner layer (meningeal layer) – outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
• venous sinuses between 2 layers • Arachnoid mater:
– subarachnoid space • Pia mater:
– adhered directly to brain surface Ventricles of the Brain • 4 ventricles
– Lateral ventricles (2) • Septum pellucidum
– Third ventricle • Connects to 4th ventricle via cerebral aqueduct
– Fourth ventricle • Connects to central canal of spinal cord
Cerebral Spinal Fluid • Choroid plexus
– Produces CSF in ventricles • ~500 ml/day
• Arachnoid villi – Reabsorbs CSF, superior cranial region
• Returns CSF to blood in venous sinus • Problems
– Hydrocephaly “watery brain” Cerebral Spinal Fluid Pathway • CSF circulates:
– from choroid plexus – thorough ventricles – to central canal of spinal cord – into subarachnoid space around cauda equina, the spinal cord, and brain – reabsorbed by arachnoid villi around brain

Functions of CSF • Cushions delicate neural structures • Supports brain • Transports nutrients, chemical messengers, and waste products Blood-Brain Barrier • Selective barrier between capillaries and extracellular space around brain • Molecules that can pass freely:
H2O, CO2, O2, glucose Fat soluble substances
• Molecules that are regulated: Ions, pH, neurotransmitters & hormones
• Molecules that do not cross: Large proteins, many medications
Blood Supply to the Brain • Supplies nutrients and oxygen to brain • Delivered by internal carotid arteries and vertebral arteries • Removed from dural sinuses by internal jugular veins
BRAIN PART I (C): VENTRICLE FORMATION
Embryonic Development of the Brain • Neural tube formation
– First month of development – Brain and spinal cord – Lumen becomes ventricles of the brain and central canal if the spinal cord
• Problems – Spina Bifida and Anencephaly
• Detected by alpha (α) fetal protein • Prevented by folic acid

BRAIN
PART II (A): CEREBRUM
Regions of the Brain • Cerebrum • Diencephalon • Brain stem
– Mesencephalon – Pons – Medulla oblongata
• Cerebellum Gray and White Matter • Gray matter:
– in cerebral cortex and basal nuclei
– cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals
– (where synapses occur) • White matter:
– myelinated axons
Structures of the Cerebrum • Gyri and sulci of neural cortex • Lobes:
– divisions of hemispheres: • Frontal • Parietal • Temporal • Occipital
Divisions of the Cerebrum • Longitudinal fissure:
– separates cerebral hemispheres • Central sulcus divides:
– frontal lobe from parietal lobe • Lateral sulcus divides:
– frontal lobe from temporal lobe • Parieto-occipital sulcus divides:
– parietal lobe from occipital lobe Functional Principles of the Cerebrum • Each cerebral hemisphere receives sensory information from, and sends
motor commands to, the opposite side of body • The 2 hemispheres have different functions although their structures are alike Hemispheric Lateralization • Functional differences between left and right hemispheres • Each cerebral hemisphere performs certain functions not performed by the
opposite hemisphere

Motor and Sensory Areas of the Cortex • Central sulcus separates motor and sensory areas Motor Areas (Frontal Lobe) • Primary motor cortex:
– is the surface of precentral gyrus
• Premotor cortex (somatic motor association area): – coordinates learned
movements • Broca’s area:
– control muscles used in speech
Somatosensory Areas (Parietal Lobe) • Primary somatosensory cortex:
– surface of postcentral gyrus • Proprioception, touch,
pressure, pain, vibration, taste, and temperature
• Somatosensory association area: – Interpretation of sensations
• Gustatory area: – Region for taste sensation
Cerebral Cortex: Sensory Areas • Parietal Lobes: Feel and Taste • Temporal Lobes: Hear and Smell • Occipital Lobes: Vision Hear & Smell (Temporal Lobe) • Primary auditory cortex:
– Receives information about pitch and volume • Auditory association area:
– Interpretation of sounds • Wernicke’s area: (different from text)
– Understanding (interpreting) words we hear • Olfactory cortex:
– Region for smell sensation • Medial (deep) portion of temporal lobe
Vision (Occipital Lobe) • Primary visual cortex:
– Receives information about light, dark, shape, and color • Visual association area:
– Interpretation of visual stimuli • recognition

Higher-Order Thinking • Prefrontal cortex of frontal lobe:
– integrates information from association areas – performs abstract intellectual activities
• predicting consequences of actions • decision making • planning and future comprehension
General Interpretive Area • (NOT called Wernicke’s area ) • Complex, learned reflexes Language Integrative Areas Left side • Broca’s area:
– speech formation (motor control of muscles) • Wernicke’s area:
– speech comprehension (understanding words) Right side • Affective Language area for Broca’s
– put emotion into speech/words • Affective Language area for Wernicke’s
– understand emotion in other’s speech/words

BRAIN PART II (B): ELECTROCENCEPHALOGRAM
What are the origins and significance of the major categories of brain waves seen in an electroencephalogram? Monitoring Brain Activity • Electroencephalogram (EEG):
– patterns of electrical activity are monitored 4 Categories of Brain Waves • Alpha (α) waves:
– healthy, awake adults at rest • Beta (β) waves:
– adults concentrating or mentally stressed • Theta waves:
– found in children – found in intensely frustrated adults – may indicate brain disorder in adults
• Delta waves: – during sleep – found in awake adults with brain damage

BRAIN
PART III (A): DIENCEPHALON
What are the main components of the diencephalon and their functions? The Diencephalon • Epithalamus • Thalamus • Hypothalamus
Epithalamus, Thalamus and Hypothalamus • Epithalamus:
– melatonin secretion via pineal gland • Thalamus:
– relays and processes sensory information • Hypothalamus:
– hormone production – emotion – autonomic function – connected to pituitary gland via infundibulum
The Hypothalamus • Lies below thalamus • Mamillary bodies:
– process olfactory and other sensory information
– control reflex eating movements • Infundibulum:
– connects hypothalamus to pituitary gland
Hypothalamus Functions (some) • Controls ANS functions
– Blood pressure, heart rate, peristalsis, etc. • Emotional response
– Pain, pleasure, fear, rage, libido • Body temperature • Food intake and satiety • Water balance and thirst • Sleep-wake cycle timing • Controls pituitary gland

BRAIN PART III (B): LIMBIC SYSTEM
What are the main components of the limbic system, their locations, and functions?
The Limbic System • Conscious functions of cerebral cortex with autonomic functions of brain stem • Memory storage and retrieval • Connects smell, memory, emotions Specific Parts of the Limbic System • Amygdaloid body:
– interfaces limbic system, cerebrum, sensory systems (smell), emotions • Hippocampus:
– short-term to long-term memory

BRAIN PART IV: BRAIN STEM & CEREBELLUM
Brain Stem • Mesencephalon (midbrain) • Pons • Medulla oblongata Structures of the Mesencephalon • 2 pairs of sensory nuclei (corpora quadrigemina):
– superior colliculus (visual) – inferior colliculus (auditory)
• cerebral peduncles: – nerve fiber bundles – contain:
• descending fibers to cerebellum • motor command fibers
• reticular activating system (allow or block sensory input, see ANS chapter)
The Pons • Nuclei involved with respiration:
– apneustic center, pneumotaxic center – Work with respiratory center in medulla oblongata
The Medulla Oblongata Links spinal cord to brain • Coordinates complex autonomic functions:
– Cardiovascular center • Cardiac (HR, contractility) • Vasomotor (peripheral blood flow)
– Respiratory rhythmicity center • Motor and sensory nerve tracts cross over • Reticular formation
– Alertness Functions of the Cerebellum • Adjusts postural muscles • Fine-tunes conscious and subconscious movements • Pathology:
• Ataxia:ffrom trauma or stroke • disturbs muscle coordination
• Arbor vitae