Box Culvert Design.xls
-
Upload
premasiri-karunarathna -
Category
Documents
-
view
1.277 -
download
85
Transcript of Box Culvert Design.xls

Reference Calculation Output
Area of concrete
Area of concrete in compression
Area of tension reinforcementMinimum area of tension reinforcement
Length of that part of member traversed by shear failure plane
b With (breath) or effective width of section
c Cover to outer diameter
d Effective depth of section
Basic force used in defining compressive forces
Basic force used in defining tie forces
Characteristic strength of concrete
Estimated design service stress in the tension reinforcement
Characteristic strength of reinforcement
G Shear modulus
H Maximum horizontal force
Horizontal force in x direction
Horizontal force in y direction
h Overall depth
KEL Knife edge load
L Critical perimeter
Dimension of element on x direction
Dimension of element on y direction
Dimension of element on z direction
M Design ultimate resistance moment
Moment on x axis
Moment on y axis
Moment on z axis
q Surcharge load
r Internal radius of bend
SLS Serviceability limit state
T Traction force
t Thickness of the element
ULS Ultimate limit state
V Shear force due to design ultimate loads or design ultimate value of a
concentrated load
v Design shear stress
vc Design shear stress in concrete
x Neutral axis depth
x' Distance from Y axis to the centroid of an element
y' Distance from X axis to the centroid of an element
z Lever arm
z' Distance from X - Y plane to point where the considered resultant
force acting
Coefficient, variously defined, as appropriate
Strain in tension reinforcement
Nominal range of movement
Soil friction angle, or diameter
Active earth pressure
Unit weight of soil
Partial load factor
Partial load factor
Doc. No. DESIGN UNIT Designed
Ac
Acc
As
As min
av
Fc
Ft
fcu
fs
fy
Hx
Hy
lx
ly
lz
Mx
My
Mz
DEC
Date
β∈sδφσ aγγ fLγ f 3

EPC DIVISION Checked Date CENTRAL ENGINEERING CONSULTANCY BUREAU (CECB) Job Code Page
Reference Calculation Output
DEC

Doc. No. DESIGN UNIT Designed EPC DIVISION Checked Date CENTRAL ENGINEERING CONSULTANCY BUREAU (CECB) Job Code Page
Reference Calculation Output
DEC
Date

Doc. No. DESIGN UNIT Designed EPC DIVISION Checked Date CENTRAL ENGINEERING CONSULTANCY BUREAU (CECB) Job Code Page
Reference Calculation Output
DEC
Date

Doc. No. DESIGN UNIT Designed EPC DIVISION Checked Date CENTRAL ENGINEERING CONSULTANCY BUREAU (CECB) Job Code Page
Reference Calculation Output
DEC
Date

Doc. No. DESIGN UNIT Designed EPC DIVISION Checked Date CENTRAL ENGINEERING CONSULTANCY BUREAU (CECB) Job Code Page
DEC
Date

Reference Calculation Output
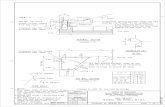
Design of Box Culvert
Figure 01
Dimentional Properties
h = 1.2 m
l = 1.5 m
Soil Cover , H = 7.2 m
Safe Bearing Pressure = 150 kN/m2
Section Thickness = 0.2 m ( hw , h = span/(10 ~15))
Main R/F = 12 mm
Cover to R/F = 45 mm
Grade of Concrete = 25 N/mm2
Properties of Soil
γc = 24 kN/m3
γs = 20 kN/m3
γw = 9.81 kN/m3
Φ' = 25
1 - Permanent Loads
1.1 Dead Loads
The nominal dead doad consist of the weight of the materials and the
part of the structure
Structural Unit Weight of Concrete shall be taken as 24 kN/m3
Engineering Becouse of the arching of soil, check whether the depth above culvert is
Design in > 3 x width of culvert ( in which case limit depth to 3 x width )
preactice
(Roger - Depth of cover (H) = 7.2 m
westbrook) 3 x width = 3 x 1.6
(page-94) = 4.8 m
3 x width < = 7.2 m So
Depth limited to = 4.8 m
Surcharge on Roof
Surcharge Presure (qr) = 4.8 x 20
qr = 96 kN/m2
Soil
Engineering Casses of conduit installation consider as Ditch Conduit
(Spangler & Ditch Conduit
Handy) A ditch conduit is defined as one which is instaled in a relatively narrow
ditch dug in passive or undisturbed soil and wich is then covered with earth
backfill.
Ceylon Electricity Board Doc. No.Dam Safety Designed S.M.P 31.05.2010
Environmental & Checked Date
o
C E B
Date
Y
hs
hw
Ground Level
hs
hw
A B
D C
H
l
h
X

Civil Structure Maintanance Job Code Page 1
Reference Calculation Output
Maximum load on ditch condition
Depth of cover = 7.2 m
Surcharge on Roof
Surcharge Presure (qr) ,
(qr) =
Cd =
=
K =
- coedicient of friction between fill material
and side of ditch
K - Active Lateral earth pressure coeficient
- Horizontal width of ditch at top of conduit
γ - Unit weight (wet density) of filling material
H - Height of fill above top of conduite
Cd - Load coeficient for ditch condition
So, K = Bd = 3.60 m, Consider 1m length of Roof slab
= 0.406
=
= 0.466
2.K.µ'.(H/Bd) = 0.76
Cd = 1.403
(qr) =
(qr) = 101.0 kN/m2
Structural 1.2 Horizontal Earth Pressure
Engineering
Design in If the backfill properties are known,
preactice If wall friction is to be ignored (δ = 0 )
(Roger -
westbrook) = 1-sin Φ' = 0.577
(page-94) = ( 1-sin Φ' ) / ( 1+sin Φ' ) = 0.406
q max = γ.Ka.h
= 20 x 0.41 x 9.1
= 73.9 kN/m2
= 20 x 0.41 x 1.9
= 15.42 kN/m2
q =
q = 58.44 kN/m2
Ceylon Electricity Board Doc. No.Dam Safety Designed S.M.P 31.05.2010
C E B
Cd.γ.Bd2
1-e-2Kµ'(H/Bd)
2.K.µ'
µ' tan φ'
1-sin φ1+sin φ
µ'
Bd
1-sin φ1+sin φ
µ' tan φ'
Cd.γ.Bd2
K0
Ka
qep
qmax - qep
C E B
Date

Environmental & Checked DateCivil Structure Maintanance Job Code Page 1
Reference Calculation Output
AASHTO 2 - Vertical Live Loads
3.7.1
For Fill Depths H ≥ 8 feet (2400 mm) and Culvert Clear Span Length,
The effect of live load is neglected in design when the depth of fill is more than
8 feet
3 - Hydrostatic Pressure (Internal)
= C.h
= 9.81 x 1.7
= 16.68 kN/m2
4 - Analysis
Reinforced
Concrete Constant K = h { hs } 3 = 1.21
Designers l
Manual k1 = K+1 = 2.21
(ref-5.1) k3 = K+3 = 4.21
k5 = 2K+3 = 5.43
k7 = 2K+7 = 9.43
k8 = 3K+8 = 11.64
4.1 Load Case -01 Testing Condition
4.1.1 Hydrostatic Pressure-(Internal)
Reinforced = =
Concrete 60.k1.k3
Designers = 0.99 kN.m/m
Manual
(ref-5.1) = = Ma. K8
k7
= 1.217 kN.m/m
4.1.2 Flexure due to weight of wall
Wall weight ( G ) = hw.γ.h q1 = 2.G = 10.20 kN/m2
= 8.2 kN/m l.hw
Reinforced
Concrete = =
Designers 12.k1.k3
Manual = 0.22 kN.m/m
(ref-5.1)
= = Ma. K5
K
= -0.97 kN.m/m
4.1.3 Flexure due to weight of Roof
q = hs.γc = 4.8 kN/m2
Doc. No.
C E B
q ip
hw
MA MB qip.h2.K.k7
MC MD
MA MB q1.l2.K
MC MD
A B
D C
qip
q = qipB.M.DPressures
A B
D Cq1
G G
B.M.DPressures

Dam Safety Designed S.M.P 31.05.2010
Environmental & Checked DateCivil Structure Maintanance Job Code Page 2
Reference Calculation Output
= = =
=
12.k1
= -0.35 kN.m/m
Addition of moment for Load case 01
Position γf Walls Roof γf
A and B 0.99 1.4 1.38 0.22 -0.35 -0.14 1.4 -0.19 1.19
C and D 1.22 1.4 1.70 -0.97 -0.35 -1.32 1.4 -1.85 -0.15
0.99 1.4 1.38 0.22**
1.04 1.4 1.45 2.830.82
1.22 1.4 1.70** **
2.35 1.4 3.29 5.001.53 0.82
*1.4 -2.88 -0.38 -0.35 -0.73 1.4 -1.02 -3.90
-2.06
Table - 01
Fixed end mement of the wall for Hydrostatic load
= W.L = W.L
15 10
= 1.607 kN.m/m = 2.41 kN.m/m
Maximum (-ve) moment = W.L
(Where x is 0.45L from C) 23.3
= -1.0 kN.m/m
* Calculation of moment at mid span of walls done by aproximatly by adding
moment transferred to mid span from FEM to the Maximum negative meoment
occurred at 0.45L after moment distribution
** Moment at mid span of the wall is calculated by considering full bending
Calculation of midspan moment due to wall load
Niutral axis depth from A = 0.26 m
4.2 Load Case -02 Culvert empty and trench filled
Lateral soil pressurees giving rise to flexture in the structure
4.2.1
Reinforced
Concrete = =
Designers 60.k1.k3
Manual = -0.91 kN.m/m
(ref-5.1)
= =
k7
= -1.13 kN.m/m
C E B
Date
MA MB MC MD
q.l2
Hydrost-atic
uls- Mb
Walls + Roof
uls-Mb
Total uls
Roof mid-Span
Base mid-Span
Walls middle
MA MC
"q"is the rectanguler pressure and "qep" is the triangular pressure
Trianguler Pressure,qep
MA MB qep.h2.K.k7
MC MD MA. K8
A B
D Cqepqep
B.M.DPressures
A B
D Cq = q1
B.M.DPressures

Doc. No.Dam Safety Designed S.M.P 31.05.2010
Environmental & Checked DateCivil Structure Maintanance Job Code Page 3
Reference Calculation Output
4.2.2 Surcharge on walls,q
= = =
Reinforced =
Concrete 12.k1
Designers = -7.72 kN.m/m
Manual 4.2.3 Surcharge on Roof ,qr
(ref-5.1) = = =
=
12.k1
= -7.45 kN.m/m
Addition of moment for Load Case 2
Posotion q γf
A and B -0.91 -7.72 -0.14 -7.45 -16.22 1.4 -22.70
C and D -1.13 -7.72 -1.32 -7.45 -17.62 1.4 -24.66
-0.91 -7.72 1.04 17.29 9.70 1.4 13.58
-1.13 -7.72 2.35 17.29 10.80 1.4 15.12
Walls middle* **
-0.73 -7.45 6.65 1.4 9.311.43 13.39
= W.L = W.L
15 10
= 1.486 kN.m/m = 2.229 kN.m/m
Maximum (-ve) moment = W.L
(Where x is 0.45L from C) 23.3
= -1.0 kN.m/m
4.2 Load Case -03
4.2.1 This is load case 02 + Hydrostatic load from Load case 01
Posotion
A and B -16.22 0.99 -15.23 -22.70 1.38 -21.32
C and D -17.62 1.22 -16.40 -24.66 1.70 -22.96
9.70 0.99 10.69 13.58 1.38 14.96
10.80 1.22 12.02 15.12 1.70 16.83
Walls middle 6.65 -2.06 4.59 9.31 -2.88 6.43
C E B
Date
MA MB MC MD
q.h2.K
MA MB MC MD
q.l2
qepWalls &
Roof(LC-1)Surcharg -e (Roof)
Total (Survice)
Total U.L.S.
Roof mid-Span
Base mid-Span
Fixed end mement of the wall due to qep
MA MC
L.C.02 (Service)
Hydrost. (Service)
Total (Service)
L.C.02 (U.L.S.)
Hydrost. (U.L.S.)
Total (U.L.S.)
Roof mid-Span
Base mid-Span
A B
D C
B.M.DPressures
Pressures
A B
D C
B.M.D

Doc. No.Dam Safety Designed S.M.P 31.05.2010
Environmental & Checked DateCivil Structure Maintanance Job Code Page 4
Reference Calculation Output
5 - Check on ground safe bearing pressure
5.1 Load Case -01
Hydrostatic Pressure = 16.68 kN/m2
Weight of walls = 10.20 kN/m2
Weight of Roof + Floor = 9.60 kN/m2
Total Pressure = 36.48 kN/m2
Total Pressure < 150 kN/m2 hence ok
5.2 Load Case -02
Weight of walls = 10.20 kN/m2
Weight of Roof + Floor = 9.60 kN/m2
Surcharge on Roof = 96.00 kN/m2
Total Pressure = 115.80 kN/m2
Total Pressure < 150 kN/m2 hence ok
5.3 Load Case -03
Weight of walls = 10.20 kN/m2
Weight of Roof + Floor = 9.60 kN/m2
Surcharge on Roof = 96.00 kN/m2
Hydrostatic Pressure = 16.68 kN/m2
Total Pressure = 122.28 kN/m2
Total Pressure < 150 kN/m2 hence ok
6 - U.L.S. of Flexture
Maximum Moments kN.m/m
Member Hogging Sagging
Roof -22.70 (L.C-01) 14.96 (L.C-03)
Walls -24.66 (L.C-02) 9.31 (L.C-02)
Base -24.66 (L.C-02) 16.83 (L.C-03)
i - Slabs
Maximum Moment = 24.15 kN.m/m
C E B
Date

Doc. No.Dam Safety Designed S.M.P 31.05.2010
Environmental & Checked DateCivil Structure Maintanance Job Code Page 5
Reference Calculation Output
6 - Design Calculation for Box Culvert
6.1 U.L.S. of Flexture
Analysis was carried out for several load cases of various loading
arrangements to find out the maximum effect on the Box culvert
Diameter of main reinforcement = 12 mm
Diameter of secondary reinforcement = 12 mm
Section Thickness = 200 mm
Maximum Bending Moment = 24.15 kN.m/m
Assume severe environment condition, for driving rain
Cover = 45 mm
Effective depth, d = 200 - 45 - 6 d = 149 mm
= 149 mm
k = 2
=
= 0.044 < 0.156
Hence no compression r/f is required
M = equation 1
z = equation 5 from these two equations
z =
z =
= 141.41 < 0.950 d
Take Z as 0.95d
Z = 0.95 d
= 0.95 x 149 = 142 mm
6.1.1 Design of main reinforcement
=
= =
= 426 426
Use T 12 @ 250 ( As = 452 =
452
Minimum area of main rainforcement for slabs
= 100x452/(1000x149) = 0.30 ### 0.13 Main r/f
T 12 @ 250
Hence o.k
6.2 Design for Shear Reinforcement
Check shear in U.L.S. on roof and floor slabs
Take Load case 02
Shear across support = ( 115.80 - Wt of Base x γf )
= 109.08 kN/m2
C E B
Date
M / (bd2fcu)
(24.15x106 /(1000x1492x25)
(0.87fy)Asz
(1 - 1.1fyAs/ fcubd) d
d (0.5+(0.25-k/0.9)1/2
d [0.5+(0.25-0.044/0.9)1/2
As M / 0.87fyz
24.15 x106 / 0.87x460x142 As req
mm2/m mm2/m
mm2/m As pro
mm2/m
100As / bad

Therefore shear in the support = 109.08 x 1.2 /2
= 65.45 kN/m
Doc. No.Dam Safety Designed S.M.P 31.05.2010
Environmental & Checked DateCivil Structure Maintanance Job Code Page 6
Reference Calculation Output
Design shear force, V design = 65.45 kN/m
Effective depth, d = 149 mm
Tension steel across shear plane = Y12 -250 c/c
100 As/bd = 100 x 452
1000x149
= 0.30
BS 8110 Effective depth = 149 mm
Part 01 =
table 3.1 = 0.54
Design shear stress v = V/bd
=
= 0.44
v < vc Hence o.k
6.3 Check in U.L.S. on the ability of the wall to trasmit the axial loads
Bs 8110 Treat as a column with bending at right angle to wall
3.9.3.6.2 Check h/hw = 1.7 / 0.2
3.4.4.1 = 8.5 < 12
hence column is short
BS 8110 indicates that the effect of the axial load may be ignored if this force does
hence 0.1.fcu.(C.S.A) = 0.1 x 30 x 200
= 600 kN/m
Ultimate Load /m/Wall = 1/2( 96.0 x 1.7 x 1.4
+ 0.2 x 1.7 x 24x1.4 )
= 120 kN/m < 600 kN/m
hence o.k.
The above calculation assumes that the wall is cosidered as reignfoced and not
mass concrete
vertical R/F provided = Y 12 @ 200 2 Layers
so Area = 1131.0 mm2
Percentage of Concrete area = 1131.0 x 100
1000 x 149
= 0.759 % > 0.4 %
This is > Minimum of 0.4% hence o.k.
C E B
Date
vc 0.79x{(100As/bd)1/3.(400/d)1/4/1.25
(65.45x103)/(1000x149)
N/mm2
not exceed 0.1.fcu.(c.s.a.)

Doc. No.Dam Safety Designed S.M.P 31.05.2010
Environmental & Checked DateCivil Structure Maintanance Job Code Page 7
Reference Calculation Output
C E B
Date

Doc. No.Dam Safety Designed S.M.P 31.05.2010
Environmental & Checked DateCivil Structure Maintanance Job Code Page 8
C E B
Date