Bones and Skeletal Tissues Structure and Function of Cartilage and Bone.
Bones: Structure & Function. Learning Objectives By the end of this class you should understand: The...
-
Upload
edgar-hall -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Bones: Structure & Function. Learning Objectives By the end of this class you should understand: The...

Bones: Structure & Function

Learning Objectives
By the end of this class you should understand:
The five functions of bones in the human body The structure and composition of compact and spongy bone The purposes of the different bone cells The processes of bone development, growth and repair The difference between the axial and appendicular skeletons

Skeletal System
• The skeletal system is an organ system composed of many connected body parts– Bones– Cartilage– Ligaments: attach bone to
bone– Tendons: attach bone to
muscle

Five Functions of Bone
• Support• Protection• Movement• Blood production• Mineral balance

Bone Tissue
• Bone is made from the following substances:– Calcium phosphate crystals
(hardness)– Matrix of protein such as
collagen (flexibility)– Living cells– Blood vessels to feed said cells– Marrow in the middle

Bone Structure• Bones are incredibly strong
due to their dual nature– Too hard: brittle, can
crack/shatter– Too flexible: can’t support
weight
• Bone is made from a combination of compact bone and spongy bone

Compact vs. Spongy Bone• Compact bone: layers of
dense bone material (crystals + matrix) wrapped around blood vessels
• Spongy bone: network of bone material filled with yellow or red marrow
• Many bones have a compact layer around a spongy center

Osteon
• Compact bone is made of many osteons
• An osteon is an arrangement of bone material around a blood vessel
• Many osteocytes (bone cells) produce and maintain the osteon

Spongy Bone
• Spongy bone is not made of osteons– The osteon is designed to
maximize blood delivery to a densely packed tissue
• Spongy bone is filled with marrow– Red marrow: produces blood– Yellow marrow: stores fat

Bone Growth/Decay
• All bone growth and decay is managed by two competing types of cells
• Osteoblasts build new bone tissue
• Osteoclasts degrade/remove bone tissue

Osteoblasts
• “Blast” is a suffix for a cell that produces something– Fibroblasts produce fibrous
connective tissue– Chondroblasts produce
cartilage– Osteoblasts produce bone
• The fetus begins its skeleton as cartilage bones formed by chondroblasts

Osteoblast Activity
• Osteoblasts produce bones• The first osteoblasts form in
the cartilage of fetal cartilage-bones and create the bone
• Osteoblasts are slowly converting cartilage to bone even as adults– The sternum is 3 different bones
in children but one fused bone in the elderly

Bone Growth• The cartilage skeleton in fetuses is
produced by chondroblasts– Osteoblasts convert the cartilage to bone
• Most bones have finished their shape early in childhood, but long bones (femur, etc) do not– They have a growth plate made of cartilage
that allows them to continue to lengthen until age 18-21
– Defective growth plate can lead to dwarfism

Osteoblast Activity
• Osteoblasts grow more bone matrix throughout life– Responsible for
thickening of bone in response to stress
– Forensic analysis can determine whether someone was right- or left-handed!

Osteoclasts• Osteoclasts break down bone
material• Release calcium into bloodstream
when active– Low blood calcium stimulates osteoclasts
to break down bones to replace calcium– Drink your milk!– Chronic low bone density can lead to
osteoporosis in old age
• Wear down jagged edges of damaged bone

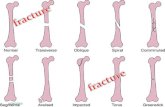
Bone Repair
• Damaged bone attracts chondroblasts to grow cartilage and knit the bone fragments together
• Osteoclasts wear down the damaged bone matrix
• Osteoblasts regrow the bone tissue thicker than it was before

Skeleton(s)
• The human skeleton is divided into two parts:
• Axial skeleton: head, torso, hips
• Appendicular skeleton: arms and legs


More on Wednesday!