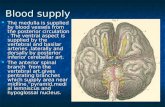
Blood supply to the brain. Blood serves the brain like food serves the body. The brain uses 20% of...
-
Upload
margery-flynn -
Category
Documents
-
view
230 -
download
1
Transcript of Blood supply to the brain. Blood serves the brain like food serves the body. The brain uses 20% of...

Blood supply to the brainBlood supply to the brain

• Blood serves the brain like food serves Blood serves the brain like food serves the body. The brain uses 20% of the the body. The brain uses 20% of the blood in the body. blood in the body. Arterial bloodArterial blood (carried (carried in arteries, arterioles, capillaries) in arteries, arterioles, capillaries) nourishes the brain by supplying: nourishes the brain by supplying: – oxygen: The brain requires 25% of the oxygen: The brain requires 25% of the
body’s oxygen to function maximallybody’s oxygen to function maximally– glucoseglucose– other nutrientsother nutrients
• Venous blood Venous blood (carried in veins) removes (carried in veins) removes metabolic waste (carbon dioxide, lactic metabolic waste (carbon dioxide, lactic acid, etc.)acid, etc.)
The brain is dependent on The brain is dependent on cerebral vasculaturecerebral vasculature
Which is the
high-pressure system? Which is the low-
pressure system? Why?

The brain is highly vulnerable The brain is highly vulnerable to disturbance of its blood to disturbance of its blood supplysupply• Interruption of blood supply lasting only Interruption of blood supply lasting only
second can cause neurological second can cause neurological symptomssymptoms
• Within minutes, interruptions of blood Within minutes, interruptions of blood supply can cause irreversible neuronal supply can cause irreversible neuronal damagedamage
• StrokeStroke, also called , also called cerebrovascular cerebrovascular accident accident ((CVACVA) = brain damage cause ) = brain damage cause by vascular disruptions, eitherby vascular disruptions, either– Loss of blood supply, when an artery Loss of blood supply, when an artery
is blocked (is blocked (occlusive strokeocclusive stroke))– Bleeding (Bleeding (hemorrhagic strokehemorrhagic stroke))

Overview of arterial blood supply to Overview of arterial blood supply to brainbrain
• Two systems of arteries deliver Two systems of arteries deliver glucose-, nutrient-, and oxygen-glucose-, nutrient-, and oxygen-rich blood from the heart and rich blood from the heart and aorta toward the brainaorta toward the brain– Internal carotids (L&R)Internal carotids (L&R)– Vertebral (L&R)-basilar Vertebral (L&R)-basilar
systemsystem
• These two systems are the These two systems are the inputs to a circular arterial loop inputs to a circular arterial loop at the base of the brain, called at the base of the brain, called the the Circle of WillisCircle of Willis – There is a in the middle of the There is a in the middle of the
circlecircle– The interconnections between The interconnections between
blood vessels (anastomoses) in the blood vessels (anastomoses) in the Circle of Willis protect the brain Circle of Willis protect the brain when part of its vascular supply is when part of its vascular supply is blockedblocked
– Common locations of blockages are Common locations of blockages are indicated by the dark areas indicated by the dark areas

Input from the internal Input from the internal carotids to the Circle of Williscarotids to the Circle of Willis
• HeartHeart Aorta Aorta – Left common carotidLeft common carotid branches directly off the aorta branches directly off the aorta– Right common carotid Right common carotid branches off of the branches off of the right subclavianright subclavian which which
branches off the aortabranches off the aorta
• Each common carotid (L&R) splits into two arteries Each common carotid (L&R) splits into two arteries – External carotid arteryExternal carotid artery– Internal carotid arteryInternal carotid artery
• The internal carotids (L&R) connect to The internal carotids (L&R) connect to opposite sides of Circle of Willisopposite sides of Circle of Willis
leftright

Input from the vertebral-basilar Input from the vertebral-basilar system to the Circle of Willissystem to the Circle of Willis
• HeartHeart Aorta Aorta – SubclaviansSubclavians (L & R) (L & R)
• Vertebral arteries Vertebral arteries (L&R) branch off of the subclavians(L&R) branch off of the subclavians
• The two vertebrals join to form one The two vertebrals join to form one basilar arterybasilar artery
• The basilar artery connects to The basilar artery connects to posterior portion of Circle of posterior portion of Circle of WillisWillis
leftright
Note that branches off of the vertebral arteries and the basilar artery supply the cerebellum, spinal cord, and brain stem

Arterial outputs from the Circle of Willis Arterial outputs from the Circle of Willis to the brainto the brain
• Three sets of paired Three sets of paired outputs from the Circle outputs from the Circle of Willis deliver of Willis deliver glucose-, nutrient-, and glucose-, nutrient-, and oxygen-rich blood into oxygen-rich blood into the brainthe brain– Middle cerebral Middle cerebral
arteries arteries – Posterior cerebral Posterior cerebral
arteries arteries – Anterior cerebral Anterior cerebral
arteriesarteries


Circle of WillisCircle of Willis::
Schematic review of Schematic review of
--the locations of inputs (green)--the locations of inputs (green)Internal carotidInternal carotid
Basilar arteryBasilar artery
--the output arteries (blue)--the output arteries (blue)ACAs ACAs
MCAsMCAs
PCAsPCAs
--communicating arteries which --communicating arteries which complete the circle (pink)complete the circle (pink)
Anterior communicating (1)Anterior communicating (1)
Posterior communicating (2)Posterior communicating (2)

Arterial blood supply to brain, in Arterial blood supply to brain, in situsitu
Two systems of inputs (#s 3; 8 & 10), three systems of outputs (#s 2, 4, 6), plus two “communicating arteries” (#s 1, 5). (Note: #s 7, 9, and 11, are branches off of the vertebral and basilar arteries, and supply the cerebellum.)
anterior
posterior
Inferior view of brain

Where do MCAs, ACAs, PCAs Where do MCAs, ACAs, PCAs branch out after exiting Circle of branch out after exiting Circle of Willis?Willis?
Lateral view of left hemisphere
Medial view of right hemisphere
Approx. location of Circle of
Willis
Note location of watershed region (where supply is received from >1 cerebral artery


Small branches of cerebral Small branches of cerebral arteries supply core areas of arteries supply core areas of brainbrain
• E.g. MCAE.g. MCA

A coronal section, showing how A coronal section, showing how cerebral arteries supply deep cerebral arteries supply deep structures and white matter of brain, structures and white matter of brain, as well as cortexas well as cortex
• MCAMCA
• ACAACA
• PCAPCA
Midbrain
Branch of internal carotid
PCA
MCA
MCA branches
ACA

Strokes disrupt blood supply: Strokes disrupt blood supply: Two types of strokeTwo types of stroke
• Stroke / cerebrovascular accident (CVA)Stroke / cerebrovascular accident (CVA)– Occlusive (ischemic) stroke: Occlusive (ischemic) stroke:
Thrombosis or embolismThrombosis or embolism– Hemorrhagic: Hemorrhaged Hemorrhagic: Hemorrhaged
aneurysm, or bleed of aneurysm, or bleed of
arteriovenous malformationarteriovenous malformation
Area of infarct +
surrounding penumbra




What does blood supply have to do with the What does blood supply have to do with the brain, and with practice of SLP? brain, and with practice of SLP?
• Knowing principle that “different structures in brain Knowing principle that “different structures in brain contribute to different functions” and using the contribute to different functions” and using the clinicopathologic methodclinicopathologic method– SLP can make clinical (diagnostic and therapeutic) SLP can make clinical (diagnostic and therapeutic)
predictions and plans, based on predictions and plans, based on
•the site(s) where arterial blood supply is lostthe site(s) where arterial blood supply is lost
•knowledge that nervous tissue will be damaged knowledge that nervous tissue will be damaged or die at those sitesor die at those sites
•knowledge of the kinds of functional changes knowledge of the kinds of functional changes associated with damage in that/those place(s) associated with damage in that/those place(s)
– E.g. left side of cerebrum vs. right side of cerebrumE.g. left side of cerebrum vs. right side of cerebrum– E.g. cerebellumE.g. cerebellum– E.g. brainstemE.g. brainstem

Some clinical applications (a preview)Some clinical applications (a preview)• The internal carotids supply more blood to cerebrum than vertebral-basilar systemThe internal carotids supply more blood to cerebrum than vertebral-basilar system
• Left MCA supplies the lateral left cortex, which is associated with the function of ______________Left MCA supplies the lateral left cortex, which is associated with the function of ______________
• Right MCA supplies the lateral right cortex, associated with the function of __________________Right MCA supplies the lateral right cortex, associated with the function of __________________
• Proximal branches of both MCAs supply the putamen and caudate, which are part of ______, Proximal branches of both MCAs supply the putamen and caudate, which are part of ______, important for movementimportant for movement
• PCAs supply thalamus, which is a gateway for all neural pathways going to the cerebral cortex, PCAs supply thalamus, which is a gateway for all neural pathways going to the cerebral cortex, including those that arouse (wake up) the cortex. (Remember limbic/olfactory?)including those that arouse (wake up) the cortex. (Remember limbic/olfactory?)
• PCAs supply occipital lobe, important for __________PCAs supply occipital lobe, important for __________
• ACAs supply medial cerebrum, important for sensori-motor functions of _________________ ACAs supply medial cerebrum, important for sensori-motor functions of _________________
• Vertebral-basilar system supplies the brain stem important for ___________ and cerebellum, Vertebral-basilar system supplies the brain stem important for ___________ and cerebellum, important for _________important for _________

Blood supply to the spinal cordBlood supply to the spinal cord

Spinal cord: Clinico-Spinal cord: Clinico-pathologic methodpathologic method
– Anterior spinal arteryAnterior spinal artery•Supply anterior two-Supply anterior two-
thirds of spinal cordthirds of spinal cord•SymptomsSymptoms
– Hemiplegia & loss Hemiplegia & loss of pain & of pain & temperaturetemperature
– Posterior spinal arteryPosterior spinal artery•Supply dorsal Supply dorsal
surface of the cordsurface of the cord•SymptomsSymptoms
– Loss of Loss of discriminative discriminative touchtouch

Blood-Brain BarrierBlood-Brain Barrier

Blood-Brain BarrierBlood-Brain Barrier• First Line of DefenseFirst Line of Defense
– Functional in only Functional in only CNS vessels CNS vessels
– Restriction of Restriction of movement of movement of harmful (infectious harmful (infectious microorganisms) microorganisms) substances from substances from blood to brain tissueblood to brain tissue
– Medical implicationsMedical implications
•Exclusion of Exclusion of antibodies, antibodies, making treatment making treatment of cerebral of cerebral infections difficultinfections difficult

Venous sinus system of Venous sinus system of the brainthe brain

VENOUS SINUS SYSTEMVENOUS SINUS SYSTEM
• FunctionsFunctions– Collection of deoxygenated blood Collection of deoxygenated blood – Transportation back to heart Transportation back to heart
•Veins emptying into sinusesVeins emptying into sinuses
•Dural sinusesDural sinuses–Separation of periosteal & Separation of periosteal & meningeal dural layers meningeal dural layers











![Beyond the Blood-Brain Barrier - UCLA CTSI · Beyond the Blood-Brain Barrier: ... Circumventing the blood-brain barrier ... K30 presentation final clean.ppt [Read-Only] Author:](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5b0543887f8b9a0a548e9fa1/beyond-the-blood-brain-barrier-ucla-ctsi-the-blood-brain-barrier-circumventing.jpg)