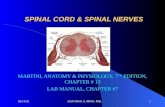
Blood supply of spinal cord
-
Upload
kurian-joseph -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
42 -
download
0
Transcript of Blood supply of spinal cord
BLOOD SUPPLY OF SPINAL CORD
VENOUS DRAINAGE OF SPINAL CORD.
Venous drainage is by
- six irregular plexiform channels
- There is one each along the, anterior and posterior midlines and along the line of attachment of dorsal and ventral roots.
- These are drained by radicular veins into epidural venous plexus
- Batson’s plexus (valveless spinovertebral venous plexus) continues upwards into the intracranial cavity, which may be a means of transport of tumor cells.
ARTERIAL SUPPLY OF SPINAL CORD.
Arterial supply is via
1) One anterior spinal artery
– a branch of vertebral artery
– descends the entire length of spinal cord at the anterior median fissure
– supplies anterior 2/3rd of spinal cord
2) Unpaired anterior medullary arteries
- branch of lateral spinal artery, which in turn is a branch of intercostal artery
- divides into anterior and posterior radicular branches to anastamose with anterior spinal and posterior spinal arteries respectively
- supply the peripheral areas of the cord
3) A pair of posterior spinal arteries
- branches of vertebral arteries
- supply posterior horns and dorsal funiculi
4) Central arteries
- branch of anterior spinal artery
- supply central portions of the cord on both sides
5) Artery of Adamkiewicz
- largest medullary artery
- arises between T9 to L2 levels
- reinforces the supply to lumbar segments
Special points::
1. Anastomosis is least efficient at the region of lateral columns
2. Cervical and lumbar segments have rich vascular supply
3. T1 to T4 segments are most vulnerable to ischemia
4. Anterior spinal artery thrombosis causes ischemia of anterior 2/3rd of the cord, sparing the posterior column, hence leads to dissociated sensory loss.