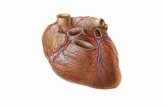
Blood supply of heart (1)
-
Upload
puneet-mahajan -
Category
Education
-
view
489 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Blood supply of heart (1)

Blood supply of the Blood supply of the Heart & Conduction Heart & Conduction
SystemSystem

Arterial supply of HeartArterial supply of Heart
Right coronary artery
Left coronary artery

Right Coronary ArteryRight Coronary Artery
Arises from anterior aortic sinus of the Ascending Aorta.It descends in the right atrioventricular groove.Near inferior border continuous posteriorly along the atrioventricular groove. Anastomose with left coronary artery in the posterior interventricular groove.

Right Coronary ArteryRight Coronary Artery

Branches of Right Branches of Right Coronary ArteryCoronary Artery
1.Right conus artery: Supplies rt ventricular outflow tract.
2.Rt marginal branch:Supply free wall of rt ventricle.

Branches of Right Branches of Right Coronary ArteryCoronary Artery
3. Rt posterolateral branch:goes back of lt ventricle
supply inferior aspect of interventricular septum4. Atrial branches:
Supply anterior and lateral surface of the right atrium. One branch supply posterior surface of both right and left atria. Artery of Sinuatrial Node (60%)

Branches of Right Branches of Right Coronary ArteryCoronary Artery
5. Posterior interventricular (descending) artery Runs towards apex in the posterior interventricular groove. Supply right & left ventricles, including
its inferior wall. Supply posterior part of the ventricular septum (Excluding Apex). Large septal branch Supply Atrioventricular Node.

Clinical division of the Clinical division of the RCARCA
Proximal - Ostium to 1Proximal - Ostium to 1stst main RV branch main RV branch Mid - 1Mid - 1stst RV branch to acute marginal RV branch to acute marginal
branchbranch Distal - acute margin to the cruxDistal - acute margin to the crux

Area of distribution RCAArea of distribution RCA
Rt atriumRt atrium Greater part of rt ventricle except area Greater part of rt ventricle except area
adjoining ant interventricular grooveadjoining ant interventricular groove Small part of lt ventricle adjoining post Small part of lt ventricle adjoining post
interventricular grooveinterventricular groove Whole of conducting system of heart Whole of conducting system of heart
except part of lt branch of AV bundleexcept part of lt branch of AV bundle SA Node –supplied by LCA (40%)SA Node –supplied by LCA (40%)

Left Coronary ArteryLeft Coronary Artery
Larger then Right coronary artery.Arises from posterior aortic sinus of the Ascending Aorta.Passes between pulmonary trunk and left auricle.It enters in the atrioventricular groove and divides into an anterior interventricular branch and a circumflex branch.Supply greater part of the left Atrium, left ventricle and ventricular septum.

1. Anterior interventricular (descending) artery: Runs in the anterior interventricular groove to the Apex. Passes around the Apex to enter the posterior interventricular groove & anastomoses with the terminal branches of Right coronary artery. Supply right and left ventricles & anterior part of ventricular septum. Left diagonal branch wrap over anterolateral free wall of lt ventricleSeptal branch curves into interventricular septum
Branches of Left Branches of Left Coronary ArteryCoronary Artery

Left Coronary ArteryLeft Coronary Artery

Branches of Left Branches of Left Coronary ArteryCoronary Artery
2. Circumflex artery: Winds around the left margin of the heart
in the atrioventricular groove. obtuse marginal branch: supply lateral free wall of lt ventricle does not reach crux in pt with rt dominant circulation
Atrial branches: Supply left atrium. Artery of Sinuatrial Node (40%)

ClinicalClinical divisiondivision ofof thethe LADLAD
Proximal - Ostium to 1Proximal - Ostium to 1stst major septal major septal perforatorperforator
Mid - 1Mid - 1stst perforator to D2 (90 degree perforator to D2 (90 degree angle)angle)
Distal - D2 to endDistal - D2 to end

ClinicalClinical divisiondivision ofof thethe LCXLCX
Proximal - Ostium to 1Proximal - Ostium to 1stst major obtuse major obtuse marginal branchmarginal branch
Mid - OM1 to OM2Mid - OM1 to OM2 Distal - OM2 to endDistal - OM2 to end

Area of distribution of LCAArea of distribution of LCA
Lt atriumLt atrium Greater Prt of lt ventricle except post Greater Prt of lt ventricle except post
interventricular grooveinterventricular groove Small part of rt ventricle adjoining Small part of rt ventricle adjoining
ant interventricular grooveant interventricular groove Ant part of interventricular septumAnt part of interventricular septum Lt branch of AV bundleLt branch of AV bundle

Conducting system of Conducting system of HeartHeart S-A Node: Right coronary artery (60%)
Left coronary artery (40%) A-V Node and A-V Bundle: Right coronary artery
Right Bundle branch: Left coronary artery
Left Bundle branch: Right & Left coronary arteries

Coronary segment Coronary segment classification systemclassification system
CASS investigators – 27 segmentsCASS investigators – 27 segments BARI – 29 segments ( ramus BARI – 29 segments ( ramus
intermedius and 3intermedius and 3rdrd diagonal branch) diagonal branch)
- Obstructive CAD : > 50% stenosis- Obstructive CAD : > 50% stenosis

CardiacCardiac dominancedominance
85%-rt dominant coronary artery85%-rt dominant coronary artery 8%-8%- lt dominant-post descending,posterolateral lt lt dominant-post descending,posterolateral lt
ventricular and AVnodal artery all supplied by ventricular and AVnodal artery all supplied by terminal portion of lt circumflex coronary terminal portion of lt circumflex coronary artery.rt coronary artery small and supply only artery.rt coronary artery small and supply only rt atrium and rt ventriclert atrium and rt ventricle
7%-codominant 7%-codominant RCA-PDA and terminates,circumflex artery-all RCA-PDA and terminates,circumflex artery-all
post post Lt ventricular branchesLt ventricular branches

Congenital anomaly of Congenital anomaly of coronarycoronary
circulationcirculation Anomalous pulmary origin of Anomalous pulmary origin of
coronary artery(APOCA)coronary artery(APOCA) Most common-origin of LCA from Most common-origin of LCA from
pulmonary arterypulmonary artery
Aortography-large RCA with absence Aortography-large RCA with absence of lt coronary ostium in lt aortic sinusof lt coronary ostium in lt aortic sinus

Anomalous coronary artery Anomalous coronary artery from opposite sinusfrom opposite sinus
Origin of LCA from rt aortic sinusOrigin of LCA from rt aortic sinus
causes sudden cardiac death after causes sudden cardiac death after exerciseexercise
in young personin young person

Coronary artery fistulaCoronary artery fistula
Abnormal communication between Abnormal communication between coronary artery and major vessels coronary artery and major vessels such as such as
venacava,pulmonary artery or veinvenacava,pulmonary artery or vein

Myocardial bridgingMyocardial bridging
All 3 major coronary artery generally All 3 major coronary artery generally course along epicardial surface of course along epicardial surface of heartheart
sometime short coronary artery sometime short coronary artery segment descend into myocardium segment descend into myocardium for variable distancefor variable distance
occurs in 5-12% of pt and confined to occurs in 5-12% of pt and confined to LADLAD

Coronary artery spasmCoronary artery spasm
Dynamic and reversible occlusion of Dynamic and reversible occlusion of epicardial coronary artery caused by epicardial coronary artery caused by focal constriction of smooth muscle focal constriction of smooth muscle cell within arterial wallcell within arterial wall
occurs in prinzmetal anginaoccurs in prinzmetal angina aggrevated by cigaratte aggrevated by cigaratte
smoking,cocainesmoking,cocaine alcohal,GAalcohal,GANot aggrevated by emotion,coldNot aggrevated by emotion,cold

Most common-separate ostium for Most common-separate ostium for LAD and lcx,simillarly in RCA-conus LAD and lcx,simillarly in RCA-conus branch may havebranch may have
Separate ostiumSeparate ostium
Origin of circumflex from rt coronary Origin of circumflex from rt coronary arteryartery
RCA-originate high in aortic rootRCA-originate high in aortic root

“ “DominanceDominance”” A misnomerA misnomer giving rise to PDA, at least 1 PLV & giving rise to PDA, at least 1 PLV &
AV nodal AAV nodal A (BARI classification)(BARI classification)
- 85% right dominant - 85% right dominant - 8% left dominant8% left dominant- 7% co-dominant7% co-dominant(70%/ 10%/ 20% – Hurst’s THE HEART)(70%/ 10%/ 20% – Hurst’s THE HEART)
Left dominance is 25-30% in Bi-AoVLeft dominance is 25-30% in Bi-AoV
Gensini GG. Coronary Arteriography. Mount Kisco,NY: Futura Publishing Co; 1975:260–274.

Venous Drainage of Venous Drainage of HeartHeart
Coronary Sinus: Runs in the coronary sulcus (posterior atrioventricular groove).Largest vein of heartAbout 3 cm longEnds by opening into post wall of rt atriumTributaries:
Great cardiac vein Middle cardiac vein

Small cardiac vein Small cardiac vein
Post vein of lt ventriclePost vein of lt ventricle Oblique vein of lt atrium Oblique vein of lt atrium Rt marginal veinRt marginal vein
All drains into coronary sinus which opens All drains into coronary sinus which opens into rt atrium into rt atrium

1.1. Great cardiac vein-accompany ant Great cardiac vein-accompany ant interventricular artery and then interventricular artery and then LCALCA
2.2. Middle cardiac vein –accompany post Middle cardiac vein –accompany post interventricular artery and joins middle interventricular artery and joins middle part of coronary sinuspart of coronary sinus
3.3. Small cardiac vein-accompany rt Small cardiac vein-accompany rt coronary arterycoronary artery
4.4. Post vein of lt ventricle-runs on Post vein of lt ventricle-runs on diaphragmatic diaphragmatic

Surrface of lt ventricle and ends in Surrface of lt ventricle and ends in middle of coronary sinusmiddle of coronary sinus
5 oblique vein of lt atrium-small vein 5 oblique vein of lt atrium-small vein running on post surface of lt atriumrunning on post surface of lt atrium
6 rt marginal vein-accompany 6 rt marginal vein-accompany marginal branch of rt coronary marginal branch of rt coronary arteryartery

Contents of Heart Contents of Heart groovesgrooves
1. Right atrioventricular groove: Right coronary artery Small cardiac vein2. Left anterior atrioventricular groove: Left coronary artery 3. Left posterior atrioventricular groove: Coronary sinus4. Anterior interventricular groove: Anterior interventricular artery Great cardiac vein5. Posterior interventricular groove: Posterior interventricular artery Middle cardiac vein

Venous drainageVenous drainage
Ant cardiac vein and venae cordis minimiAnt cardiac vein and venae cordis minimi opens directly into rt atriumopens directly into rt atrium Ant cardiac vein Ant cardiac vein 3-4 small vein running parrelel to one 3-4 small vein running parrelel to one
another on ant wall of rt ventricleanother on ant wall of rt ventricle venae cordis minimi-Thebesian vein or venae cordis minimi-Thebesian vein or
smallest cardiac vein smallest cardiac vein Small vein present in all chambers of heartSmall vein present in all chambers of heart

Cardiac Veins (Sternocostal Cardiac Veins (Sternocostal Surface)Surface)
Anterior cardiac veins

Cardiac Veins (Diaphragmatic Cardiac Veins (Diaphragmatic Surface)Surface)

Conducting SystemConducting System
Network of specialized tissue that stimulates contraction
Modified cardiac myocytes
The heart can contract without any innervation

TheThe CardiacCardiac ConductionConduction SystemSystem The impulse conduction system of the heart consists of four structures:
1. The sinoatrial node (SA node)
2. The atrioventricular node (AV node)
3. The atrioventricular bundle (AV bundle)
4. The Purkinje fibers
The cardiac muscle fibers that compose these structures are specialized for impulse
conduction,rather than the normal specialization of muscle fibers for contraction.

The sinoatrial nodeThe sinoatrial node
”. SA node-located at junction of sup vena cava and rt atrium SA node-discharge mostrapidly,depolarisationSpread from it to other region before they discharge spontaneouslyIts rate of dischage determine rate at which heart beat
This is also why the SA node is said to be the “pacemaker” of the heart

Spread of cardiac exitationSpread of cardiac exitation
Atrial activationAtrial activation Septal activationSeptal activation Activation of anteroseptal region Activation of anteroseptal region Activation of major portion of Activation of major portion of
ventricular myocardiumventricular myocardium Activation of posterobasal portion of Activation of posterobasal portion of
lt ventriclelt ventricle

When both the right and left atria are completely depolarized, they contract simultaneously.
Impulses from the SA node are then conducted across the atria from right to left. The impulse does not however pass directly to the ventricles.

As the atria depolarize, the impulse is picked up by another group of specialized muscle fibers called the atrioventricular node. The AV node is located in the floor of the right atrium next to the interatrial septum. This group of fibers is the only conduction pathway between the atria and ventricles.
As the impulse is conducted through the AV node, its speed is reduced. This is due to the extremely small diameter of the conducting fibers.

This is an extremely important phenomenon because the delay in the transmission from atria to ventricles allows time for the atria to completely depolarize and contract, thus emptying their contents into the still fully relaxed ventricles.

From the AV node, the impulse travels down the atrioventricular bundle. The AV bundle divides into two lines of transmission just below the AV node and these conduct the impulse down the length of the interventricular septum. An important fact about the fibers that make up the AV bundle is that they are large in diameter and therefore the impulse speed increases so it is conducted very rapidly down them.

About halfway down the interventricular septum the “bundle branches” themselves begin to branch off into enlarged conduction fibers called Purkinje fibers. These fibers extend out to all areas of the two ventricles and since they are further enlarged, the speed of the impulse conduction is also additionally increased. Upon completion of impulse transmission through the Purkinje fibers, the ventricles will fully depolarize and then contract simultaneously.

What causes what ?What causes what ?
Conduction problem in Conduction problem in AV NODEAV NODE & & HIS HIS BUNDLE- BUNDLE- 11stst, 2, 2ndnd & 3 & 3rdrd degree heart blocksdegree heart blocks
Conduction problems in Conduction problems in leftleft & & right bundle right bundle branches- branches- RBBBRBBB
LBBBLBBB LAHBLAHB LPHBLPHB Bi & Tri –Bi & Tri – fascicular fascicular
blockblock

Ventricular Conduction Ventricular Conduction Disorders.Disorders.
Left Bundle Branch Block.Left Bundle Branch Block.
Right Bundle Branch Block.Right Bundle Branch Block.
Other related blocks.Other related blocks.

Left Bundle Branch Block.Left Bundle Branch Block.
Block of the left Block of the left bundle or both fasicles bundle or both fasicles of the left bundle.of the left bundle.
Electrical potential Electrical potential must travel down RBB.must travel down RBB.
De-polarisation from De-polarisation from right to left via cell right to left via cell transmission.transmission.
Cell transmission Cell transmission longer due to LV mass.longer due to LV mass.

Left Bundle Branch Block Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB).(LBBB).

ECG Criteria for LBBB.ECG Criteria for LBBB.
QRS Duration >0.12secs.QRS Duration >0.12secs. Broad, mono-morphic R wave leads I Broad, mono-morphic R wave leads I
and V6.and V6. Broad mono-morphic S waves in V1 Broad mono-morphic S waves in V1
(can also have small 'r' wave).(can also have small 'r' wave).

LBBB consequence.LBBB consequence.
Mostly abnormal ECG finding - indicates Mostly abnormal ECG finding - indicates heart disease.heart disease. Coronary artery disease (indication for Coronary artery disease (indication for
thrombolysis - if associated with chest pain thrombolysis - if associated with chest pain and raised Troponin).and raised Troponin).
Valvular heart disease.Valvular heart disease. Hypertension.Hypertension. Cardiomegaly.Cardiomegaly. Heart failure.Heart failure. Impacts on prognosis - QRS duration.Impacts on prognosis - QRS duration. Use of Bi-Ventricular Pacemakers.Use of Bi-Ventricular Pacemakers.

Right Bundle Branch Block.Right Bundle Branch Block.
Impulse transmitted Impulse transmitted normally by left normally by left bundle.bundle.
Blocked right bundle Blocked right bundle results in cell results in cell depolarisation to depolarisation to spread impulse spread impulse (slower).(slower).
Impulse to IV septum Impulse to IV septum and RV delayed.and RV delayed.
Results in an additional Results in an additional vector.vector.

Right Bundle Branch Block Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB).(RBBB).

Additional Info RBBB.Additional Info RBBB.
Can be normal.Can be normal. Sometimes related to asthma or other Sometimes related to asthma or other
airway conditions.airway conditions. Possibly due to RVH in young individuals.Possibly due to RVH in young individuals. Usually due to CAD in older persons.Usually due to CAD in older persons. Often related to congenital heart disease Often related to congenital heart disease
(particularly ASD).(particularly ASD). Often apparent following cardiac surgery.Often apparent following cardiac surgery.

Left Anterior Hemi-block Left Anterior Hemi-block Appearance.Appearance.

ECG Features of Left Anterior ECG Features of Left Anterior Hemi-block.Hemi-block.
Abnormal left axis deviation (between Abnormal left axis deviation (between -30 and -90-30 and -9000).).
Either a qR complex or an R wave in Either a qR complex or an R wave in lead I.lead I.
rS complex in lead III (possibly also II rS complex in lead III (possibly also II and aVF).and aVF).
Extremely common and un-diagnosed Extremely common and un-diagnosed ECG feature.ECG feature.
NOT NOT ALWAYSALWAYS ASSOCIATED WITH BBB. ASSOCIATED WITH BBB.

ECG Features Left Posterior ECG Features Left Posterior Hemi-block.Hemi-block.
Axis of 90 - 180Axis of 90 - 180oo - (right axis). - (right axis). An s wave in lead I and a q wave in lead III.An s wave in lead I and a q wave in lead III. Exclusion of RAE or RVH.Exclusion of RAE or RVH.
REMEMBER - most common cause of right REMEMBER - most common cause of right axis is RVH so this must be excluded axis is RVH so this must be excluded before you diagnose LPH.before you diagnose LPH.

Left Posterior Hemi-block.Left Posterior Hemi-block.

INTRODUCTION TO HEART INTRODUCTION TO HEART BLOCKSBLOCKS
OCCUR WHEN THERE IS A PARTIAL OCCUR WHEN THERE IS A PARTIAL OR COMPLETE INTERRUPTION IN THE OR COMPLETE INTERRUPTION IN THE CARDIAC ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION CARDIAC ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION SYSTEM.SYSTEM.
CAN OCCUR ANYWHERE IN THE CAN OCCUR ANYWHERE IN THE ATRIA BETWEEN THE SA NODE AND ATRIA BETWEEN THE SA NODE AND THE AV JUNCTION.THE AV JUNCTION.
IN THE VENTRICLES BETWEEN THE IN THE VENTRICLES BETWEEN THE AV JUNCTION AND PURKINJE FIBERS.AV JUNCTION AND PURKINJE FIBERS.
For more medical presentations - www.pmcosa.com

FIRST-DEGREE HEART FIRST-DEGREE HEART BLOCKBLOCK
DELAY OF IMPULSE BETWEEN THE DELAY OF IMPULSE BETWEEN THE ATRIA AND BUNDLE OF HIS.ATRIA AND BUNDLE OF HIS.
OCCURS WHEN THERE IS A PARTIAL OCCURS WHEN THERE IS A PARTIAL INTERRUPTION ANYWHERE IN THE INTERRUPTION ANYWHERE IN THE ATRIAL OR AV JUNCTIONAL ATRIAL OR AV JUNCTIONAL CONDUCTION SYSTEM.CONDUCTION SYSTEM.
THE IMPULSE IS EVENTUALLY THE IMPULSE IS EVENTUALLY CONDUCTED BUT IS DELAYED.CONDUCTED BUT IS DELAYED.
For more medical presentations - www.pmcosa.com

degree heart blockdegree heart block
Just Just prolongation of prolongation of PR interval.PR interval.
Normal PR Normal PR 11stst
= .2 Sec= .2 Sec Here it is .28 Here it is .28
SecSec

MOBITZ I HEART BLOCKMOBITZ I HEART BLOCK MOBITZ I ( WENCKEBACH OR SECOND-MOBITZ I ( WENCKEBACH OR SECOND-
DEGREE HEART BLOCK, TYPE I).DEGREE HEART BLOCK, TYPE I). PROGRESSIVE BLOCK.PROGRESSIVE BLOCK. IMPULSE FROM THE ATRIA IS INTERRUPTED IMPULSE FROM THE ATRIA IS INTERRUPTED
AT THE AV JUNCTION.AT THE AV JUNCTION. THE INTERRUPTION BECOMES LONGER WITH THE INTERRUPTION BECOMES LONGER WITH
EACH IMPULSE DELAYING DEPOLARIZATION EACH IMPULSE DELAYING DEPOLARIZATION OF THE VENTRICLES UNTIL A COMPLETE OF THE VENTRICLES UNTIL A COMPLETE INTERRUPTION BLOCKS THE IMPULSE.INTERRUPTION BLOCKS THE IMPULSE.
For more medical presentations - www.pmcosa.com

For more medical presentations - www.pmcosa.com

MOBITZ II HEART MOBITZ II HEART BLOCKBLOCK
OCCURS DUE TO AN INTERMITTENT OCCURS DUE TO AN INTERMITTENT INTERRUPTION NEAR OR BELOW THE AV INTERRUPTION NEAR OR BELOW THE AV JUNCTION.JUNCTION.
INTERRUPTION IS NOT PROGRESSIVE, INTERRUPTION IS NOT PROGRESSIVE, BUT OCCURS SUDDENLY AND WITHOUT BUT OCCURS SUDDENLY AND WITHOUT WARNING!!WARNING!!
P WAVES BEFORE EVERY QRS COMPLEX P WAVES BEFORE EVERY QRS COMPLEX AND ALL ARE THE SAME SIZE AND AND ALL ARE THE SAME SIZE AND SHAPE.SHAPE.
For more medical presentations - www.pmcosa.com

For more medical presentations - www.pmcosa.com

THIRD-DEGREE HEART THIRD-DEGREE HEART BLOCKBLOCK
COMPLETE HEART BLOCK OR COMPLETE HEART BLOCK OR COMPLETE AV DISSOCIATION.COMPLETE AV DISSOCIATION.
IMPULSE IS COMPLETELY BLOCKED IMPULSE IS COMPLETELY BLOCKED BETWEEN THE ATRIA AND THE BETWEEN THE ATRIA AND THE VENTRICLES.VENTRICLES.
USUALLY TAKES PLACE BETWEEN THE USUALLY TAKES PLACE BETWEEN THE AV JUNCTION AND BUNDLE OF HIS.AV JUNCTION AND BUNDLE OF HIS.
For more medical presentations - www.pmcosa.com

Third degree heart block
For more medical presentations - www.pmcosa.com