Blood Flukes Life Cycle
-
Upload
pratita-ayu-pinasthika -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of Blood Flukes Life Cycle
-
7/24/2019 Blood Flukes Life Cycle
1/5
BLOOD FLUKES LIFE CYCLE
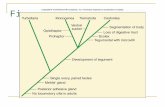
1. Mature fukes live in the blood vessels o the human intestine2. Sexual reproduction in the human; ertilized eggs exit host in eces3. ggs develop in !ater into miracidium "ciliated larvae#. Miracidium
inect snails and develop into redia$. %sexual reproduction !ithin snails results cercaria&. 'ercaria penetrate skin and blood vessels o human
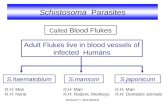
Schistosoma - Blood Flukes
Schistosomiasis "also kno!n as snail ever or bilharzia# is causedb( blood fukes rom the genus Schistosoma. More than 2))million people are inected !orld!ide. Mostl( in resh!aters!here there are man( snails !hich are the intermediate host.
*here are +ve main species inecting humans, Schistosomamansoni- S. haematobium- S. japonicumand t!o geographicall(
localized species S. intercalatumand S. mekongi.
Schistosomareuires the use o t!o hosts to complete its lifecycle. /epending on the Schistosomaspecies their eggs are shedeither in the eces or urine o an inected human. ggs cansurvive up to a !eek in dr( land. 0 the eces end up in !ater-larvae called miracidia hatch and start +nding certain species oresh!ater snails. hen the( +nd a snail the( penetrate its ootand transorm into sporoc(sts "another larval orm#. *hese
primar( sporoc(sts multipl( asexuall( into secondar( sporoc(stsand travel to the snails hepatopancreas. *he( multipl( asexuall(
-
7/24/2019 Blood Flukes Life Cycle
2/5
producing hundreds o cercariae "another larval orm#. "*heprocess rom sporoc(st to cercaria takes a e! months.# 'ercariaeexit the snail and start !aiting in the !ater. *he( can surviveabout $ hours in avourable conditions. hen the( sense
that humanskin is near- the( uickl( s!im and attach !ithsuckers. *he( +nd a suitable spot "usuall( a hair ollicle# andpenetrate the skin using special enz(mes. %s the( enter the(transorm into schistosomulae "another larval orm#. 4nl( headparts enter- the( leave tails behind. ach schistosomula sta(s ae! da(s in the skin and then enters the bloodstream throughdermal l(mphatic vessels or blood venules. *he( travel in thebloodstream to get to speci+c blood veins. 0nhumans Schistosomareaches ertilit( in 56 !eeks. *he ne!l(developed adult emales and males +nd each other and pair up.
%dult blood fukes are 162 cm long. Males make a g(naecophoricchannel or the longer and thinner emales to reside. *he !ormpair then travel to rectal or mesenteric veins. *he( attach to thevenous !all !ith oral and ventral suckers and can live or man((ears. 7emales la( eggs on the endothelial lining o the venouscapillar( !alls at the rate o 3))63))) eggs per da( depending onthe Schistosomaspecies. Some eggs are fushed b( circulatingblood ending up causing infammation in organs such as liver orlungs. Most eggs ho!ever travel to the lumen o the intestinal
tract "S. japonicumand S. mansoni# and o the ureters andbladder "S. haematobium#- thus exiting the bod( in the eces orurine. Mature eggs produce special enz(mes and can penetrateman( membranes such as rectal veins or intestinal !all. *he eggsget out o the bod( and the c(cle starts again.
-
7/24/2019 Blood Flukes Life Cycle
3/5
Schistosomaspecies can migrate around and are not bound to8ust one location. 9ut each species has a preerred location. 7orexample- S. japonicumresides more reuentl( in the veins thatdrain the small intestine. S. mansoniis ound more oten in the
veins that drain the large intestine. S. haematobiumoccursusuall( in the venous plexus o bladder- but can also be ound inthe rectal venules.
*he +rst symptomsare a rash or itch during the +rst e! da(s.ithin t!o months chills- cough- diarrhea- atigue- ever andmuscle aches can occur. :suall( ho!ever during the +rst e!!eeks schistosomiasis is as(mptomatic. *he disease is !orse orchildren !ho can develop anemia- learning diculties andmalnutrition. %ter (ears o inection eggs infame organs such as
the liver- bladder and lungs. 0 eggs end up in the brain or spinalcord- the( can cause paral(sis- seizures or infammation o thespinal cord.
Dianosis is done rom a stool or urine sample b( microscopicexamination.
-
7/24/2019 Blood Flukes Life Cycle
4/5
into reproducing adult and onl( ater that time !ill there be eggspresent.
Schistosomiasis is t!eated!ith praziuantel according to the
advice o (our health care provider. 7or inections caused b( S.mansonioxamniuine can be used in areas !here praziuantel isless e=ective.
"eo!aphic dist!i#ution
%rica, all resh!ater in sub>Saharan and southern %rica-
also in the ?ile @iver valle( in g(pt
'aribbean, %ntigua- /ominican @epublic- Auadeloupe-
Martiniue- Montserrat- Saint Bucia "lo! risk#
South %merica, 9razil- Suriname- Cenezuela
Southern 'hina
Southeast %sia, 'ambodia- central 0ndonesia- Baos- Mekong
delta and Dhilippines
*he Middle ast, 0ran- 0ra- Saudi %rabia-
-
7/24/2019 Blood Flukes Life Cycle
5/5