Biomas
description
Transcript of Biomas

BIOMES

What is a biome?
• major division of the ecological communities on Earth characterized by the plant and animal life of that region

1.- Freshwater
Water with low salt concentration

Freshwaters are
Ponds and lakes
Streams and rivers
Wetlands

Pond
lake Wetlands

2.- Marine
Overfishing and pollution are serious problems

Marine:
Oceans
Coral reef
Estuaries

ocean
Coral reef
Estuaries

Freshwater and marine are the most
importantBiomes because water
Is the basis of lifePeople must be educatedAbout the consequences
Of our actions

3.- Forests
They are important because they are home to the most diverse biotic communities in the world

Forest are in danger because of the explotation and burns

4.- Deserts
Rainfall is less than 50/cm year

Sahara Mexico
Australia
Temperatures are very hot during the day and very cold in the night.
Hot and dry

5.- Grasslands
Lands dominated by grasses

Savanna is a grassland with some Individual trees
Savannas are in warm and hot climates where the rain is concentrated in six or eight months of the year followed by a dry period.

6.- Tundra
It is the coldest of all the biomes, extremely low temperatures.

There are a wide variety of plants that are able to resist the cold climate. There are about 1,700 kinds of plants in the arctic and subarctic

Arctic tundra is located in the northern hemisphere, encircling the north pole. winter temperature is -34° CSummer temperature: 3-12°

Alpine tundra is located on mountains throughout the world at high altitude where trees cannot grow. The plants are very similar to those of the arctic ones.

7.- Taiga
The taiga is the largest biome in the world. It covers large parts of Canada, Europe, and Asia. This forest is covered with coniferous trees. In fact, sometimes the taiga is called a coniferous forest.

What is the Weather Like in the Taiga?
In the taiga, summers are warm and rainy, and the winters are very cold. There is lots of snow in the forests too.During the summer, it is usually around 21 º .In the winter it´s about 0º.

Compare the rainfall in the taiga to the other biomes

There is not much diversity in the taiga, because many plants cannot survive such hard conditions. Lichens and mosses are important, but most of the plants are evergreen trees. The trees are narrow and grow very close together. This is so they can help protect each other from the weather.

8.- Mediterranean
It is found surrounding large parts of the Mediterranean Sea. It is also called “Chaparral”

The summers are very hot and dry.The winters are relativily warm and rainy

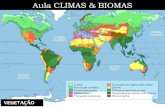
Can you indentify the biomes?














Biomes map

Marine biome map

Forests map

Deserts map

Tundra map

Grasslands map

Taiga map

Mediterranean map

If you want to learn more, visit:
http://www.longmeadow.k12.ma.us/wms/pages1/renius/biome.html
http://www.mbgnet.net/