Biology 322 Human Anatomy I Female Reproductive System.
-
Upload
joseph-poole -
Category
Documents
-
view
233 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Biology 322 Human Anatomy I Female Reproductive System.

Biology 322Human Anatomy I
Female Reproductive System

Human Reproductive System:
- Begins developing
- Remains “sexually indifferent”

7th & 8th Testes, penis, Clitoris, labia beginweeks scrotum begin development development
Male Female
Both sexes: Gonads (ovaries & testes) remain inactive until puberty, when anterior pituitary stimulates maturation

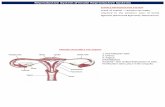
Organs of adult female reproductive system - Midsagittal

Pubic Bone

Organs of female reproductive system – Coronal from back

Broad Ligament: Parasagittal section

Ovary:
Site of oocyte development & ovulation after puberty

Ovary
Medulla
Tunica Albuginea
Cortex

Maturation of an oocyte is called oogenesis
Cell with 46 chromosomes (“2n”) divides twice, unevenly, to produce one large oocyte with 23 chromosomes (“n”) and two small polar bodies.
During oogenesis, oocyte surrounded by follicle composed of follicular cells or granulosa cells

The developing oocyte and its follicle:Four stages before ovulation
1.

The developing oocyte and its follicle:Four stages before ovulation
2.

The developing oocyte and its follicle:Four stages before ovulation
3.

The developing oocyte and its follicle:Four stages before ovulation
4.
Oocyte covered with thick, clear membrane called pushed to one side in follicle and surrounded by mass of follicular cells called

Ovulation:
Secondary oocyte, surrounded by zona pellucida and cumulus oophorus, released from surface of ovary, where it can be captured by the open end of the oviduct.
The cumulus oophorus now called the corona radiata.

After ovulation,


Oviduct:
Lateral End:
Middle Part:
Medial End:

Layers of Oviduct:

By mechanisms not completely understood:• The oviduct moves the oocyte toward the uterus• The oviduct moves sperm away from the uterus
Fertilization occurs in ampulla of oviduct, forming the zygote, which goes through repeated mitotic cell divisions (“cleavage”) to form a morula, then a blastocyst, and eventually the embryo.

Uterus:
Anterior Posterior & superior
Narrowed inferiorly

Uterus: Three Layers
: Lots of glands & blood vessels
Thick layer of smooth muscle
Visceral peritoneum over thin layer of C.T.
(external)
(internal)

Two layers
Closer to myometrium; Remains after menstruation; Regrows functional layer.
Closer to cavity; Thickens every cycle; Embryo implants here during pregnancy; Dies and falls off during menstruation

Vagina:
Thin-walled, tubularInferiorAnterior Posterior

Layers of Vagina:
Mucosa:
Muscularis:
Adventitia:

External Genitalia: