Kidney, Kidney-Pancreas, Pancreas, Islet Cell Transplant Brochure
BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
-
Upload
ismail-simsek -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
1/64
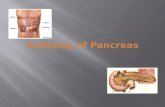
THE PANCREAS
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
2/64
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
3/64
The Pancreas in situ
Right lobe of liver
Falciform ligament
Gallbladder
Pancreas
Duodenum
L-3
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
4/64
Pancreas, Introduction, continued
D. Head fills concavity of duodenum
E. Body crosses left kidney
F. Tail reaches hilus of the spleen
G. Related anteriorly to transversecolon
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
5/64
Pancreas in situ
Duodenum
Head of Pancreas
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
6/64
Pancreas, Introduction, continued
H. Aorta, IVC lie posterior
I. Uncinate process:
a. Lies posterior to SMA and SMV
b. Lies anterior to aortaJ. Neck lies anterior to SMV, with
pylorus just above
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
7/64
Venous Drainage of the PancreasIVC
SMV
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
8/64
Introduction, continued
L. Body relatedposteriorly to left
crus, left adrenal,left renal vein, andsplenic vein
K. Celiac Axis(trunk, artery) liessuperior to body
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
9/64
II. Detailed Anatomy
A. Landmark structures
1. Splenic Artery:
a. Branch of celiactrunk
b. passes right toleft
c. Course is alongupper margin ofbody and tail
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
10/64
Detailed Anatomy, cont
2. Hepatic Artery:a. Branch of celiac trunk
b. courses left to rightc. along upper margin of neck and
head
3. Superior Mesenteric Artery: at itsorigin from aorta, points at body of
pancreas
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
11/64
Arterial Supply to Pancreas
Common HepaticArtery
Proper HepaticArtery
SuperiorMesenteric Artery
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
12/64
Landmark structures, continued
4. Splenic Vein:a. runs parallel
to arteryb. on posterior
surface ofpancreas
c. Terminates inportal vein
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
13/64
Landmark structures, continued
5. Superior & InferiorMesenteric Veins:
a. pass (inferior tosuperior) deepto pancreas
b. merge with splenicvein
c. Terminate in portalvein
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
14/64
Landmark structures, continued
6. Common Bile Duct:a. passes behind first portion of
duodenumb. then through head of pancreas
c. Terminates at ampulla of vater
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
15/64
Detailed Anatomy continued
B. Head of Pancreas
1. Important clinically because:a. Numerous ducts and vessels traverse it
b. Carcinoma usually located here
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
16/64
Head of Pancreas, Detailed Anatomy, continued
2. Tumor will compress surrounding
structuresa. First indication may be jaundiceb. Tumor may compress
duodenumc. May involve local vessels
*Metastases may spread through these vessels*
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
17/64
Head of Pancreas, Detailed Anatomy, continued
3. Lymphatics from head of pancreas
a. Drain to celiac nodesb. metastases may follow lymph
c. Metastases may spread vialesser omentum to liver
d. Some terminate in lumbar nodes
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
18/64
Head of Pancreas, Detailed Anatomy, continued
4. Vessels supplying head of pancreasa. Superior & inferiorpancreaticoduodenal arteries
b. Both divide into two parallelvessels
c. one anterior and one posterior tohead
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
19/64
Head of Pancreas, Detailed Anatomy, continued
1. Anterior branch ofpancreaticoduodenal
arterya. superior branch:
anterior superiorpancreaticoduodenalartery
b. inferior branch:anterior inferior
pancreaticoduodenalartery
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
20/64
Head of Pancreas, Detailed Anatomy, continued
2. Posterior branch ofpancreaticoduodenal
arterya. superior branch:
posterior superiorpancreaticoduodenal artery
b. inferior branch:posterior inferior
pancreaticoduodenal artery
**extensive blood supply**
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
21/64
Anterior Pancreaticoduodenal Artery
Branches arecontinuous withone another
Superiorbranchesoriginate from theGDA
Inferior branchesoriginate from theSMA
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
22/64
Detailed Anatomy, continued
C. Body & Tail of Pancreas:
1. Supplied by splenic artery2. Have three surfaces:
a. Anterior surface
1. Concave2. Deep to stomach3. Separated from stomach by
lesser sac of peritoneum
(aka omental bursa)
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
23/64
Anterior surface of pancreas
Anterior surfaceof pancreas
Epiploicforamen
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
24/64
Lesser sac, continued
4. Lesser sac bounded by:
a. Liver, superiorlyb. Below, extends to
greater omentumc. Anteriorly: lesser
omentum, stomach,greater omentum
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
25/64
Lesser sac, continued
d. Posteriorly: greateromentum
transverse colon,transverse mesocolon
e. Laterally:
1. Foramen of Winslow onright
2. Spleen on left
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
26/64
Detailed Anatomy, continued
f. Foramen of Winslow (AKA: Epiploic
Foramen):
1. Lies between greater & lesser
sacs of peritoneum
2. posterior to free edge oflesser omentum
3. close to porta hepatis
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
27/64
Three Surfaces, continued
2. Posterior surface: separated from vertebrae by
a. Aorta
b. Splenic veinc. Left kidney and renal vesselsd. Left adrenal glande. Left Crus of diaphragmf. SMA and SMV
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
28/64
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
29/64
Detailed Anatomy, continued
D. Pancreatic Duct System
1. Pancreatic Duct (of Wirsung)a. Course is left to rightb. Receives numerous small ducts
c. @ neck of pancreas, duct turnsinferior, posterior & to the rightd. AKAmain pancreatic duct
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
30/64
Duct of Wirsung (Main pancreatic duct)
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
31/64
Pancreatic Duct System, continued
d. joins CBD at Ampulla of Vater
3 - 4 below pyloruse. results from fusion of ducts during
fetal development
1. One from ventral pancreas2. One from dorsal pancreas
(see Netters Embryology, p. 142, for Pancreasdevelopment)
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
32/64
Duct of Wirsung
Duct ofWirsung
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
33/64
Pancreatic Duct System, continued
2. Duct of Santorini:a. accessory pancreatic duct
b. Not universally identified
c. joins duodenum @ minor papilla
d. part of duct from dorsal pancreas
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
34/64
Duct of Santorini
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
35/64
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
36/64
III. Scanning AnatomyA. Depends on recognition of pancreatic
margins
B. Sonography best used as screeningprocedure
1. May be interference from bowelgas (especially in tail region)
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
37/64
Scanning Anatomy, continued
2. Extremely accurate in detectionof pseudocysts
3. U/S can show texture of organ
4. By ID-ing vessels, can delineate
head, portions of body
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
38/64
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
39/64
Scanning Anatomy, continued
C. Head:1. SMV outlines medial head to neck
region2. Duodenum & GB outline lateral
head
3. Superiorly, delineated bygastroduodenal artery (GDA)
4. Inferiorly, bounded by CBD
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
40/64
Scanning Anatomy, continued
D. Further delineation by vascularlandmarks:
1. SMA:
a. Lies immediately posterior to
body, points to it!b. Recognized by echogenic fat
collar surrounding vessel
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
41/64
Vascular Landmarks of the Pancreas
Pancreaticsonography
depends largelyon identifyingsurroundinglandmark vessels
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
42/64
Scanning Anatomy, continued
2. SMV:a. Delineates medial headb. Larger diameter than SMAc. Lies to right of SMAd. Uncinate process wraps it (and
SMA), lies posterior & medial
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
43/64
Vascular Landmarks of the Pancreas
Venouslandmarks of the
pancreasinclude the SMVand renal veins
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
44/64
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
45/64
Scanning Anatomy, continued
E. Tail of Pancreas
1. May be visualized through fluid-filledstomach
2. Tail seen as 2-3 cm roundedmass anterior to hilus of left kidney
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
46/64
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
47/64
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
48/64
Pancreatitis, Pancreatic Disorders, continued
5. Important factor is release of proteinkinins
a. Increase permeability of vessels& cells
b. Releases tissue fluidc. Edema may compress vesselsd. Tissue damage occurs
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
49/64
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
50/64
Pancreatic Disorders, continued
B. Pseudocysts:
1. False cysts that may arisea. due to tissue necrosis
b. From enzymatic destruction
2. May persist after inflammation subsides
3. Usually near or in pancreas
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
51/64
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
52/64
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
53/64
Pancreatic Diseases, continued
D. Chronic Pancreatitis
1. organ usually appears as small,atrophic
2. Contains scattered echoes fromcalcifications
3. Primary cause is alcoholism
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
54/64
Pancreatic Diseases, continued
E. Dilation of Pancreatic Duct
1. Seen in acute or chronicpancreatitis
2. Frequently associated withneoplasm of pancreas
3. Biliary tract problems
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
55/64
Pancreatic Diseases, continued
F. Abscess or Hemorrhagic Pancreatitis
1. Similar in sonographic appearance2. Hemorrhagic:a. Mass with inhomogeneous texture
b. Acute hemorrhage: sonolucent to
echogenicc. CT scan used for differentiation
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
56/64
Pancreatic Disorders, continued
G. Pancreatic Tumors
1. Malignant tumors usually ariseas adenocarcinomas
2. In head of Pancreas: Sx
a. Painless jaundiceb. Anorexia
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
57/64
Pancreatic Tumors, In head, continued
c. Nausea
d. Weight losse. Increased plasma amylase
f. Increased alkaline phosphatase
g. May involve compression ofpancreatic duct, CBD
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
58/64
Pancreatic Tumors in the Head
Tumors in the headmay compressbiliary ducts orpancreatic ducts
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
59/64
Pancreatic tumors, continued
3. In Body of Pancreas: Sxa. Gnawing pain radiating to back
b. Pain increases after eating orlying down
c. Weight loss, anorexia
d. Large tumor may compress IVC,portal vein
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
60/64
Pancreatic tumors, continued
4. In Tail ofPancreas: Sx
a. Often silent until localmetastasis occurs
b. May metastasize to:1. para-aortic lymph
nodes2. spleen
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
61/64
Pancreatic tumors, continued
5. Identified by organ enlargement,
subtle echo changes, irregular outline
6. Metastases to stomach, liver & lungsare common
7. Often causes dilation of ducts
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
62/64
Pancreatic Disorders, continued
H. Fibrocystic Disease1. Result of cystic fibrosis
2. Diagnosed by methods other than
ultrasound
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
63/64
Pancreatic Disorders, continued
I. Pancreaticolithiasis
1. Characteristic stone echoes in pancreatic duct
2. May see atrophied pancreatic parenchyma
3. Associated with chronic alcoholic pancreatitis
4. Contours of body, tail show irregularities
-
7/31/2019 BIOL226Lec07_ the Pancreas
64/64
Pancreatolithiasis, continued
5. Incidence slightly higher in head
6. Associated with occult pancreaticcarcinoma
a. Mass < 2mm diameter
b. Seen with dilation of pancreaticduct or CBD