BIO 391- The Excretory System The Structure and Function of the Kidney.
-
Upload
allan-mckenzie -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
0
description
Transcript of BIO 391- The Excretory System The Structure and Function of the Kidney.

BIO 391- The Excretory System
The Structure and Function of the Kidney

Function of kidney: Filter blood, reabsorb materials & form
urine

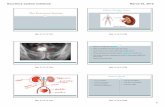
Cross section of the kidney
• Over 1 million nephrons in each kidney
• Nephrons span both the cortex and medulla
• Renal pelvis: collects urine, passes it to ureter
• Renal artery: brings blood to kidney
• Renal vein: transports purified blood back to heart

Structure of the nephron

Functional Regions

Homeostasis by the Kidney
• Maintain volume of extracellular fluid • Maintain ionic balance in extracellular fluid• Maintain pH and osmotic concentration of the
extracellular fluid. • Excrete toxic metabolic by-products such as urea,
ammonia, and uric acid.

Steps of urine formation• Glomerular filtration:
o removes solutes from bloodo 1st step in urine formation
• Tubular reabsorption: o almost all nutrients are reabsorbed by passive or active
transporto 2nd step in urine formation
• Tubular secretion:o Solutes and waste are secreted into the tubules and
collecting ducto Last step in urine formation

Production of Urine

What is urine made of?• 96% water• 2% urea• 2% other substances• e.g.: ammonia, sodium, potassium, chloride, sulphates,
phosphates, excess vitamins, drugs
• Normal urine is acidic, but it depends on diet and other factors