Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
-
Upload
nityaprasanta4679 -
Category
Documents
-
view
235 -
download
0
Transcript of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
1/25
Benign
Prostatic HyperplasiaDR.Gehan Mohamed
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
2/25
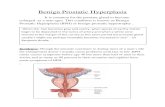
Normal Prostate Anatomy
Prostate weights ~20g
Measures ~3 by 4 by 2 cm
Apex = inferior portion of prostate, continuous with striatedsphincter. Base = superior portion and continuous with bladderneck.
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
3/25
PROSTATE histology
Prostatic tissue is formed of two
components :
fibromuscular tissue (30%)
glandular epithelial cells (70%)
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
4/25
Normal histology of prostate:
formed of glands and
fibromuscular stroma
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
5/25
Normal histology of the prostate formed ofglands and stroma
glands: lined by two layers of cells which are inner cuboidal cells
and outer basal cells
stroma :fibro muscular stroma
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
6/25
Prostate zones
Central zone (CZ) Cone shaped region that surround the ejaculatory ducts (extends from
bladder base to the verumontanum)
Only 1-5% of prostate cancer from this region .
Peripheral zone (PZ)
Posteriolateral prostate
Majority of prostatic glandular tissue
Origin of up to 70% of prostate adenocarcinoma
Transitional zone (TZ)
Surrounds the prostatic urethra
Commonest site for benign prostatic hyperplasia.
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
7/25
http://www.marinurology.com/ -
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
8/25
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
9/25
What causes BPH?
BPH is part of the natural
aging process, like getting
gray hair or wearing glasses
BPH cannot be prevented
BPH can be treated
n
n
n
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
10/25
Half of all men over the age of 60 willdevelop an enlarged prostate.
By the time men reach their 70s and 80s,80% will experience urinary symptoms
But only 25% of men aged 80 will bereceiving BPH treatment
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
11/25
BPH
Proposed Etiologies
1-alterations in the testosterone/estrogenbalance:enlarged prostate may be caused by lower levels oftestosterone (male hormone) production in middle to old age. As
men age, the levels of testosterone in their blood decreases,
leaving a higher proportion of estrogen (female hormone), so a
higher amount of estrogen within the prostate gland can
increase activity that promotes cell growth.
2-Induction of prostatic growth factors.
3- Increased stem cells/decreased stromal cell death
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
12/25
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
13/25
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
14/25
Whats Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms secondary to
prostatic urethra obstruction?
Abnormal Voiding
(obstructive)symptoms
Hesitancy
Weak stream
Straining to pass urine Prolonged micturition
Feeling of incomplete
bladder emptying
Urinary retention
Storage (irritative or
filling) symptoms Urgency:an increasingly
strong desire to void)
Frequency
Nocturia Urge incontinence
LUTS is not specific to BPH not everyone with
LUTS has BPH and not everyone with BPH has LUTS
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
15/25
BPHSigns and Symptoms
Initial signs
Obstruction of urine flow
Hesitancy : delay between trying to urinate and the flow
actually beginning.
dribbling
decreased force of urine stream
Incomplete bladder emptying
Frequency,
nocturia : need to urinate at night
recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
16/25
BPH
complications hypertrophy of the prostatedetrussor muscle of the
bladder undergo hypertrophy to overcome the obstruction
in the prostatic urethra. Later on decompensation occur .
Increase pressure inside bladderdiverticula
formation
increasing urine retention
hydronephrosisrenal failure.
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
17/25
Diverticula in bladder
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
18/25
Di i f BPH
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
19/25
Diagnosis of BPH Symptom assessment
Digital rectal examination(DRE) inaccurate for size but can detect shape and consistency Prostate Volume (PV) determination by ultrasonography
Urodynamic analysis
Measurement of prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
high correlation between PSA and PV,
men with larger prostates have higher PSA levels
PSA is a predictor of disease progression and screening tool for Cancer Prostate.
as PSA values tend to increase with increasing Prostatic Volume and increasing
age, PSA may be used as a prognostic marker for BPH.
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
20/25
BPH : show marked hyperplasia in the number of prostatic glands
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
21/25
When should BPH be treated?
BPH needs to be treated ONLy IF:
Symptoms are severe enough to botherthe patient and affect his quality of life
Complications related to BPHn
n
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
22/25
Medication : blockers - relax the smooth muscle of prostate
and provide a larger urethral opening
Surgical approaches
1- Transurethral resection of theprostate (TURP)
2- Open simple prostatectomy
Treatment options
n
n
n
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
23/25
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
24/25
Differential Diagnosis
of BPH(i.e from other causes of urinary
obstruction) Urethral stricture
Bladder neck contracture
Carcinoma of the prostate
Carcinoma of the bladder
Bladder calculi
Urinary tract infection and prostatitis
Neurogenic bladder
-
7/27/2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Ggb
25/25