Benchmark 2 Recap Units 3-4 typical plant cell is larger than a typical animal cell, but still has...
Transcript of Benchmark 2 Recap Units 3-4 typical plant cell is larger than a typical animal cell, but still has...

Benchmark 2 Recap Units 3-4
Unit 3: Cells
Part 1 Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: There are 2 main types of cells and they are very different. Prokaryotes are cells that are very small and simple, and include all bacteria. Prokaryotes are very ancient. Eukaryotes are much more complex, with a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. Eukaryotes are the cells of protists, fungi, plants and animals, including humans.
Prokaryote Eukaryote
No nucleus Nucleus
No membrane- bound organelles
Membrane-bound Organelles
Unicellular Uni and multicellular
Very small Larger
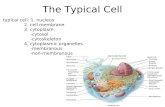
Part 2 Structure of Cells: Different cell types may look different but they all contain the same organelles, or specialized parts. A typical animal cell has the following features.
Since prokaryotes and eukaryotes are both cells they do share some similarities. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have ribosomes, cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material.
Nucleus- The nucleus contains chromosomes, this is the DNA information of the cell. The nucleus is surrounded by a Nuclear membrane or envelope with nuclear pores for the transport of molecules. The membrane is selectively permeable only letting certain substances in or out. Nucleolus- In the cell’s nucleus is the nucleolus, a concentration of DNA where ribosomes are produced. Ribosomes- The ribosomes are where protein synthesis occurs in the cell. Ribosomes are responsible for making protein. Cytoplasm-The cytoplasm is made of a gelatin fluid or cytosol outside the nucleus of the cell---cell goo! Endoplasmic Reticulum-There are 2 types of ER. Rough ER has ribosomes, is the site of protein synthesis. Smooth ER, with no ribosomes, has several functions, including the making of lipids and hormones. Golgi Apparatus- The golgi bodies package proteins and lipids in vesicles and ship throughout the cell like a post office. Vacuoles- Membrane sacs that are used for storing substances for the cell. Vesicles are smaller vacuoles. Lysosomes- Their function in the cell is to break down food, debris, invading bacteria. The clean-up crew! Mitochondria- Cellular respiration, in which energy in the form of ATP is produced from carbohydrates, is carried out in the mitochondria. Cytoskeleton- Cell skeleton used to support the cell. Flagella and Cilia- These are structures that extend from the cell membrane. Flagella are long and few; cilia are short and numerous.
A typical plant cell is larger than a typical animal cell, but still has the same structures. It also has unique parts. A plant cell has the following structures that animal cells lack: -Rigid cell wall made of cellulose -Chloroplasts where photosynthesis is carried out -A large central vacuole used for water storage

Part 3 The Plasma Membrane The cell membrane protects a cell from its immediate environment. It is also selectively permeable, meaning that it allows some substances to pass through but not others. The plasma membrane consists mainly of a phospholipid bilayer with proteins embedded in the layers. The phospholipid bi-layer is made of two layers of phospholipids that have a hydrophilic head (water-loving) and hydrophobic tails (water fearing). The heads face the outside environment and the inside of the cell while the tails face each other protected from water.
Part 4 Cellular Transport: The movement of substances into and out of a cell is called cellular transport. There is active transport and passive transport. Active transport requires energy (usually ATP), while passive transport does not. Two main types of passive transport are diffusion and osmosis. -Diffusion is the movement of substances from an area of high to low concentration. (also known as moving down the concentration gradient). The substances transported are small, uncharged molecules such as carbon dioxide and oxygen. In diffusion, the molecules move directly across the lipid bilayer until equilibrium is reached. Facilitated diffusion is the movement of charged molecules and larger molecules into and out of the cell. Like simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion moves substances from areas of high to low concentration without the use of ATP. Unlike diffusion however, the substance moves with the aid of carrier proteins or through a channel protein.
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across the selectively permeable cell membrane. The molecules move from a high to low concentration. A hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes (dissolved substances--sugar) and more water. A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solutes (dissolved substances—sugar) and less water. When water flows into a cell it causes the cell to swell or become turgid. Animal cells will burst but plant cells have a cell wall creating turgor pressure. This helps to keep plants standing up right and celery crisp. A solution that has equal concentrations of solutes is called isotonic.

Active transport involves the movement of molecules against a concentration gradient from Low to High. This movement requires the cell to use energy, usually ATP. The sodium –potassium pump is a type of carrier protein called a cell membrane pump. This pump uses energy to move substances (in this case sodium (Na) and potassium (K)) from low to high concentration. In animal cells, the sodium potassium pump is important in maintaining a charge across the cell membrane.
Part 5
Cell Energy:
Photosynthesis: is the process by which energy in sunlight is converted into energy in the form of glucose. In eukaryotes, photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts. In prokaryotes, it occurs in the plasma membrane and cytoplasm. The overall equation for photosynthesis is: 6CO2 + 6H2O + Light Energy C6H12O6 (Glucose) + 6O2
(Reactants) (Products) The absorption and conversion of light energy to ATP and NADPH (electron carrier) are called the light reactions because they require light. The use of ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 to sugars is called the light-independent reactions because light is not required. The pigment that allows for the absorption of light is called chlorophyll. Certain environmental factors affect the rate of photosynthesis. The intensity of light increases photosynthesis as well as the amount of carbon dioxide in the air. Temperature will also increase the rate of photosynthesis but will decline at extremely high temperatures.
Cellular Respiration: is the process by which cells break down glucose to extract energy and transfer that energy to molecules of ATP for cells to use. The chemical equation for aerobic cellular respiration is: C6H12O6 (Glucose) + 6O26CO2 +6H2O + energy (ATP)
The equation for cellular respiration is the reverse of photosynthesis. Cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria of the cell. Cellular respiration can use an anaerobic pathway (fermentation) that does not require oxygen, or an aerobic pathway that does require oxygen. In aerobic cellular respiration, the reactants are glucose and oxygen and the products are carbon dioxide, water and energy in the form of ATP. Anaerobic respiration is also called fermentation. It is the process by which cells convert pyruvic acid from glycolysis (first step of cellular respiration) into ethyl alcohol or lactic acid.
Alcoholic fermentation includes glycolysis plus additional reactions that produce NAD+, ethanol and CO2. Single celled organisms, such as year and some plant cells have special enzymes to carry out this process. Yeast is used in bread making because CO2 gas causes the bread to rise. The ethanol is removed by baking. Yeast is also used in making beer because it produces ethanol alcohol. CO2 in an enclosed container makes carbonation.
Lactic acid fermentation: certain fungi, bacteria, and muscle cells have special enzymes that carry out lactic acid fermentation. In the manufacture of dairy products, such as cheese and yogurt, lactic acid adds tart flavors to the final product. In muscle cells during heavy exercise, lactic acid fermentation provides ATP when the circulatory system cannot keep up with the demand for oxygen by the muscle cells. This build-up of lactic acid causes your muscles to ache.
Vesicular transport is a form of active transport that uses vesicles or other organs in the cytoplasm to move large molecules and food particles across the cell membrane using energy. The two main types are: 1. Exocytosis is the process where vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents to the outside of the cell---cell pooping 2. Endocytosis—is basically the opposite of exocytosis. Substances outside the cell are captured by an in-folding cell membrane and brought into the cell. In pinocytosis, or cell drinking, dissolved substances enter the cell as a liquid. In phagocytosis, or cellular eating, un-dissolved or solid substances enter the cell.

Comparing Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Item compared Cellular respiration Photosynthesis
Main purpose Break down carbon compounds to make ATP Use light energy to make glucose
Organisms Almost all organisms including plants Some bacteria, protists and plants
Organelle Mitochondria Chloroplasts
Initial energy source Glucose Light
Gas used Oxygen CO2
Gas released CO2 Oxygen
Part 6
Cellular Reproduction:
Mitosis: Asexual reproduction is when offspring are produced from a single parent. In cell division, a single cell divides to become two cells. Each offspring cell is identical to the parent. Simple organisms such as bacteria reproduce using cell division. Multicellular organisms use cell division to grow or replace tissues. The process of cell division in eukaryotes is called the cell cycle. It is divided into 5 main phases but is a continuous process. The first 3 phases of the cell cycle are part of interphase. This is the activity in between actual cell division. Cells spend most of their time in interphase. G1 Phase: The new cell grows to mature size S Phase: If the cell is going to divide again, it copies its chromosomes (DNA) during this phase through DNA replication. G2 Phase: Once the DNA is replicated, the cell enters G2, during which it prepares for cell division by completing its checklist to make sure everything is copied correctly. The last two phases of the cell cycle are part of cell division. This will result in the production of two nearly identical cells. The cell that divides is a diploid cell, which contains 2 complete sets (2n) of chromosomes. Mitosis: This is the division of the nucleus, which leads to the splitting of chromosomes (DNA) which was copied during the S phase. Body cells reproduce using mitosis producing 2 identical diploid cells. In humans, a body cell contains 46 chromosomes. Mitosis contains 4 stages followed by cytokinesis (cell splitting)
1. Prophase- nucleus starts to break down and sister chromosomes appear. 2. Metaphase-chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell 3. Anaphase- chromosomes will split and move to opposite sides of the cell 4. Telophase-the cell will start to split and nucleus will start to reform
Cytokinesis: the cell splits into 2 brand new cells
Meiosis: Sexual reproduction is the union of sex cells called gametes (sperm and egg). This requires 2 parents. Both sex cells—the sperm and egg—are haploid cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as diploid cells. When haploid cells unite, they form a zygote(first body cell) that is diploid (n + n =2n). The zygote then divides by mitosis many times to produce multi-cellular organism composed of diploid cells.
Cancer is a disease caused by uncontrolled division of human cells. It basically is a failure to control the cell cycle. Mutations in genes that encode the steps of cell division can cause damaged cells to divide. If special proteins fail to repair the damaged cells or eliminate them, the cells can accumulate into cancerous tumors.

Meiosis produces haploid cells from a diploid cell by two rounds of cell division: meiosis I and meiosis II. Each round includes stages of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Meiosis I: Prophase I:is like prophase of mitosis however prophase I features a process of crossing over. In crossing over the chromosomes exchange a portion of DNA making them genetically different. During metaphase I and anaphase I, there is independent assortment of chromosomes. This creates a variety of outcomes (that is gametes) that contain different combinations of chromosomes. During telophase I, the movement of chromosomes is completed. Meiosis II: -2 new daughter cells go through another round of division to result in 4 genetically different haploid daughter cells. In humans these sex cells created would only have 23 chromosomes half of the 46 chromosomes that normal body cells contain in humans. At the end of mitosis 4 sperm will be created for males and females will create 4 eggs; 1 egg will be good the other 3 will be thrown away as polar bodies.
Part 7
DNA Replication is the making of an exact copy of the DNA molecule. This process takes place before cell division in all living organisms. The important steps in DNA replication include the following: 1. DNA molecule consists of two strands in a spiral formation called a double helix. In DNA replication, the double helix “unzips”. Each strand becomes a template (model) for a new complementary strand, so each DNA contains one old and one new strand. This process is called semiconservative replication. 2. Replication begins when enzyme helicase unzips the DNA. This produces a Y-shaped replication fork.
Trait Mitosis Meiosis
Cell Type Body Cells (somatic)
Sex cells (gametes)
# of divisions 1 2
# cells created 2 4
Asexual or sexual?
Asexual Sexual
Crossing Over? No crossing over Crossing over
Haploid or diploid cells
Diploid Haploid
Genetically identical or different
Identical Different
# times DNA copied
1 1
# chromosomes found in each human cell
46 chromosomes
23 chromosomes

3. Another enzyme called DNA polymerase bonds to the DNA strand and adds DNA nucleotides to each complementary strand.
Transcription and Translation: The function of DNA is to store genetic information. Genetic instructions in DNA cause cells to grow and develop in certain ways. This determines what kind of organism the cells will form, such as an oak, a mouse, or a human. All of this happens because of a chemical process called protein synthesis, in which enzymes and other proteins are formed from DNA. The two steps of this process are transcription and translation.
1. Transcription: makes an RNA copy (a “transcription”) of a DNA molecule. The main functions of RNA are to decode and express genetic information as protein. In transcription, three types of RNA produced: messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Messenger RNA sends the DNA “message” to the ribosome.
2. Translation: RNA is translated into the language of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Transfer RNA carries amino acids to the correct place on the mRNA template. Ribosomes synthesize the proteins using the final mRNA transcript. Ribosomal RNA builds ribosomes from various proteins. The proteins bond together to form a growing polypeptide chain. Altogether, this process allows for gene expression, or expression of different genetic traits in organisms.
The Genetic Code: The bonding that takes place in translation is accomplished with blocks of information that together make up the genetic code. Each 3 letter code represents one amino acid. The 3-letter codes in the mRNA are called codons. For example the codon AUG signals the start of translation. There are also 3 letter codes in the tRNA that stop the bonding process and are called anticodons. The genetic code is virtually universal for organisms. The fact that the basic components of DNA are nearly universal shows that organisms from bacteria to humans have a common ancestry and have evolved through the process of inheritance.
Part 8
Mutations: Sometimes errors occur in DNA replication. Such errors generally occur spontaneously and at random. An error that is not repaired becomes a mutation. -A mutation in a body cell (somatic mutation), can result in a disease such as cancer. A somatic mutation may also be caused by radiation or chemicals, which are called mutagens. Somatic mutations do not occur in cells that give rise to

gametes (sex cells), so they are not passed on by sexual means and are not inherited by the next generation. For example, skin cells that develop cancer do not pass on the mutation to the next generation. -A mutation in a cell that gives rise to gametes, or germ cells, is called a germinal mutation. Some gametes will pass the mutation on to the next generation by sexual reproduction. A germinal mutation is not expressed in the carrier, only in the carrier’s offspring. Thus a mutation in gametes may result in a phenotype change in the next generation. The most basic type of mutation is point mutation. It is an error in only one nucleotide. Forms of point mutation include the following:
-Substitution- is when the DNA sequence has an incorrect nucleotide in place of a correct one. Original DNA: AAT GCC TTA Mutated TAT GCC TTA
-Deletion is when one nucleotide is left out of the sequence. Original DNA: AAT GCC TTA Mutated: AAG CCT TA
Insertion- is when one nucleotide is added to the DNA sequence. Both a deletion and an insertion result in a frameshift mutation. All the nucleotides in the sequence are shifted by one place. Original DNA: AAT GCC TTA Mutated: AAT GAC CTT A
A point mutation or frameshift may alter a codon in a gene to a stop codon. This causes the translation to produce a missense mutation. In a missense mutation, proteins may not be able to form into their proper shapes. Sickle cell disease, in which red blood cells bend into a sickle shape is an example of a missense mutation.
Part 9 Biotechnology: Biotechnology is the branch of science that manipulates genes in a laboratory. One of the basic tools of biotechnology is recombinant DNA, in which DNA from two different sources is combined into a single molecule. This process is possible because all organisms contain the same type of genetic material. Scientists are now able to use genetic engineering to remove, modify, or add genes to DNA molecules. -Bioengineered crop plants such as wheat, corn, potatoes, and cotton, can be fortified against diseases and pests with special genes, increasing crop production. These crops can be engineered to have better taste, texture, color and nutrients. -Biofertilizers- employ microorganisms to add nitrogen to soils and increase their fertility. Genetically engineered bacteria can clean up toxic waste oil spills by “eating” unwanted products. -Gene cloning-a specific sequence of DNA is isolated and reproduced. The technique is used to make helpful protein products such as insulin, which is a treatment for persons with diabetes, and certain vaccines. -Human gene therapy-a nonfunctioning gene in human cells is replaced with a functioning one. In theory, the replacement gene can develop antibodies to fight cancer and sexually transmitted diseases. So far scientists have had mixed results with gene therapy. -DNA fingerprinting- different fragments of DNA, or unique “markers” are used to identify criminals from blood or hair at the scene of a crime. Such DNA testing can also reveal the paternity of children. While biotechnology has many benefits, it also raises some ethical concerns: Reduced genetic diversity-Bioengineered crops and animals could crowd out other possible genetic developments that could be beneficial. Safety of Genetically modified foods- there are persistent concerns about whether these foods are safe for humans, animals, or the environment. Discrimination by DNA- Biotechnology enables scientists to detect genetic defects and potential diseases in individuals. The possibility also exists that these individuals could suffer discrimination in the work place. Bioterroism-Genetic engineering raises the possibility that deadly bacteria or disease could be developed to attack society. Interference with Nature-Some people believe that biotechnology is an immoral attempt to change the natural order of life on Earth.

Part 10
1. You find a cell of a type you have never seen before. The cell has both a nucleus and a cell wall. What can you conclude about this cell? A. It is a plant cell. B. It is a bacterial cell. C. It is an animal cell. D. It is a prokaryotic cell.
2. The diagram below represents the beginning and end products of a process that occurs in the nucleus of a cell. Which process does the diagram represent? A. recombination B. transcription C. replication D. translation
4. The diagrams to the right show two different cells in two different salt solutions. What will most likely happen in each cell? A. Equal amounts of water will exit the cells in both samples. B. Equal amounts of water will enter the cells in both samples. C. There will be net movement of water into cell 1 and out of cell 2. D. There will be net movement of water into cell 2 and out of cell 1.
5. During meiosis I, cells begin to divide in a way that is very similar to the process of mitosis. However, what major event takes place in meiosis I that does not occur in mitosis? A. crossing over B. interphase C. chromosome replication D. mutation
6. The genetic code is nearly universal, meaning that almost all organisms use the same genetic code. Which statement does NOT help explain why the genetic code is nearly universal? A. All organisms encode their genes using DNA or RNA. B. All organisms use the same codon for the same amino acid. C. All organisms can grow, respond to stimuli, and reproduce. D. All organisms are genetically related to all other organisms.
7. Which of the following statements correctly explains the function of the Golgi apparatus within a cell? A. The Golgi apparatus uses oxygen to convert sugar into chemical energy and also controls the metabolism of the cell. B. The Golgi apparatus prepares new macromolecules such as fats and lipids by sorting and encasing them before sending them to the correct destination within a cell. C. The Golgi apparatus contains most of the genetic material within the cell and is responsible for gene expression and DNA replication when the cell divides. D. The Golgi apparatus breaks down molecules that are not needed within the cell, and returns some of the products of digestion of the cell for use in building new cell parts.
3. Which equation best describes photosynthesis? A. Water and energy yield carbohydrates and carbon dioxide. B. Energy, water, and chlorophyll yield carbon dioxide and oxygen. C. Carbohydrates and carbon dioxide yield energy and oxygen. D. Carbon dioxide, water, and energy yield carbohydrates and oxygen.

8. Why does sexual reproduction result in greater diversity among offspring than does asexual reproduction? A. only mitosis must occur in sexual reproduction B. mutations are more likely to occur in asexual reproduction C. sexual reproduction may occur at a faster rate D. new combinations of genes result from sexual reproduction
9. Which of the following statements describes processes that occur during DNA replication? A. A DNA sequence is read by RNA polymerase, which produces another RNA strand complementary to the first strand. B. Messenger RNA is decoded by a ribosome to produce an amino acid chain. In the cell’s cytoplasm, transfer RNA join the messenger RNA, forming a polypeptide. C. Two free-floating single strands of DNA are joined by polymerase. The polymerase finds the point at which the two strands will match up into a double strand. D. A double-stranded DNA molecule is unwound into single strands. Polymerase matches the right nucleotides to the single strand so that each forms a double strand of DNA.
10. Some animal species are able to reproduce both asexually and sexually. Which of these is an advantage of an organism with this ability? A. Beneficial traits arise more quickly. B. Fewer harmful genetic mutations occur. C. New genetic traits are exchanged with mates more easily. D. Organisms can still reproduce even when unable to find a mate.
11. Which statement accurately describes the way that adenosine triphosphate (ATP) transfers energy within a cell? A. ATP molecules break up sugars such as glucose into energy-rich compounds like lactose. B. ATP molecules ionize oxygen molecules, which give up electrons that can then be used for energy. C. ATP molecules split carbon dioxide molecules, and the carbon is used as fuel by the cell. D. An ATP molecule reacts with water and loses a phosphate group, breaking a bond and releasing energy.
12. A segment of a DNA strand has the following bases: TAC GAT What is the complimentary strand of DNA? A. UAG CAU B. ATG CTA C. TAG CAT D. AUG CUA 13. Which cellular process is shown in the diagram to the right? A. mitosis B. phagocytosis C. meiosis D. endocytosis
14. The body cells of an individual plant have 50 chromosomes. How many chromosomes would be found in the gametes produced by this plant? A. 5 B. 25 C. 10 D. 50
15. Which is a reactant (or a substrate) in photosynthesis but a product in cellular respiration? A. oxygen B. glucose C. nitrogen D. carbon dioxide 16. In periods of hot, dry weather, the pores on the leaf surfaces of most plants close in order to reduce water loss during the day. When these pores are closed, plants cannot take in carbon dioxide. As a direct result, the rate of which of the following processes decreases? A. cellular respiration B. nitrogen fixation C. mitosis D. photosynthesis
17. A marathoner’s leg muscles often feel heavy and prone to cramping after 20 or more miles. Which of the following is the best explanation for this? A. A marathoner’s muscle cells cannot store glucose for use as energy B. A marathoner’s muscle cells contract when glucose reacts with oxygen C. A marathoner’s circulatory system cannot take in sufficient oxygen, and then muscle cells must switch to anaerobic respiration for energy D. A marathoner’s circulatory system takes in too much oxygen during a race, which causes muscle cramping

18. The plasma membrane in a eukaryotic cell mainly consists of which of the following? A. a phospholipid bilayer with proteins embedded in the layers B. a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail C. a protein layer with phospholipids embedded in the layers D. a phospholipid layer and a protein layer 19. Which of the following uses energy to move substances across the plasma membrane and against the concentration gradient from areas of low concentration to high concentration? A. osmosis B. facilitated diffusion C. exocytosis D. the sodium-potassium pump
20. Which of the following is found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes? A. ribosomes B. lysosomes C. mitochondria D. vacuole
21. A key difference between plant and animal cells is that plant cells have cell walls and animal cells do not. This difference results in which of the following? A. Plant cells can form themselves into many different shapes in order to perform different functions B. Plant cells cannot transport materials among other cells C. Animal cells have increased flexibility for advanced cell or tissue specialization D. Animal cells depend entirely upon the cells membranes for structural support
22. Which of the following is the site of aerobic cellular respiration? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
23. What process is occurring in the diagram below to make different gametes? A. Mitosis B. Replication C. Mutation D. Crossing over
24. What process is occurring at the ribosome in the picture to the right? A. Transcription B. Translation C. Replication D. Mitosis
25. Which statement accurately describes the way that adenosine triphosphate (ATP) transfers energy within a cell? A. ATP molecules break up sugars such as glucose into energy-rich compounds like lactose. B. ATP molecules split carbon dioxide molecules, and the carbon is used as fuel by the cell. C. ATP molecules ionize oxygen molecules, which give up electrons that can then be used for energy. D. An ATP molecule reacts with water and loses a phosphate group, breaking a bond and releasing energy.
26. Which of the following does NOT describe a similarity between photosynthesis and cellular respiration? A. Both transform food into energy. B. Both are transformations of energy. C. Both involve the exchange of gases. D. Both are necessary for life on Earth.
27. Some organisms are capable of reproducing asexually through processes such as budding or parthenogenesis. What is an advantage of asexual production for an organism? A. It allows organisms to increase population rapidly. B. It allows haploid cells to unite to produce a zygote. C. It allows for greater genetic diversity within a species. D. It allows crossing over to take place during replication.

28. Errors sometimes occur during DNA replication. If a DNA nucleotide that contains guanine is accidently substituted for a DNA nucleotide that contains thymine, which of the following will always occur as a result of the error in DNA replication? A. The cell will die when it divides B. The cell will become a rapidly dividing cancer cell. C. The cell will have a better chance of surviving under different conditions D. The cell will produce messenger RNA with a different nucleotide sequence 29. Recently, many farmers have started growing genetically modified crops. These crops have been engineered to have specific traits to avoid diseases and grow in a wider range of climates. What effect might genetically modified crops have on their surroundings?
A. The rainfall would increase B. The soil type would change C. The pests would develop a resistance D. The human population would decrease
30. Which technology below would probably be the most important to a person who had diabetes and had to take insulin every day? A. testing parents for genetic disorders before they have children B. engineering fruits and vegetables that resist insects and other pests C. developing ways to identify criminals through DNA fingerprinting D. using recombinant DNA to produce human hormones from bacteria
31. Stem cell research has been a controversial subject in past years. What is the reason for this? A. Cells for study are often taken from human embryos. B. Stem cell techniques will not accomplish the intended purpose. C. The cells cannot be isolated. D. Replacement tissue will never be grown from a person's own stem cells.
32. Bioengineered crop plants such as wheat and corn can be fortified against damaging insects to increase crop yields. Yet some experts have expressed concerns about these modified plants. Which of the following might result from increased use of bioengineered crop plants? A. an increased chance of contaminating ground water supplies B. an increase in the need for strong pesticides C. a decreasing amount of genetic diversity in the genes of crop plants D. an increasing amount of genetic diversity in the genes of crop plants
33. Great strides are being made in identifying genetic markers for disease within the human genome. Which of the following would be considered an ethical misuse of this information? A. hospitals using genetic information about specific patients in order to develop treatments for those individuals B. individuals deciding not to have children based on the results of genetic testing showing they carry the allele for a fatal disease C. insurance companies refusing to insure a person based on information they required about the person's genome indicating a high risk for a certain disease D. doctors informing their patients that they are likely to develop a debilitating illness for which there is no treatment based on patient-requested genetic tests 34. Which of the following would most likely cause a mutation? A. the placement of ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum B. the insertion of a nucleotide into DNA C. the movement of transfer RNA out of the nucleus D. the release of messenger RNA from DNA
35. Which of the following may result in a phenotypic change in the next generation? A. a somatic mutation B. a gamete mutation C. either a somatic or gamete mutation D. any mutation due to exposure to radiation or chemicals

36. Which of the following accurately describes the difference between transcription and translation? A. In transcription, the genetic code of a DNA molecule is first encoded. Translation is the process of converting the DNA code into code that RNA can use. B. In transcription, an amino acid chain is encoded in a DNA molecule. Translation is the process of turning the amino acids into nucleic acids in an RNA molecule. C. In transcription, the genetic code of a DNA molecule is transferred to a messenger RNA molecule. Translation is the process of creating an amino acid chain using the encoded messenger RNA. D. In transcription, a double helix DNA molecule is split into two separate single strands. Translation is the process of joining each single DNA strand with a single strand of matching RNA.
37. A scientist is developing a potential treatment for cancer. She grows cells in hundreds of petri dishes and exposes the dishes to environments that are known to cause cancer. After exposure, the scientist determines that some of the petri dishes have cancer cells.What factor do all the petri dishes that contain cancer cells have in common? A. All the petri dishes with cancer cells have a disrupted cell cycle. B. All the petri dishes with cancer cells have been exposed to tobacco smoke. C. All the petri dishes with cancer cells could be treated successfully if they receive the same treatment. D. All the petri dishes with cancer cells have genetically identical cells that make them susceptible to cancer.
38. Which of the following is a characteristic shared by both plant and animal cells? A. chloroplasts B. large central vacuole C. mitochondria D. rigid cell walls
39. Which of the following is a structure that is present in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? A. Golgi complex B. plasma membrane C. nucleus D. vacuole
Benchmark Recap #2 Answer Sheet Part 1
1. What is an example of a prokaryotic cell?_______________________________________________________________
2. What are 3 differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?__________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
3. What is an example of a eukaryotic cell?_______________________________________________________________
4. What are 2 similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?___________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Part 2
5. What part of the cell makes protein? __________________________________________________________________
6. What would the cell no longer be able to do if the golgi apparatus stopped working? ___________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
7. Where does cellular respiration take place in the cell?___________________________________________________
8. Where is the nucleolus found and what does it make? ____________________________________________________
9. What is the difference between smooth and rough ER?___________________________________________________
10. Where is DNA found in a eukaryotic cell? ____________________________________________________________
11. What is the fluid inside of the cell called? ____________________________________________________________
12. What 3 features does a plant cell have that an animal cell lacks? __________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________

Part 3
13. What structures make up the cell membrane? _________________________________________________________
14. What is the role of the cell membrane?_______________________________________________________________
15. Why are the hydrophilic heads facing the inside and outside of the cell? ____________________________________
16. What part of the cell membrane fears water? _________________________________________________________
17. What does selectively permeable mean? _____________________________________________________________
Part 4
18. What type of transport requires energy to move molecules from low to high concentration? ____________________
19. The movement of water from High to Low concentration is called? _________________________________________
20. A solution high in water and low in solute is called ____________________________________.
21. A solution with equal amounts of water and solute is called?______________________________________
22. What way will the water move if the cell has 20% sugar inside the cell and 50% water outside the cell?
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
23. What type of diffusion requires the help of a protein to move molecules from High to low concentration without
energy? _______________________________________________________________________________________
24. What processes require energy? ____________________________________________________________________
25. What is the difference between exocytosis and endocytosis? _____________________________________________
26. How is pinocytosis and phagocytosis different? ________________________________________________________
Part 5
27. What are the reactants of photosynthesis? ___________________________________________________________
28. What is produced from photosynthesis? _____________________________________________________________
29. Where does photosynthesis occur? _________________________________________________________________
30. What two cycles make up photosynthesis? ___________________________________________________________
31. What does each of the two cycles of photosynthesis do? _________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
32. Why are most plants green? ________________________________________________________________________
33. What are the reactants of cellular respiration? _________________________________________________________
34. Where does cellular respiration occur? _______________________________________________________________
35. What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration? _________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
36. What is produced from alcoholic fermentation? ___________________________________________________
37. What type of organisms perform this process?________________________________________________________
38. What is produced from lactic acid fermentation? ______________________________________________________
39. Why does it create muscle soreness? _________________________________________________________________

40. How do cellular respiration and photosynthesis depend upon each other? ___________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
41. Why do plants have both chloroplasts and mitochondria? _______________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
42. When do plants perform cellular respiration? ________________________________________________________
Part 6
43. What is the longest phase of the cell cycle called? ____________________________________________________
44. What does asexual mean? _______________________________________________________________________
45. What happens to a cell during the G1 phase? ________________________________________________________
46. What happens to a cell during the S phase? _________________________________________________________
47. What happens to a cell during the G2 phase? ________________________________________________________
48. Mitosis is the reproduction of _______________________________________________.
49. State the phase of mitosis and explain what is happening:
A. ____________________________ B.__________________________________
C.________________________________ D. ___________________________________
50. How many cells are created from mitosis? ___________________________________________________________
51. Are the daughter cells identical or genetically different from the parent cell? _______________________________
52. What is cancer?_________________________________________________________________________________
53. What causes cells to start reproducing out of control? __________________________________________________
54. What types of cells go through meiosis? _____________________________________________________________
55. Are sperm and egg considered haploids or diploids? ____________________________________________________
56. How many cells are created from meiosis? _________ 57. How many times does a cell divide in meiosis? ______
58. What is crossing over? __________________________________________________________________________

59. How many chromosomes does a human sex cell have? ___ 60. How many sperm and eggs are created in meiosis? __
61. How does meiosis result in cells that are genetically different from the daughter cell? _________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
Part 7
62. What is the process that makes exact copies of DNA? __________________________________________________ 63. What does DNA look like? ________________________________________________________________________
64. What are the 3 steps of DNA replication? ____________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
65. What is the purpose of the enzyme helicase? ________________________________________________________
66. What is the purpose of the enzyme DNA polymerase? _________________________________________________
67. Describe the process of transcription. _______________________________________________________________
68. What is created from the DNA strand? ______________________________________________________________
69. Where does mRNA travel to in order to be translated? _________________________________________________
70. Who translates the mRNA strand? __________________________________________________________________
71. What is created at the end of transcription and translation? ______________________________________________
72. Amino acids are the building blocks of _______________________________________________.
73. Transcribe the DNA molecule into an mRNA molecule: TAC AAA CAG TTA mRNA: ____________ __________ __________ _________
74. Translate the mRNA strand from above into amino acids. _______________, __________________, ___________________, ____________________
75. Every 3 bases is called a __________________________________.
Part 8
76. What is a mutation? _____________________________________________________________________________
77. What are mutagens? ______________________________________________________________________________
78. What is the difference between somatic and germinal mutation? __________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
79. Determine the type of mutation: Original DNA: TTA GGC AGA
A. TGA GGC AGA = ____________________________
B. TTG GCA GA = ______________________________
C. TTA GGC AAG A = ____________________________
Part 9
80. What is biotechnology? ___________________________________________________________________________
81. What is recombinant DNA? ________________________________________________________________________

82. How do scientists use genetic engineering? ____________________________________________________________
83. What type of biotechnology involves genetically engineered wheat and cotton? ______________________________
84. What type of biotechnology involves the creation of insulin to treat diabetes? _______________________________
85. What type of biotechnology involves microorganisms that can act as fertilizers or help clean up toxic waste? _______
86. What type of biotechnology is used at crime scenes or paternity tests? _____________________________________
87. What type of biotechnology is used to replace nonfunctioning genes with functioning genes? ___________________
88. What are the ethical concerns behind biotechnology? ___________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
PART 10-Circle your answer on the multiple choice questions