Basic Electricity & Magneto Ignition In order to understand the operation of the Ignition system on...
-
Upload
agnes-butler -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
2
Transcript of Basic Electricity & Magneto Ignition In order to understand the operation of the Ignition system on...
Basic Electricity & Magneto IgnitionIn order to understand the operation of the Ignition system on a small engine, we must understand Basic Electricity!
What is electricity ? The movement of free electronsthrough a conductor !
What are Electrons ?
ProtonsProtons – positively chargedNeutrons Neutrons – neutral chargeElectrons Electrons – negatively charged
Electrons are part of a Atom!
What is an Atom ? Atoms are everything around you!
Atoms consist of :
Basic Electricity & Magneto Ignition
Conductors !Conductors ! - are materials that allow the flow of “free electrons” to move from atom to atom easily!
Insulators !Insulators ! - are materials that do not allow the flow of “free electrons”
Simple Circuits, Conductors, and Insulators
Simple Circuits!Simple Circuits! – must have a Power source, conductor and a load.
Examples of conductors: gold, silver, copper, aluminum
Examples of insulators: air, plastics, silicon, porcelain
Basic Electricity & Magneto IgnitionMethods of producing Electricity
MagnetismStaticHeat ChemicalLight
Laws and Rules of Magnetism
#1 Unlike Poles (North, South) attract !, Like Poles Repel !
#2 A moving magnetic passing a wire in a complete circuit creates electron movement within that wire (Electricity)
#3 Electron flow in a wire creates a magnetic field around that wire (Electro Magnets)
Factors that determine amount of electrical current created- Speed of the moving magnetic field- Strenght of the magnetic field- Size and type of conductor
Basic Electricity & Magneto IgnitionElectricity Terminology
Voltage: -electrical pressure or force behind the electron movement,-measured in Volts ( V or E )
Amperage: -measurement of electron flow-measured in Amps ( A or I )-6.28 x 10(18th) electrons past a single point in one second = 1 Amp
Resistance: -opposition to current flow-measured in Ohms ( R or )
Ohms Law:
Basic Electricity & Magneto IgnitionCreating the Magneto Ignition !
Important Measurements and Adjustments !
! Armature Air Gap !! Breaker Point Gap !! Spark Plug Gap !
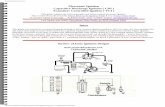
Basic Electricity & Magneto IgnitionThe Complete Magneto Cycle
a) – Magnet approaches the armature, lines of force cut across the windings , causing current flow in the primary circuit.
b) – Electron flow creates a magnetic field around the windings.
c) – Piston arrives at TDC on the compression stroke, breaker points open
d) – Primary circuit is broken causing the magnetic field to collapse very FAST!
e) –Collapsing lines of force cut across the secondary winding, causing HIGH electrical current to be induced in the circuit
f) – High electron current causes a spark to jump across the spark plug gap.