Background Objectives Findings Conclusions Data 10% sample of the 2000 Mexican Census by the...
-
Upload
alyssa-hammond -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
3
Transcript of Background Objectives Findings Conclusions Data 10% sample of the 2000 Mexican Census by the...

Background
Objectives
Findings
Conclusions
Data 10% sample of the 2000 Mexican Census by the National Institute of
Statistics, Geography and Information of Mexico (INEGI).14
Sample size for multivariate analysis: 55,677 women aged 15-39 with information about Children Ever Born (CEB), religion, ethnicity and other socioeconomic and demographic characteristics (see TABLE 2).
Information about indigenous language is used to define indigenous ethnicity of Chiapanecan women (34.4% are indigenous and 65.6% are not).
We follow INEGI’s general classification of religious affiliation. Presbyterians and Baptists are considered Historical Protestants; religions with Charismatic background and non denominational, Pentecostal and Evangelical; and Adventists of the 7th day, Jehovah Witnesses and Mormons, Biblical Non-Evangelical.
**
*
Among indigenous women, Historical Protestants present 17% lower incidence of child mortality and Pentecostal-Evangelical 11% lower incidence of child mortality in comparison to Catholics, after controlling for socioeconomic covariates (see TABLES 3 and 4).
Among non-indigenous women, religious affiliation did not affect the incidence of child mortality.
The social and cultural transformations that tend to accompany religious conversion may have an impact on the health of disadvantaged populations such as the indigenous people in Chiapas. For instance, people expand their networks beyond the kinship, learn about hygiene and preventive health care, and re-orient patterns of consumption.6-10 Also, men stop alcohol abuse and are expected to look after their family as a personal goal.10,11 In addition, Presbyterians train indigenous health promoters as part of their social mission.12,13
Further research should pay attention to unmeasured variables at the community level (influence of the religion in the community) and socioeconomic indicators such as access to educational and medical services.
Also, regional mortality differentials need to be studied to understand the reasons for Selva’s better child survival indicators.
We use information of Children Ever Born (CEB) and Surviving CEB (SCEB) to estimate child mortality indirectly.
The analysis includes:
Brass-type estimates for the probability of child mortality using the adjustment factors developed by Trussel for the West Model.15-16
Negative binomial regression17 to calculate the incidence rate ratios of child mortality among different religions by ethnicity controlling for various socioeconomic and demographic factors (see TABLE 2).
Methodology
Bibliography1. Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Informática. La diversidad religiosa en México. Aguascalientes: INEGI, 2000. 2. Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Informática. La población hablante de lengua indígena de Chiapas.
Aguascalientes: INEGI, 2000.3. Van Poppel F, Schellekens J, Liefbroer A C. Religious differentials in infant and child mortality in Holland, 1855-1912.
Popul Stud 2002; 56:277-289.4. Kemkes-Grottenthaler A. God, faith and death: The impact of biological and religious correlates on mortality, Hum Biol 2003;
75(6):897-915.5. Wood C, Williams P, Chijiwa K. Religion and child mortality in Brazil. In: Meeting of the Latin American Studies Association
[CD-Room]; 2006 March 15-18; San Juan: Latin American Studies Association.6. Turner P R. Religious conversion and community development. J Sci Stud Relig 1979; 18(3): 252-260.7. Martin D. Tongues of fire: the explosion of Protestantism in Latin America. Oxford, UK: Balckwell, 1990.8. Mariz C. Coping with poverty: Pentecostals and Christian Base Communities in Brazil, Philadelphia: Temple University Press,
1994.9. Rostas S A. A grass roots view of religious change amongst women in an indigenous community in Chiapas, Mexico, Bull
Latin Am Res 1999; 18 (3):327-341.10. Robledo-Hernández G P. Religiosidad y estrategias de reproducción de los grupos domésticos en una comunidad indígena.
Tesis de doctorado. San Cristóbal de las Casas (Chiapas, México): ECOSUR, 2002.11. Brusco E. The reformation of machismo: asceticism and masculinity among Colombian Evangelicals. In: Garrad-Burnett V,
Stoll D, editors. Rethinking Protestantism in Latin America, Philadelphia: Temple University Press, 1993:143-158.12. Ocampo-Torres M. La obra médica Tzotzil, México: Publicaciones El Faro, enero-febrero 1994:14-17.13. Ruiz-Guerra R. Identidades sociales y cambio religioso en Chiapas (Los vínculos de la identidad protestante). In: Guillen D.
coordinator. Chiapas: rupturas y continuidades de una sociedad fragmentada, México: Instituto de Investigaciones José Maria Luis Mora, 2003:129-175.
14. Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Informática. XII Censo de Población y Vivienda [CD-Room]. Aguascalientes: INEGI; 2000.
15. Brass W. Methods for estimating fertility and mortality from limited and defective data. Chapel Hill (NC): International Program of Laboratories for Population Statistics, 1975.
16. United Nations. Estimation of child mortality from information on children ever born and children surviving. In: Manual X: Indirect techniques for demographic estimation. New York: United Nations Publications,1983.
17. Long J, Freese J. Regression models for categorical dependent variables using Stata, College Station: Stata Press, 2001.Statacorp.
Child Mortality and Religious Affiliation by Ethnicity in Chiapas, MexicoChild Mortality and Religious Affiliation by Ethnicity in Chiapas, Mexico
A considerable number of indigenous people in Mexico have converted to Protestant religions in recent years.
Chiapas is characterized by large regional variations in religious affiliation by ethnicity (see TABLE 1).
From 1970 to 2000, the proportion of the population of Chiapas affiliated to Protestantism increased from 5 to 22%.1
For indigenous populations, the rate of affiliation to Protestant religions was higher in 2000 than for non-indigenous groups.2
Religious affiliation has been associated with child survival in other populations, i.e. Protestantism in the case of historical populations 3-4 and in northeast Brazil.5
It has been suggested that conversion and adherence to Protestantism may buffer gender inequalities and reduce social isolation, economic instability and ignorance about health care and hygiene.6-13 These factors are likely to have an impact on children’s health and risks of mortality.
We investigate whether:
there is a statistical relationship between religious affiliation and child mortality within indigenous and non-indigenous groups in Chiapas, Mexico
this effect is explained by socioeconomic differentials among churches
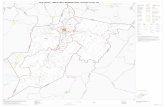
Source: El Colegio de la Frontera SUR. San Cristóbal de las Casas: Laboratorio de Análisis de Información Geográfica y Estadística, 2006. [updated 2006 January 5]. Available from: www.ecosur.mx
FIGURE 1. Municipalities by economic regions in Chiapas, Mexico
Ind N-Ind Ind N-Ind Ind N-Ind Ind N-Ind
% % % % % % % %
Catholic 53.8 60.8 53.6 88.5 51.0 65.1 66.7 69.8
Historical 7.7 1.7 14.8 1.1 23.0 4.7 4.1 3.5
Pentecostal/Evangelical 7.3 6.8 10.7 4.8 12.8 10.8 5.9 7.8
Biblical non-evangelical 22.8 17.1 4.9 2.1 3.1 8.3 15.2 8.4
No affiliation 8.3 13.1 15.4 2.8 8.9 10.3 7.9 10.4
Undetermined 0.2 0.4 0.5 0.7 1.4 0.8 0.2 0.2
TOTAL 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0
* Weighted percentages. Ind= Indigenous women, N-Ind= Non-Indigenous women
Selva OtherREGION
Religious affiliationNorte Altos
TABLE1. Religious affiliation by ethnicity and region of residence, Chiapanecan women aged 15-49
TABLE 2. Descriptive statistics, women 15-39 years old with CEB
0.00
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
0.06
0.07
0.08
0.09
0.10
0.11
0.12
q(1) q(2) q(3) q(5) q(10)
Indigenous Non-Indigenous
FIGURE 2. Brass-type estimates of the probability of child mortality by ethnicity, women aged 15-39
FIGURE 3. Brass-type estimates of the probability of child mortality by religious affiliation, women aged 15-39
TABLE 3. Incidence-rate ratios of child mortality by religious affiliation, indigenous women aged 15-39 with CEB TABLE 4. Incidence-rate ratios of child mortality by religious
affiliation, non-indigenous women aged 15-39 with CEB
VARIABLE Categories Ind N-Ind VARIABLE Categories Ind N-Ind
Catholic 53.6 67.9 Floor Dirt 72.8 29.7
Historical 15.1 3.4
Pentecostal/Evangelical 11.0 8.2 - - - 72.3 42.4
Biblical non-evangelical 9.0 8.5
No affiliation 11.4 11.9 Norte 13.7 7.2
Altos 33.1 4.1
Age 15-19 9.8 7.3 Selva 36.7 4.4
20-24 24.8 21.6 Other 16.5 84.4
25-29 24.9 24.8
30-34 20.1 23.9 None 14.0 3.0
35-39 20.5 22.5 IMSS/ISSSTE/Pemex 11.4 20.2
SSA/IMSS Solidaridad 62.0 45.4
Bilingual - - - 53.0 - - - Private or other 12.7 31.4
Education No instruction 45.0 15.1 - - - 38.4 19.3
1-5 years 32.4 30.1
6-8 years 16.6 24.3 Unweighted N 19127 36550
9 years and more 6.0 30.4
Note: Weighted sample Ind= Indigenous women, N-Ind= Non-Indigenous women
*Participation in Progresa and Procampo, governmental programs of development.
Medical service commonly used
Progresa or Procampo *
Religious affiliation
Rural place of residence
Region of residence
0.00
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
0.06
0.07
0.08
0.09
0.10
q(1) q(2) q(3) q(5) q(10)
Catholic Historical Pentecostal/Evangelical Biblical Non-Evangelical No affiliation
Eunice D Vargas-Valle, University of Texas at Austin, [email protected] D Vargas-Valle, University of Texas at Austin, [email protected] Fernández, University of Texas at El Paso, [email protected] Fernández, University of Texas at El Paso, [email protected]
IRR p>z IRR p>z IRR p>z
Religious affiliation Historical Protestant 0.81 *** 0.83 *** 0.83 ***
(Catholic) Pentecostal/Evangelical 0.88 * 0.89 * 0.89 *
Biblical Non-Evangelical 0.94 0.92 0.93
No religious affiliation 0.98 0.92 + 0.92 +
Age 20-24 1.27 * 1.27 * 1.27 *(15-19) 25-29 1.73 *** 1.68 *** 1.70 ***
30-34 2.11 *** 1.99 *** 2.02 ***35-39 2.56 *** 2.36 *** 2.40 ***
Language Bilingual 0.86 *** 0.86 ***(Monolingual)Education 1-5 years 0.87 *** 0.87 ***(No formal instruction) 6-8 years 0.72 *** 0.72 ***
9 years and more 0.61 *** 0.61 ***
Floor (Dirt) Other 0.85 *** 0.85 ***
Place of residence Rural 0.94 0.96(Urban)Region Altos 1.02 1.01(Norte ) Selva 0.80 *** 0.80 ***
Other 1.16 *** 1.13 *
Medical service used IMSS, ISSSTE or Pemex 0.88 *(None ) SSA/IMSS Solidaridad 0.90 *
Private or other 0.95
Progresa or Procampo (No) Yes 0.93 ****p<=.001 **p<=.01 *p<=.05 +p<=.1 Reference category in parenthesis.Unweighted sample. Number of children ever born is taken as exposure.
Independent variables Categories Model 1 Model 2 Model 3
IRR p>z IRR p>z IRR p>z
Religious affiliation Historical Protestant 1.04 1.00 0.99
(Catholic) Pentecostal/Evangelical 1.06 1.01 1.00
Biblical Non-Evangelical 1.07 0.97 0.96
No religious affiliation 1.09 * 0.98 0.97
Age 20-24 1.14 1.18 + 1.19 +(15-19) 25-29 1.25 ** 1.32 *** 1.33 ***
30-34 1.40 *** 1.44 *** 1.46 ***35-39 1.85 *** 1.79 *** 1.82 ***
Education 1-5 years 0.88 *** 0.89 ***(No formal instruction) 6-8 years 0.66 *** 0.67 ***
9 years and more 0.45 *** 0.49 ***
Floor (Dirt) Other 0.82 *** 0.83 ***
Place of residence Rural 1.06 + 1.04(Urban)Region Altos 0.97 0.95(Norte ) Selva 0.66 *** 0.65 ***
Other 0.98 0.98
Medical service used IMSS, ISSSTE or Pemex 0.68 ***(None ) SSA or IMSS Solidaridad 0.92
Private or other 0.87 *
Progresa or Procampo (No) Yes 1.00***p<=.001 **p<=.01 *p<=.05 +p<=.1 Reference category in parenthesis. Unweighted sample. Number of live children ever born is taken as exposure.
Independent variables CategoriesModel 1 Model 2 Model 3