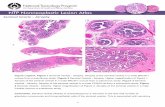
Histological Structure of Skeletal Muscle in Disuse Muscle ...
Atrophy of Disuse
-
Upload
joe-thesecondmonth -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Atrophy of Disuse

Mahatmasara Adhiwasa (0906550865)
Atrophy of Disuse
Muscles, when not used can cause a decrease in its actin and myosin content. Its fibers become smaller, and the muscle will decrease in mass and becomes weakeri. Complete immobilization due to bed rest or loss of neural stimulation results in disuse atrophy. Sedentary activity can also result in loss of muscle tone and muscular atrophy. The atrophy of the muscle can initiate almost as soon as the muscles are immobilized. Under these conditions, muscle strength can decrease at the rate of 5% per day. ii
Studies show that disuse atrophy can worsen a muscle held in a shortened position. When the knee is in extension, the quadriceps are passively shortened and the hamstrings are held in a lengthened position. This is one of the primary reasons of why range of motion is limited following immobilization. Immediately after the immobilization, a proper stretching of the quadriceps fibers is needed to regain the return to optimal function.iii
The most common treatment for muscular atrophy is regular exercise, which can be seen in physical therapies. The aim is to help strengthen the affected muscles and restore as much normal function as possible. As the patient gains increased range of motion and stamina, more varieties of exercises may be added. Regardless of injury type, various methods of water therapy can be used to increase range of motion and facilitate weight bearing without imposing maximal forces of gravity.iv
i Sherwood L. Human Physiology From Cells to Systems. 5th ed. Thomson; 2005. P.283ii Marieb EN, Hoehn K. Human Anatomy and Physiology. Pearson education; 2007iii Anonymous. Muscular Atrophy. [cited 2 Jan 2011] Available from the URL http://www.mdguidelines.com/atrophy-musculariv Lowe W. Understanding Disuse Atrophy. [cited 1 Jan 2011] Available from the URL http://www.massagetoday.com/mpacms/mt/article.php?id=13296