Atomic Structure Chapter 4. Dalton’s Atomic Theory All elements are composed indivisible particles...
-
Upload
griselda-hudson -
Category
Documents
-
view
228 -
download
3
Transcript of Atomic Structure Chapter 4. Dalton’s Atomic Theory All elements are composed indivisible particles...

Atomic StructureAtomic Structure
Chapter 4Chapter 4

Dalton’s Atomic TheoryDalton’s Atomic Theory
All elements are composed indivisible All elements are composed indivisible particles called atomsparticles called atoms
Atoms of the same element are identical Atoms of the same element are identical and different from all other elementsand different from all other elements
Atoms can physically mix together or Atoms can physically mix together or combine chemically to form compoundscombine chemically to form compounds
When atoms are separated, joined or When atoms are separated, joined or rearranged a chemical reaction occurs; but rearranged a chemical reaction occurs; but atoms of one element never change into atoms of one element never change into atoms of another element.atoms of another element.

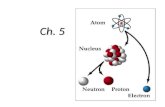
Subatomic ParticlesSubatomic Particles ProtonsProtons
PositivePositive charge charge Found Found inin the the nucleusnucleus Relative mass of 1Relative mass of 1
NeutronsNeutrons NONO charge charge Found Found inin the the nucleusnucleus Relative mass of 1Relative mass of 1
ElectronsElectrons NegativeNegative charge charge Found Found outsideoutside the nucleus the nucleus Relative mass of 1/1840Relative mass of 1/1840

Atomic Number vs. Mass Atomic Number vs. Mass NumberNumber
Atomic Number = Protons in an atomAtomic Number = Protons in an atom Atomic Number = Electrons in an Atomic Number = Electrons in an
atomatom
Mass Number = Protons + NeutronsMass Number = Protons + Neutrons

Complete the TableComplete the Table
ElementElement Atomic #Atomic # ProtonsProtons ElectronsElectrons
KK 1919 1919
55
SS 1616
VV 2323
1919
BB 55 55
1616 1616
2323 2323

How many protons, electrons How many protons, electrons and neutrons in each atom?and neutrons in each atom?
Atomic Atomic ##
Mass Mass
##protonsprotons electroelectro
nsnsneutronneutron
ss
BerylliuBeryllium (Be)m (Be) 44 99
NeonNeon
(Ne)(Ne)1010 2020
Sodium Sodium (Na)(Na) 1111 2323
44 44 55
1010 1010 1010
1111 1111 1212

IsotopesIsotopes
Elements with the same atomic Elements with the same atomic number but different mass numbersnumber but different mass numbers Same number of _________________Same number of _________________ Different number of _______________Different number of _______________
Examples:Examples: Carbon-12Carbon-12 Carbon-13Carbon-13

Atomic MassAtomic Mass
Atomic Mass Unit (amu)Atomic Mass Unit (amu) – the – the mass of 1/12 the mass of a Carbon-mass of 1/12 the mass of a Carbon-12 atom12 atom
Weighted averageWeighted average of the masses of the masses of all the isotopes of an elementof all the isotopes of an element

Calculating Atomic MassCalculating Atomic Mass
Need to know:Need to know: Percent abundance of each isotopePercent abundance of each isotope Mass of each isotopeMass of each isotope
1 H1
2 H1
99.985%99.985% 1.0078 1.0078 amuamu
0.015%0.015% 2.0141 2.0141 amuamu
.99985 x .99985 x 1.00781.0078
.00015 x 2.0141.00015 x 2.0141

1 H1
2 H1
.99985 x 1.0078 = 1.0076.99985 x 1.0078 = 1.0076
.00015 x 2.0141 .00015 x 2.0141 = .000302= .000302
Add the relative masses together to get the average atomic mass
Average atomic mass:
1.0076 + .000302 = 1.0079


History of the Periodic TableHistory of the Periodic Table
MendeleevMendeleev
Tom Leher - Periodic Table Song

Periodic TablePeriodic Table
GroupsGroups PeriodsPeriods Metals Metals
Alkali MetalsAlkali Metals Alkaline Earth MetalsAlkaline Earth Metals
Non-metalsNon-metals Noble-GasesNoble-Gases HalogensHalogens MetalloidsMetalloids Transition MetalsTransition Metals






![Creating Atomic Content For Taxonomy / Content Database Driven Documents Mark Cashman mcashman@temporaldoorway.com atomic adj. [from Gk. `atomos', indivisible]](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/56649da15503460f94a8c8f2/creating-atomic-content-for-taxonomy-content-database-driven-documents-mark.jpg)











