Asymptotes and Algorithms What You’ve Forgotten Since University
Asymptotes and holes 97
Transcript of Asymptotes and holes 97

POINTS OF DISCONTINUITY (Holes and Asymptotes)
Points of discontinuity occur when the denominator of a function equals zero.
2
2
2
21.
2
32.
4 3
13.
2
x xy
x
xy
x x
xy
x x
1
1 2
xy
x x
3
3 1
xy
x x
2 1
2
x xy
x

Horizontal AsymptotesNote: The graph of a rational function has at most one horizontal asymptote.
If the degree of the numerator is less than the denominator, the horizontal asymptote is y = 0.
If the degree of the numerator is more than the denominator, there is NO horizontal asymptote .
If the degree of the numerator is equal to the degree of the denominator, the horizontal asymptote is y = a / b , where a and b are the leading coefficients of the numerator and the denominator.
1y
xExample:
2
2
2
2 1
x xy
x x
Example:
2 1y x Example:

EXAMPLE: Finding the Slant/Oblique Asymptote of a Rational Function Find the slant asymptotes of f (x)
2 4 5 .3
x xx
Solution Because the degree of the numerator, 2, is exactly one more than the degree of the denominator, 1, the graph of f has a slant asymptote. To find the equation of the slant asymptote, divide x 3 into x2 4x 5:
2 1 4 51 3 3 1 1 8
32
81 13
3 4 5
xx
x x x
Remainder
moremore

1 2
1 1
x xy
x x
2
2
2
1
x xy
x
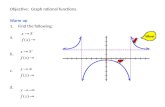
Graph the equation.

2
1
2
xy
x x
Graph the equation.
1
1 2
xy
x x