Architecture of Chromosomes
-
Upload
vipin-pandey -
Category
Education
-
view
625 -
download
0
Transcript of Architecture of Chromosomes
TOPIC: ARCHITECTURE OF CHROMOSOME IN PROKARYOTES AND
EUKARYOTES
WELCOME TO CLASS PRESENTATION OF
CYTOGENETICS
PRESNTED BY:- VIPIN PANDEY
S. NO PROKARYOTS S.NO EUKARYOTS
1 These are primitive organism like bacteria, virus, & BGA.
1 These are higher organism other than bacteria, viruses, & BGA .
2 They do not have well defined nucleus and nuclear membrane.
2 They have well defined nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
3 The DNA is free of structural proteins. 3 The DNA is tightly associated with specific proteins.
4 Prokaryote cell has DNA plus ribosomes.
4 Eukaryote cell has nucleus and various cell organelles.
5 Nucleus is absent. 5 Nucleus is present.
WHAT DIFFERENCE IN PROKARYOTES & EUKARYOTS CELLS
∗ The darkly stained, rod shaped bodies visible under light microscope in a cell during metaphase stage of mitosis are called chromosome.
CHROMOSOME
WHEAR IS FOUND CHROMOSOME?∗ Chromosome is found of all cells .
WHAT IS CHROMOSOME ?
Discovered by :- Strasburger, 1875; Coined term by :- Waldeyer, 1888
CHROMOSOME
WHEAR IS FOUND CHROMOSOME IN CELLS ?
∗ Chromosome is found of all cells in the nucleus.
Discovered by :- Strasburger, 1875; Coined term by :- Waldeyer, 1888
∗ DNA is very long.
WHY GENES/DNA ARE PACKEDED ON FORM OF CHROMOSOME ?
CHROMOSOME
~13.6cm.
~22cm.
~5.44m.WHEAT 3 TYPES GENOMIC DNA IS, PACKED IN 21 CHROMOSOMES
RICE GENOMIC DNA AREPACKED IN 12 CHROMOSOME
SORGHUM GENOMICDNA AREPACKED IN 10 CHROMOSOME
∗ Naked DNA is unstable in nucleus or cytoplasm . ∗ Time of cell division chromosome easily distribute
parental to daughter cells by the centromere. ∗ Easily regulation of gene action.
WHY GENES/DNA ARE PACKEDED ON FORM OF CHROMOSOME ?
CHROMOSOME
∗Precise distribution of DNA parental to daughter cells. In Gametic cell 2n to n.
CHROMOSOME
2n
n
n
n
n
∗ Prokaryotic chromosome is consists of single circular, double-stranded DNA molecule.
∗ It has no histone protein.∗ Chromosomes are stored in nucleoid in which DNA in
binding to some proteins.∗ The genome of prokaryotes is often significantly
larger than the cell it self. How it is possible?∗ Contain only one copy of the gene (hapolid).
Prokaryotic chromosome
∗ Non essential genes are stored outside of chromosome in plasmid.
∗ It is circular molecule of DNA but the total length of DNA molecule is very large 1100µ.
Nucleoids of prokaryotes'
AGCTAGCTAGCTAGCTAGCTAGCTAGCTAG
TCGATCGATCGATCGATCGATCGATCGATC
1100µ
∗Diameter of fully expanded E.coli circular DNA is 350µ, while an E.coli cell has the diameter of only 2-5µ.∗In chromosome have 40-50 loops or domains found, which are connected or binding with RNA or proteins. ∗Loops are coiled and, coiled loops are called super coiled loops; it is attached with central scaffold protein
Nucleoids of prokaryotes'
5µ
∗ In the bacteria other than a big chromosome 1-20 covalently closed circular DNA molecules structure which includes genetic information & presenting in cytoplasm are called plasmids.
∗ It have stored non essential genes.∗ It have capable of replication.
Plasmid
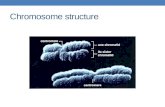
∗ Under light microscope each chromosome consists of several parts like-
∗ Centromere / primary constriction.∗ Chromatids.∗ Secondary constriction & satellite.∗ Telomere.∗ Chromomere.∗ Chromonema.∗ Matrix.
Eukaryotic chromosome
∗ Artificial chromosome refers to synthetic chromosome consisting of fragments of DNA integrated into a host chromosome.
∗ It is two type-∗ YAC-Yeast Artificial chromosome∗ BAC-Bacterial Artificial Chromosome
Artificial chromosome
YAC-Yeast Artificial chromosome
∗Yeast artificial chromosome.∗Self-replicating elements.∗Can insert segments up to 1000-2000 kb pairs.
∗Can replicate any inserted DNA via transfer to yeast cells.
∗ Tel – telomeres.∗ Cen – centromere.∗ Ori - Origin of replication.∗ Selectable markers.∗ Restriction enzyme recognition sites.
Essential elements for YACs
∗ BAC is cloning vector system in E.coli developed by Mel Simon and his colleagues.
∗ It is developed to alternative of YAC vectors.∗ BAC is maintained in E.coli as large single
copy plasmids that contain inserts of 150-350kbp.
BAC-Bacterial Artificial Chromosome
∗ It is used to map genes in genomes.∗ It is also useful in testing f function of genes. ∗ It is used to make transgenic plants. ∗ It is used for study of proteins structure.∗ It is used to desired gene cloning.
Uses of artificial chromosome
∗ Chromosomes, which differ significantly from normal chromosomes.
∗ It is differ from normal chromosome to either morphology or function.
∗ It is three types:-1.Lampbrush chromosome 2.Polytene chromosome or giant chromosome 3.B chromosome
Special types of chromosome
∗ Lampbrush chromosome are have large number of loops.∗ Loops giving a lampbrush appearance.∗ They are found in oocyte nuclei of both vertebrates &
invertebrates.
1.Lampbrush chromosome
∗ The multiple replicates of the same chromosome holding together in a parallel fashion resulting in very thick chromosome are known polytene chromosome.
∗ Found in certain tissues e.g., salivary glands of larvae, gut epithelium, Malphigian tubules and some fat bodies, of some Diptera (Drosophila, Sciara, Rhyncosciara)
∗ Giant chromosomes are made up of several dark staining regions called “bands”.
∗ It can be separated by relatively light or non-staining “interband” regions
2.Polytene chromosome or giant chromosome