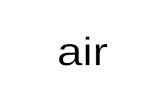APES Review! 4/24/08. Introduction Environment, biotic, abiotic Environment, biotic, abiotic Thomas...
description
Transcript of APES Review! 4/24/08. Introduction Environment, biotic, abiotic Environment, biotic, abiotic Thomas...

APES Review!APES Review!4/24/084/24/08

IntroductionIntroduction Environment, biotic, abioticEnvironment, biotic, abiotic Thomas MalthusThomas Malthus and and Paul EhrlichPaul Ehrlich: :
predicted massive population increases predicted massive population increases and subsequent problemsand subsequent problems
Environmental science is about Environmental science is about sustainabilitysustainability, which requires us to , which requires us to live in such a way as to maintain Earth’s live in such a way as to maintain Earth’s systems for the foreseeable futuresystems for the foreseeable future

Designing ExperimentsDesigning Experiments have a hypothesis that you want to have a hypothesis that you want to
testtest Make sure to have a control group Make sure to have a control group
that is not tested in order to comparethat is not tested in order to compare Only test 1 variable at a time!Only test 1 variable at a time!

Basic InformationBasic Information Properties of water: Properties of water:
– strong cohesion (helps transport of strong cohesion (helps transport of chemicals)chemicals)
– can resist temperature changecan resist temperature change– Solid form is less dense than liquid (ice Solid form is less dense than liquid (ice
floats)floats)– Bonds well (dissolves many molecules)Bonds well (dissolves many molecules)
pH scale: <7= acid, >7=basepH scale: <7= acid, >7=base

Basics on EnergyBasics on Energy Potential energyPotential energy is energy of position and is energy of position and
kinetic energykinetic energy is energy of motion is energy of motion First law of thermodynamicsFirst law of thermodynamics: the total : the total
energy of the universe remains constantenergy of the universe remains constant– Ex) the potential energy of the water behind a Ex) the potential energy of the water behind a
dam equals the kinetic energy of its eventual dam equals the kinetic energy of its eventual movementmovement
Second law of thermodynamicsSecond law of thermodynamics: the : the nature of energy will change from a more nature of energy will change from a more ordered to less ordered stateordered to less ordered state– As we burn a log, the energy is released as heat As we burn a log, the energy is released as heat
and light, becoming more disorganizedand light, becoming more disorganized

Basics on EnergyBasics on Energy PhotosynthesisPhotosynthesis: plants, or : plants, or
autotrophsautotrophs, convert sunlight energy , convert sunlight energy and CO2 into glucose and O2and CO2 into glucose and O2
Cellular respirationCellular respiration: all organisms : all organisms convert glucose into ATP energy and convert glucose into ATP energy and CO2CO2

Energy BasicsEnergy Basics Energy efficiencyEnergy efficiency: the amount of : the amount of
energy that is useful from one step to energy that is useful from one step to the nextthe next– A coal power plant is 38% efficientA coal power plant is 38% efficient– Beef cattle are 7% efficient, chickens are Beef cattle are 7% efficient, chickens are
33%33% ProductivityProductivity is the amount of is the amount of
biomass that is produced by a biomass that is produced by a communitycommunity

Basic Ecology InformationBasic Ecology Information A A speciesspecies is a group of organisms with is a group of organisms with
similar enough genetic makeup to be similar enough genetic makeup to be able to reproduce successfullyable to reproduce successfully
A A populationpopulation is an interbreeding group is an interbreeding group of organisms that lives in the same of organisms that lives in the same areaarea
A A communitycommunity is a group of is a group of interdependent populationsinterdependent populations
An An ecosystemecosystem is composed of is composed of biological communities and their biological communities and their physical surroundingsphysical surroundings

The biogeochemical cyclesThe biogeochemical cycles The The carbon cyclecarbon cycle
1.1. photosynthesis captures CO2 to form photosynthesis captures CO2 to form glucose. glucose. animals eat glucoseanimals eat glucose
2.2. cellular respiration converts glucose into cellular respiration converts glucose into CO2CO2
3.3. CO2 is captured and dissolved by the CO2 is captured and dissolved by the oceansoceans
4.4. Organisms use the carbonate ion to form Organisms use the carbonate ion to form sedimentssediments
5.5. When organisms die, they may be When organisms die, they may be compressed into fossil fuelscompressed into fossil fuels
6.6. Fossil fuels are burned to produce CO2Fossil fuels are burned to produce CO2

The biogeochemical cyclesThe biogeochemical cycles The The nitrogen cyclenitrogen cycle
1.1. Nitrogen fixation converts nitrogen gas into Nitrogen fixation converts nitrogen gas into ammonia through bacterial actionammonia through bacterial action
2.2. Nitrogen gas can form NO2 through Nitrogen gas can form NO2 through combustion and later combined with water to combustion and later combined with water to form acid rainform acid rain
3.3. Nitrification turns ammonia into nitrite and Nitrification turns ammonia into nitrite and nitrate ionsnitrate ions
4.4. Nitrates are used by plants to form proteinsNitrates are used by plants to form proteins5.5. Plant proteins are eaten by animalsPlant proteins are eaten by animals6.6. Animals decompose to form ammonia Animals decompose to form ammonia
through ammonificationthrough ammonification

The biogeochemical cyclesThe biogeochemical cycles The The phosphate cyclephosphate cycle
– There is no gaseous phase unlike There is no gaseous phase unlike other cyclesother cycles
1.1. Phosphates are used in plants and Phosphates are used in plants and animalsanimals
2.2. Decaying organic matter puts Decaying organic matter puts phosphates in soilphosphates in soil– This is often used as fertilizersThis is often used as fertilizers
3.3. Animals and plants pick up phosphates Animals and plants pick up phosphates to useto use

The biogeochemical cyclesThe biogeochemical cycles The The sulfur cyclesulfur cycle
1.1. Sulfur is used to construct proteinsSulfur is used to construct proteins2.2. Living cells are compressed into fossil Living cells are compressed into fossil
fuels, which release SO2 when fuels, which release SO2 when combustedcombusted
3.3. SO2 combines with water vapor to form SO2 combines with water vapor to form acid rainacid rain
4.4. Sulfate ions are taken in by plants to Sulfate ions are taken in by plants to form proteinsform proteins
5.5. Volcanic eruptions produce sulfidesVolcanic eruptions produce sulfides

The biogeochemical cyclesThe biogeochemical cycles The The water cyclewater cycle
– Characterized by changes in the Characterized by changes in the physical state, rather than chemical physical state, rather than chemical reactionsreactions
– Powered by solar energy and by gravityPowered by solar energy and by gravity
– A large amount of water is stored as A large amount of water is stored as groundwater in aquifersgroundwater in aquifers

The biogeochemical case The biogeochemical case studiesstudies
Wastewater treatment and Wastewater treatment and nitrogennitrogen– Plants need to be careful to have Plants need to be careful to have
bacteria convert all the ammonia into bacteria convert all the ammonia into nitrate ions, which are later removednitrate ions, which are later removed

Earth Systems and Global Earth Systems and Global ProcessesProcesses
ConvectionConvection is the circulation of is the circulation of material that occurs when the density material that occurs when the density of material is changed upon warming or of material is changed upon warming or coolingcooling– Energy from the Earth’s core heats the Energy from the Earth’s core heats the
mantle, which then rises and cools as it mantle, which then rises and cools as it contacts the crust—this drives tectonic contacts the crust—this drives tectonic actionaction
– Ocean currents are also driven by Ocean currents are also driven by differences in temperature and salinitydifferences in temperature and salinity

Earth Systems and Global Earth Systems and Global ProcessesProcesses
ConvectionConvection in the atmosphere in the atmosphere– Energy from the sun from is as UV light Energy from the sun from is as UV light
and is mostly absorbed by ozone; and is mostly absorbed by ozone; eventually all energy is reradiated as eventually all energy is reradiated as infrared radiationinfrared radiation More solar energy hits the equator than More solar energy hits the equator than
other regionsother regions– Coriolis effectCoriolis effect—circular air movements —circular air movements
that create surface windsthat create surface winds

Plate tectonicsPlate tectonics Plate tectonicsPlate tectonics describes the movements of describes the movements of
the Earth’s lithospheric platesthe Earth’s lithospheric plates– Divergent boundariesDivergent boundaries occur where magma occur where magma
is pushed up and new crust is produced; is pushed up and new crust is produced; produces rift valleys and sea floor spreadingproduces rift valleys and sea floor spreading
– Convergent boundariesConvergent boundaries occur when two occur when two plates meet and one dives under the other plates meet and one dives under the other through subduction; forms mountains and through subduction; forms mountains and trenchestrenches
– Transform boundariesTransform boundaries occur when two occur when two plates slide past each other; causes plates slide past each other; causes earthquake faultsearthquake faults

The rock cycleThe rock cycle Igneous rocksIgneous rocks are formed from magma are formed from magma
that has solidifiedthat has solidified Sedimentary rocksSedimentary rocks are formed through are formed through
weathering and depositionweathering and deposition– Mechanical weathering takes place when a Mechanical weathering takes place when a
force is applied to break up a rockforce is applied to break up a rock– Chemical weathering takes place through Chemical weathering takes place through
chemical reactions, often with waterchemical reactions, often with water Metamorphic rocksMetamorphic rocks are formed as other are formed as other
rocks are exposed to heat or pressurerocks are exposed to heat or pressure

SoilSoil Soil is formed from small particles of rock Soil is formed from small particles of rock
and mineralsand minerals Soil compositionSoil composition
– ClayClay: very fine particles, impermeable to water: very fine particles, impermeable to water– Silt:Silt: fine particles that result from weathering fine particles that result from weathering– Sand: Sand: course particles from weather; high course particles from weather; high
water permeabilitywater permeability– Humus: Humus: organic material in topsoilorganic material in topsoil– Loam: Loam: a mixture of the other types, good for a mixture of the other types, good for
agricultureagriculture

SoilSoil Soil profilesSoil profiles show the different layers show the different layers
of materialof material
Soil conservation: Soil Conservation ActSoil conservation: Soil Conservation Act– Erosion occurs when soil is moved; occurs Erosion occurs when soil is moved; occurs
through water, wind, and salinizationthrough water, wind, and salinization– Decrease erosion through no-till farming, Decrease erosion through no-till farming,
trees to break wind, monitor soil nutrients, trees to break wind, monitor soil nutrients, decrease irrigationdecrease irrigation

The atmosphereThe atmosphere Mostly nitrogen, then oxygen, then Mostly nitrogen, then oxygen, then
water vapor and other gaseswater vapor and other gases Layers: troposphere < tropopause < Layers: troposphere < tropopause <
stratosphere < mesosphere < stratosphere < mesosphere < thermosphere/ionospherethermosphere/ionosphere
Weather is caused by temperature, Weather is caused by temperature, pressure, and moisturepressure, and moisture

Global Climate ChangesGlobal Climate Changes Milankovitch cyclesMilankovitch cycles: changing of Earth’s : changing of Earth’s
orbit around the sun, exposing different orbit around the sun, exposing different latitudes to different amounts of sunlight over latitudes to different amounts of sunlight over timetime
Volcanic eruptionsVolcanic eruptions: put huge amounts of ash : put huge amounts of ash into the atmosphere, blocking suninto the atmosphere, blocking sun
El NinoEl Nino: as water moves in the surface of : as water moves in the surface of equatorial waters, it is heated and evaporates, equatorial waters, it is heated and evaporates, causing increased moisturecausing increased moisture– Causes different amounts of moisture and Causes different amounts of moisture and
precipitationprecipitation

Global Climate ChangesGlobal Climate Changes Greenhouse effectsGreenhouse effects: the increased : the increased
amounts of greenhouse gases causes amounts of greenhouse gases causes more infrared radiation to be more infrared radiation to be capturedcaptured– Increased burning of fossil fuels has Increased burning of fossil fuels has
made more CO2 than our natural made more CO2 than our natural processes can absorbprocesses can absorb

Effects of Global Climate Effects of Global Climate ChangeChange
Reduces artic sea ice, increases the level of Reduces artic sea ice, increases the level of the seathe sea
Glaciers are melting, causing less freshwater Glaciers are melting, causing less freshwater runoff for human userunoff for human use
High ocean levels will flood major population High ocean levels will flood major population centerscenters
Spreads the range of disease-causing Spreads the range of disease-causing organismsorganisms
Causes migration of plant and animal speciesCauses migration of plant and animal species Coral reefs undergo bleachingCoral reefs undergo bleaching Permafrost is meltingPermafrost is melting Causes more energetic stormsCauses more energetic storms

Species InteractionsSpecies Interactions Food websFood webs: producers—primary : producers—primary
consumer—secondary consumer—consumer—secondary consumer—tertiary consumer—decomposerstertiary consumer—decomposers
Keystone speciesKeystone species have a particularly have a particularly strong impact on ecosystemsstrong impact on ecosystems– Often a large, tertiary consumerOften a large, tertiary consumer
SuccessionSuccession shows the pattern of shows the pattern of restoration when an ecosystem is restoration when an ecosystem is disturbeddisturbed

Species InteractionsSpecies Interactions The The nicheniche is a species’ ecological role is a species’ ecological role
– The niche is determined by competitionThe niche is determined by competition PredationPredation: the process by which : the process by which
individuals of one species hunt and killindividuals of one species hunt and kill ParasitismParasitism: one organism depends : one organism depends
on another for nourishment or other on another for nourishment or other benefit while causing the host harmbenefit while causing the host harm
HerbivoryHerbivory: animals feed on the : animals feed on the tissues of plantstissues of plants

Species InteractionsSpecies Interactions Mutualism: Mutualism: two or more species benefit two or more species benefit
from the interaction with one anotherfrom the interaction with one another Symbiosis: Symbiosis: physical close mutualitistic physical close mutualitistic
associationassociation– Ex) plant roots and fungi, bacteria in Ex) plant roots and fungi, bacteria in
intestineintestine AmensalismAmensalism: one organism is harmed : one organism is harmed
and the other is unaffectedand the other is unaffected CommensalismCommensalism: one species benefits : one species benefits
and the other is unaffectedand the other is unaffected

EvolutionEvolution EvolutionEvolution is the process of change is the process of change
in a population over timein a population over time– Evolution occurs through the process of Evolution occurs through the process of
natural selectionnatural selection, where the best , where the best genetically adapted individuals survive genetically adapted individuals survive and reproduceand reproduce
– Proposed by Proposed by Charles DarwinCharles Darwin The result of evolution is The result of evolution is speciationspeciation
– Allopatric speciationAllopatric speciation is a result of is a result of geographic barriersgeographic barriers

The disappearance of a species from The disappearance of a species from Earth is called Earth is called extinctionextinction– Extinctions occur when rapid Extinctions occur when rapid
environmental change occurs and environmental change occurs and species cannot adaptspecies cannot adapt
– There have been 5 mass extinctions on There have been 5 mass extinctions on Earth Earth
– The The K-T extinctionK-T extinction occurred when the occurred when the dinosaurs were wiped outdinosaurs were wiped out
ExtinctionExtinction

The BiomesThe Biomes BiomesBiomes: a major region classified by its : a major region classified by its
dominant plant typedominant plant type– TundraTundra: few trees, extreme cold, frozen : few trees, extreme cold, frozen
ground (permafrost)ground (permafrost)– desertdesert: very low moisture, adapted plants, : very low moisture, adapted plants,
small animalssmall animals– grasslandgrassland: medium rainfall, grazing : medium rainfall, grazing
animalsanimals– SavannahsSavannahs: tropical grasslands: tropical grasslands– ChaparralChaparral: dry ecosystem with low woody : dry ecosystem with low woody
treestrees

The BiomesThe Biomes– Temperate deciduous forestTemperate deciduous forest: trees : trees
loose leaves every fall; even loose leaves every fall; even precipitationprecipitation
– TaigaTaiga: boreal forests with long, snowy : boreal forests with long, snowy winters and conifer treeswinters and conifer trees
– Temperate rainforestTemperate rainforest: heavy rainfall; : heavy rainfall; many coniferous treesmany coniferous trees
– Tropical rainforestTropical rainforest: heavy rainfall; : heavy rainfall; warm year-round; high biodiversitywarm year-round; high biodiversity

The BiomesThe Biomes Pelagic marine ecosystemsPelagic marine ecosystems: open : open
ocean; ocean; phytoplanktonphytoplankton→→zooplanktonzooplankton→small →small fish →top carnivoresfish →top carnivores
Benthic marine ecosystemsBenthic marine ecosystems: near the : near the bottom of the seabottom of the sea– Coral reefs: Coral reefs: mutualistic relationship between mutualistic relationship between
algae and marine inverterates, as well as algae and marine inverterates, as well as great biodiversitygreat biodiversity

The BiomesThe Biomes Benthic marine ecosystemsBenthic marine ecosystems
– Mangrove swampsMangrove swamps: occur near the shore : occur near the shore where salt-adapted trees grown with their where salt-adapted trees grown with their roots in the water; tropical zonesroots in the water; tropical zones
– The abyssThe abyss: great depths of the ocean: great depths of the ocean– Estuaries and salt marshesEstuaries and salt marshes: interface : interface
between ocean and rivers; brackish water; between ocean and rivers; brackish water; high biodiversityhigh biodiversity
– Intertidal zonesIntertidal zones: regions between low and : regions between low and high tideshigh tides

The BiomesThe Biomes Coastal ecosystemsCoastal ecosystems
– Supratidal zoneSupratidal zone: beach area: beach area– Barrier islandsBarrier islands: islands created by wave : islands created by wave
actionaction Streams and riversStreams and rivers: major source of : major source of
nutrients comes from terrestrial sourcesnutrients comes from terrestrial sources Lakes and pondsLakes and ponds: vary in nutrient levels: vary in nutrient levels WetlandsWetlands
– Provide essential habitatsProvide essential habitats– Reservoir for flood watersReservoir for flood waters– Natural water treatment processNatural water treatment process

BiodiversityBiodiversity Genetic biodiversityGenetic biodiversity refers to the refers to the
variety of genes within a populationvariety of genes within a population Species biodiversitySpecies biodiversity refers to the refers to the
number of species in an ecosystemnumber of species in an ecosystem– Benefits: helps ecosystem stability, Benefits: helps ecosystem stability,
medicines, aesthetic value, etcmedicines, aesthetic value, etc Ecosystem biodiversityEcosystem biodiversity refers to refers to
the variety of biome typesthe variety of biome types

Endangered SpeciesEndangered Species Generally have characteristics that make it Generally have characteristics that make it
vulnerablevulnerable– Logistic population growthLogistic population growth
Long life span, large body, carnivore, low Long life span, large body, carnivore, low reproductive ratereproductive rate
– Requires a large amount of land per Requires a large amount of land per animalanimal
– Specialist species Specialist species – Low genetic diversityLow genetic diversity– Competes for resources with a dominant Competes for resources with a dominant
speciesspecies– Low tolerance for pollution and/or human Low tolerance for pollution and/or human
activityactivity

Introduced SpeciesIntroduced Species Invasive speciesInvasive species are non-native are non-native
organisms that alter communities organisms that alter communities substantially and become dominantsubstantially and become dominant– No limiting factors to regulate their No limiting factors to regulate their
populationpopulation– Often difficult to remove or controlOften difficult to remove or control– Often on islandsOften on islands

Protecting BiodiversityProtecting Biodiversity The Endangered Species ActThe Endangered Species Act National parks and forestsNational parks and forests Wetland protection/range Wetland protection/range
managementmanagement Wildlife corridors between parksWildlife corridors between parks land reclamationland reclamation Captive breeding programs in zoosCaptive breeding programs in zoos

Biodiversity case studiesBiodiversity case studies Wolves restored to Yellowstone parkWolves restored to Yellowstone park Overharvesting for seafood marketsOverharvesting for seafood markets Silent SpringSilent Spring shows the impact of shows the impact of
pesticides on biodiversitypesticides on biodiversity

Population DefinitionsPopulation Definitions FertilityFertility: a measure of the actual : a measure of the actual
number of offspring producednumber of offspring produced Fecundity:Fecundity: the physical ability of an the physical ability of an
organism to reproduceorganism to reproduce NatalityNatality: the production of new : the production of new
individualsindividuals MorbidityMorbidity: level of illness in a : level of illness in a
populationpopulation Mortality: Mortality: measure of actual number of measure of actual number of
individuals that dieindividuals that die

Population DefinitionsPopulation Definitions SurvivorshipSurvivorship: the number of people in : the number of people in
a given age bracket who remain alivea given age bracket who remain alive Life expectancy: Life expectancy: probable number of probable number of
years an individual will surviveyears an individual will survive Life spanLife span: longest length of life : longest length of life
reachedreached total growth ratetotal growth rate: sum increases to : sum increases to
the populationthe population

Growth = (birth + immigration) – (death Growth = (birth + immigration) – (death + emigration)+ emigration)
Exponential growthExponential growth: when a population : when a population increases by a fixed amount (j-curve)increases by a fixed amount (j-curve)
Logistic growthLogistic growth: population rises : population rises sharply at first but then levels off (s-sharply at first but then levels off (s-curve)curve)– Levels off when a population reaches itsLevels off when a population reaches its
carrying capacitycarrying capacity Doubling TimeDoubling Time = 70 / % growth = 70 / % growth
Population GrowthPopulation Growth

K-selectedK-selected species are large, slow species are large, slow reproduction, lots of parental carereproduction, lots of parental care– Ex) humans, mammals, etcEx) humans, mammals, etc
R-selected R-selected species are small, short-species are small, short-lived, with quick reproductionlived, with quick reproduction– Ex) insects, rodentsEx) insects, rodents
Biotic PotentialBiotic Potential

Population sizePopulation size Population densityPopulation density Population distribution: random, Population distribution: random,
uniform, or clumpeduniform, or clumped Sex ratiosSex ratios Age structureAge structure Birth and death rates: survivorship Birth and death rates: survivorship
curvescurves
Characteristics of populationsCharacteristics of populations

Factors that affect human population Factors that affect human population sizesize
Increase sizeIncrease size– Social factors: status, comfort, prideSocial factors: status, comfort, pride– Financial factors: source of labor, securityFinancial factors: source of labor, security– Fertility factors: high infant mortalityFertility factors: high infant mortality– Cultural factors: producing an heir, etcCultural factors: producing an heir, etc
Reduce sizeReduce size– Personal freedom and educational Personal freedom and educational
opportunities for womenopportunities for women– Socioeconomic statusSocioeconomic status– MaterialismMaterialism

Human Age Structure Human Age Structure DiagramsDiagrams

Demographic TransitionDemographic Transition Evolution of populations from high Evolution of populations from high
birth/ death rates to low birth/death birth/ death rates to low birth/death ratesrates
Stage 1: high birth and death ratesStage 1: high birth and death rates– Little access to birth control, high infant Little access to birth control, high infant
mortalitymortality Stage 2: high birth rates, death rates Stage 2: high birth rates, death rates
fall—high population growthfall—high population growth– Improved medical care and sanitationImproved medical care and sanitation– Better food distributionBetter food distribution

Demographic TransitionDemographic Transition Stage 3: birth and death rates fall—Stage 3: birth and death rates fall—
population growth is constantpopulation growth is constant– Increased birth control, wealth Increased birth control, wealth
increases, higher educationincreases, higher education Stage 4: low birth and death rates—Stage 4: low birth and death rates—
steady population sizesteady population size

Air PollutantsAir Pollutants Primary pollutantsPrimary pollutants: harmful to : harmful to
humans in the form in which they are humans in the form in which they are emittedemitted
Secondary pollutantsSecondary pollutants: become : become toxic after they are releasedtoxic after they are released– Ex) ozoneEx) ozone

Nitrogen oxidesNitrogen oxides Description: formed when N2 is Description: formed when N2 is
combusted at high tempscombusted at high temps Sources: ½ from anthropogenic Sources: ½ from anthropogenic
sources, mostly automobilessources, mostly automobiles Effects: acid rain, causes increased Effects: acid rain, causes increased
plant growth (eutrophication and plant growth (eutrophication and decreased dissolved oxygen)decreased dissolved oxygen)

Sulfur oxidesSulfur oxides Description: has that damages Description: has that damages
tissuestissues Sources: combustion of coalSources: combustion of coal Effects: acid rain, causes breathing Effects: acid rain, causes breathing
difficulties difficulties

Carbon oxidesCarbon oxides Description: CO2 and CO most Description: CO2 and CO most
commoncommon Sources: burning fossil fuelsSources: burning fossil fuels Effects: CO2 causes global warming, Effects: CO2 causes global warming,
CO is toxic to humansCO is toxic to humans

Volatile Organic Compounds Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)(VOCs)
Description: easily vaporized and can Description: easily vaporized and can react for form ground-level ozonereact for form ground-level ozone
Sources: cleaning fluids, paints, oil, Sources: cleaning fluids, paints, oil, etcetc
Effects: can be carcinogens, irritants, Effects: can be carcinogens, irritants, neurotoxins, etcneurotoxins, etc

Particulate MatterParticulate Matter Description: solid or liquid particles Description: solid or liquid particles
suspended in the air; includes ash, suspended in the air; includes ash, dust, smoke, etcdust, smoke, etc
Effects: irritates the lungs, may be Effects: irritates the lungs, may be toxictoxic

Metals and HalogensMetals and Halogens Description: lead and mercury are the Description: lead and mercury are the
most concerning metals, and CFCs are most concerning metals, and CFCs are important halogensimportant halogens
Sources: atmospheric lead comes from Sources: atmospheric lead comes from gasoline, mercury comes from coal gasoline, mercury comes from coal power plants, CFCs from coolantspower plants, CFCs from coolants
Effects: lead and mercury lead to brain Effects: lead and mercury lead to brain damagedamage– Mercury will bioaccumulateMercury will bioaccumulate– CFCs decrease ozone protectionCFCs decrease ozone protection

Photochemical oxidantsPhotochemical oxidants Description: secondary pollutants Description: secondary pollutants
that are synthesized with the aid of that are synthesized with the aid of solar energysolar energy– Includes ozoneIncludes ozone
Sources: often nitrogen oxidesSources: often nitrogen oxides Effects: ozone is highly reactive when Effects: ozone is highly reactive when
in the troposphere and causes lung in the troposphere and causes lung damagedamage

Indoor Air PollutantsIndoor Air Pollutants Asthma triggers: secondhand smoke, Asthma triggers: secondhand smoke,
dust, etcdust, etc Toxic building materials: VOCs, Toxic building materials: VOCs,
heavy metals, asbestosheavy metals, asbestos Radon gas: radioactive gas that is Radon gas: radioactive gas that is
produced within the Earth and enters produced within the Earth and enters homeshomes
Carbon monoxide: decreases oxygen Carbon monoxide: decreases oxygen levels in tissues; created by levels in tissues; created by incomplete combustion of fuelincomplete combustion of fuel

Human Water UseHuman Water Use agriculture > industrial > municipalagriculture > industrial > municipal
Dams can be used to control water Dams can be used to control water flow and to produce electricityflow and to produce electricity
Water diversion projects change the Water diversion projects change the flow of rivers and bring water to flow of rivers and bring water to citiescities

Water pollutantsWater pollutants PathogensPathogens: highest threat to human health: highest threat to human health Oxygen-demanding wastesOxygen-demanding wastes: the addition : the addition
of nutrients or human wastes allows algae of nutrients or human wastes allows algae to grow; then they die, the organisms that to grow; then they die, the organisms that decompose them use up the oxygen in the decompose them use up the oxygen in the waterwater– Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a good Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a good
estimate of the load of oxygen-consuming estimate of the load of oxygen-consuming organismsorganisms
Inorganic wastesInorganic wastes: suspended particles : suspended particles and dissolved ions such as acid depositionand dissolved ions such as acid deposition

Water PollutantsWater Pollutants Suspended particlesSuspended particles: includes sediment : includes sediment
from erosion and runofffrom erosion and runoff Dissolved ionsDissolved ions: includes heavy metals and : includes heavy metals and
calciumcalcium Heavy metal ionsHeavy metal ions: usually extremely toxic : usually extremely toxic
and may bioaccumulateand may bioaccumulate Toxic organic wastesToxic organic wastes: may come from : may come from
dumps or fuel, as well as natural sources such dumps or fuel, as well as natural sources such as red tidesas red tides
Thermal pollutionThermal pollution: decreases dissolved : decreases dissolved oxygen levels; often comes from power plantsoxygen levels; often comes from power plants

Removing toxic wastesRemoving toxic wastes Physical methods: vaporization, Physical methods: vaporization,
filtration, UC disinfection, reverse filtration, UC disinfection, reverse osmosisosmosis
Chemical methods: acid Chemical methods: acid neutralization, precipitation, or neutralization, precipitation, or hydrolysishydrolysis
Biological methods: bioremediation, Biological methods: bioremediation, wetlands, bacterial decompositionwetlands, bacterial decomposition

Water pollution controlWater pollution control Clean Water ActClean Water Act
– Make all waters “fishable and swimmable”Make all waters “fishable and swimmable”– Require discharge permits of major pollutersRequire discharge permits of major polluters– Identify toxic pollutants and remove themIdentify toxic pollutants and remove them
Reduce emissions of nitrogen and sulfur Reduce emissions of nitrogen and sulfur dioxidesdioxides
Modify agricultural practices to reduce runoffModify agricultural practices to reduce runoff Treat wastes more effectivelyTreat wastes more effectively Decrease silt runoff from urban areasDecrease silt runoff from urban areas Reverse river channelizationReverse river channelization

Land UseLand Use Tragedy of the commonsTragedy of the commons: personal : personal
good supersedes the public goodgood supersedes the public good– Garrett HardinGarrett Hardin– Case study: Easter Island—used all of the Case study: Easter Island—used all of the
public resources until they were gonepublic resources until they were gone– Case study: overharvesting of fish or Case study: overharvesting of fish or
deforestationdeforestation Ecological FootprintEcological Footprint: the sum total : the sum total
of the impact a human has on the of the impact a human has on the Earth, including the resources usedEarth, including the resources used

Land ReuseLand Reuse ConservationConservation: not using and protecting : not using and protecting
resourcesresources PreservationPreservation: providing a reserve of : providing a reserve of
resources for the futureresources for the future RestorationRestoration: bringing a damaged : bringing a damaged
ecosystem back to its natural conditionecosystem back to its natural condition RemediationRemediation: using chemical, biological, or : using chemical, biological, or
physical methods to remove pollutantsphysical methods to remove pollutants Reclamation:Reclamation: using large water projects to using large water projects to
bring water to otherwise un-arable landsbring water to otherwise un-arable lands MitigationMitigation: finding as solution to a problem: finding as solution to a problem

Human Nutritional NeedsHuman Nutritional Needs Undernourishment—getting fewer Undernourishment—getting fewer
calories than needed to survivecalories than needed to survive– Famines are massive incidents of Famines are massive incidents of
undernourishment, often caused by undernourishment, often caused by political or economic upheaval, or political or economic upheaval, or environmental devastationenvironmental devastation
Overnutrition—in the US we eat an Overnutrition—in the US we eat an average of 1000 extra calories per average of 1000 extra calories per dayday

Human Nutritional NeedsHuman Nutritional Needs Malnourishment—inability to acquire Malnourishment—inability to acquire
adequate vitamins and nutrientsadequate vitamins and nutrients– Kwashiorkor—lack of proteinKwashiorkor—lack of protein– Anemia—lack of iron; prohibits oxygen Anemia—lack of iron; prohibits oxygen
traveling in tissuestraveling in tissues– Goiter—iodine deficiencyGoiter—iodine deficiency– Vitamin A deficiency—harms visionVitamin A deficiency—harms vision– Scurvy—vitamin C deficiencyScurvy—vitamin C deficiency

Land DegradationLand Degradation Desertification: converting farmable Desertification: converting farmable
grassland into non-arable desertgrassland into non-arable desert– Often occurs when land is over farmed Often occurs when land is over farmed
and organic material is removedand organic material is removed Erosion: soil is movedErosion: soil is moved Fertilizer Use: adds inorganic Fertilizer Use: adds inorganic
materials to soilmaterials to soil– Often causes water pollutionOften causes water pollution
Energy use: depends on fossil fuelsEnergy use: depends on fossil fuels

Land DegradationLand Degradation Pesticide usePesticide use
– Toxicity to nontarget species (animals Toxicity to nontarget species (animals and humans)and humans)
– Pest resistancePest resistance– Types: inorganic, chlorinated Types: inorganic, chlorinated
hydrocarbons (DDT), organophosphates, hydrocarbons (DDT), organophosphates, botanic pesticidesbotanic pesticides
– Integrated pest management (IPM) uses Integrated pest management (IPM) uses a variety of management techniquesa variety of management techniques

MiningMining ExtractionExtraction
– Surface mining—dig an open mine, displacing Surface mining—dig an open mine, displacing large amounts of soillarge amounts of soil
– Subsurface mining—underground mines; more Subsurface mining—underground mines; more risks to minersrisks to miners
– Well—used for liquid or gaseous depositsWell—used for liquid or gaseous deposits ProcessingProcessing
– Gold is extracted by spraying with solvent, Gold is extracted by spraying with solvent, often toxic cyanideoften toxic cyanide
– Uranium is processed, creating huge amounts Uranium is processed, creating huge amounts of toxic wasteof toxic waste
– Aluminum extraction from bauxite ore requires Aluminum extraction from bauxite ore requires large amounts of energylarge amounts of energy

Mining ReclamationMining Reclamation The Surface Mining Control and The Surface Mining Control and
Reclamation Act requires that coal Reclamation Act requires that coal mining operations reclaim sites after mining operations reclaim sites after miningmining
Involves the return of the overburden Involves the return of the overburden (land removed)(land removed)– Then, topsoil must be put down and Then, topsoil must be put down and
plants grownplants grown– Tailings must be removed to stop toxic Tailings must be removed to stop toxic
and acidic runoffand acidic runoff


Skipped pgs 123-144—human healthSkipped pgs 123-144—human health Skipped pg 181-182—sewage Skipped pg 181-182—sewage
treatmenttreatment 195-205 (building and urbanization)195-205 (building and urbanization) Energy chapterEnergy chapter