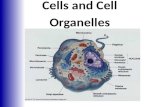
AP Biology Tour of the Cell 1 AP Biology Prokaryote bacteria cells Types of cells Eukaryote animal...
-
Upload
elfrieda-bates -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
2
Transcript of AP Biology Tour of the Cell 1 AP Biology Prokaryote bacteria cells Types of cells Eukaryote animal...

AP Biology
Tour of the Cell 1

AP Biology
Prokaryotebacteria cellsProkaryote
bacteria cellsTypes of cells
Eukaryoteanimal cellsEukaryote
animal cells
- no organelles
- organelles
Eukaryoteplant cellsEukaryoteplant cells

Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
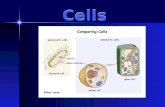
Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Basic features of all cells:
– Plasma membrane
– Cytoplasm
– Chromosomes (carry genes)
– Ribosomes (make proteins)

Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions
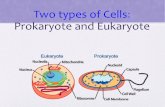
Prokaryotes
• No membrane bound nucleus
• DNA located in an area called a nucleoid
• No membrane bound organelles
• Bacteria 1-10um
Eukaryotes
• Membrane bound nucleus
• DNA located inside a nuclear membrane
• Membrane bound organelles
• Eukaryotes 10-100um

LE 6-6
A typicalrod-shapedbacterium
A thin section through thebacterium Bacilluscoagulans (TEM)
0.5 µm
Pili
Nucleoid
Ribosomes
Plasmamembrane
Cell wall
Capsule
Flagella
Bacterialchromosome

Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Prokaryotic parts
• Pili- Attachment; conjugation
• Ribosomes – make proteins
• Plasma membrane – membrane around cytoplasm
• Cell wall – structure outside cell membrane; made of peptidoglycan for many bacteria
• Capsule – jelly-like outer coating
• Flagella – tail for movement

LE 6-7
Total surface area(height x width xnumber of sides xnumber of boxes)
6
125 125
150 750
1
11
5
1.2 66
Total volume(height x width x lengthX number of boxes)
Surface-to-volumeratio(surface area volume)
Surface area increases whileTotal volume remains constant
Why can’t cells grow indefinitely in size?

Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
A Panoramic View of the Eukaryotic Cell
• A eukaryotic cell has internal membranes that partition the cell into organelles
• Plant and animal cells have most of the same organelles

AP Biology
Why organelles? Specialized structures
specialized functions cilia or flagella for locomotion
Containers partition cell into compartments create different local environments
ie. separate pH
Membranes as sites for chemical reactions
embedded enzymes & reaction centers chloroplasts & mitochondria
mitochondria
chloroplast
Golgi
ER

AP Biology
Cells gotta work to live! What jobs do cells have to do?
make proteins proteins control every
cell function make energy
for daily life for growth
make more cells growth repair renewal

AP Biology 2007-2008
Building Proteins

AP Biology
Proteins do all the work!
cellscells
DNADNA
proteinsproteins
organismorganismRepeat after me…
Proteins do all the work!

AP Biology
Cells functions Building proteins overview
read DNA instructions build proteins process proteins
folding modifying
removing amino acids adding other molecules
e.g, making glycoproteinsfor cell membrane
address & transport proteins

AP Biology
Building Proteins Organelles involved
nucleus ribosomes endoplasmic reticulum
(ER) Golgi apparatus vesicles
nucleus ribosome ERGolgi
apparatusvesicles
The Protein Assembly Line

AP Biology
nuclearpores
nuclearpore
nuclear envelopenucleolus
histone protein
chromosome
DNA
Function protects DNA
Structure nuclear envelope
double membrane membrane fused in spots to create pores
allows large macromolecules to pass through
Nucleus
What kind of molecules need to
pass through?

AP Biology
DNA
NucleusmRNA
nuclearmembrane
smallribosomal
subunit
largeribosomal
subunit
cytoplasm
mRNA
nuclear pore
production of mRNA from DNA in nucleusproduction of mRNA from DNA in nucleus
mRNA travels from nucleus to ribosome in cytoplasm through nuclear pore
mRNA travels from nucleus to ribosome in cytoplasm through nuclear pore
1
2

AP Biology

AP Biology
Nucleolus Function
ribosome production build ribosome subunits from rRNA & proteins exit through nuclear pores to cytoplasm &
combine to form functional ribosomes
smallsubunit
large subunit
ribosome
rRNA &proteins
nucleolus

AP Biology
smallsubunit
largesubunitRibosomes
Function protein production
Structure rRNA & protein 2 subunits combine 0.08m
RibosomesRough
ER
SmoothER

AP Biology membrane proteins
Types of Ribosomes Free ribosomes
suspended in cytosol synthesize proteins that
function in cytosol
Bound ribosomes attached to endoplasmic
reticulum synthesize proteins
for export or for membranes

AP Biology
Endoplasmic Reticulum Function
processes proteins manufactures membranes synthesis & hydrolysis of many compounds
Structure membrane connected to nuclear envelope &
extends throughout cell

AP Biology
Types of ER
rough smooth

AP Biology
Smooth ER function Membrane production Many metabolic processes
synthesis synthesize lipids
oils, phospholipids, steroids & sex hormones
hydrolysis hydrolyze glycogen into glucose
in liver
detoxify drugs & poisons in liver ex. alcohol & barbiturates

AP Biology
Membrane Factory Build new
membrane synthesize
phospholipids builds membranes
ER membrane expands bud off & transfer
to other parts of cell that need membranes

AP Biology
Rough ER function Produce proteins for export out of cell
protein secreting cells packaged into transport vesicles for export
Which cellshave lot of rough ER?

AP Biology
Synthesizing proteins
cytoplasm
cisternalspace
mRNA
ribosome
membrane ofendoplasmic reticulum
polypeptide
signalsequence
ribosome

AP Biology
Golgi Apparatus
Which cellshave lots of Golgi?
transport vesicles
secretoryvesicles
Function finishes, sorts, tags & ships cell products
like “UPS shipping department” ships products in vesicles
membrane sacs “UPS trucks”

AP Biology
Golgi Apparatus

AP Biology
Vesicle transport
vesiclebuddingfrom roughER
fusionof vesiclewith Golgiapparatus
migratingtransportvesicle
protein
ribosome

Regents Biology
DNA
RNA
ribosomes
endoplasmicreticulum
vesicle
Golgi apparatus
vesicle
proteinon its way!
protein finishedprotein
Making Proteins
TO:
TO:
TO:
TO:
nucleus

AP Biology
proteins
transportvesicle
Golgiapparatus
vesicle
smooth ER
rough ER
nuclear porenucleus
ribosome
cellmembrane protein secreted
cytoplasm
Making proteinsPutting it together…

AP Biology

AP Biology

AP Biology 2007-2008
Any Questions!!