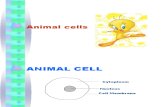
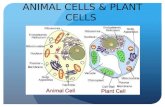
Animal and Plant Cells. Animal vs. Plant Cell AnimalPlant.
-
Upload
calvin-conley -
Category
Documents
-
view
244 -
download
0
Transcript of Animal and Plant Cells. Animal vs. Plant Cell AnimalPlant.
Plasma Membrane
• Surrounds the cell• system that allows nutrients to enter the
cell and waste products to leave
Nucleus• A large, membrane-bound structure • containing the cell's hereditary material• controls its metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
Ribosomes
• Round• Made of proteins and RNA• Assemble amino acids to make proteins• Free floating in cytoplasm• On ER
ER
• Endoplasmic Reticulum • Membranes within the cytoplasm of cells
involved in the synthesis, modification, and transport of cellular materials.
Smooth ER
• No ribosomes• synthesis of lipids• Metabolizes
carbohydrates • Detoxification of
drugs and poisons
Plant Cell Structures
• Plant cells are slightly different from animals cell because they can photosynthesize
Cell Wall
• The rigid outermost cell layer found in plants and certain algae, bacteria, and fungi
• Composed of cellulose
• Give plant stems and wood their stiffness
Vacuole
• A small cavity in the cytoplasm of a cell
• bound by a single membrane
• contains water, food, or metabolic waste.